The Problem
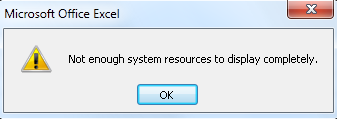
When opening an Excel file or running calculations within an Excel file, you may get the following error
This is a very miscellaneous error and one that is not easily solved sometimes but here are a few things to try
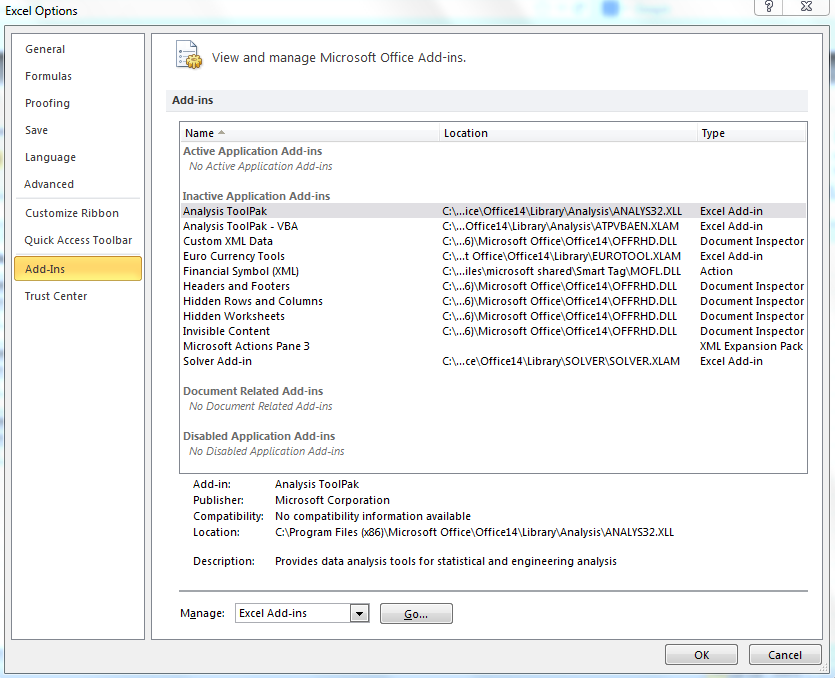
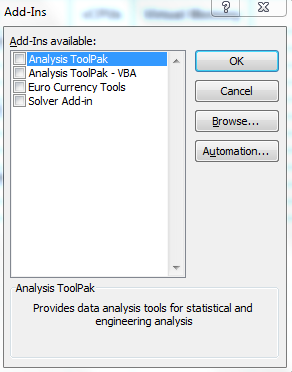
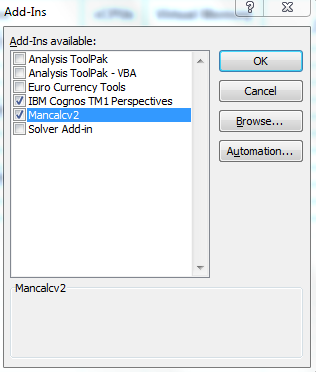
- If you have any COM add-ins installed, un-install them unless they are absolutely required or just untick them to test. COM add-ins are a special type of add-in written in machine language. They are often installed without explicit approval. COM add-ins are often reported as causing memory problems
- To see if you have multiple sessions open, press CTL-ALT-DELETE and check how any Excel applications are running. There should be just one running. If a new Excel session opens each time you double click on a workbook, try unchecking the Excel Option “Ignore other applications” if it is checked on the Options General tab.
- Excel may think your worksheets are larger than you do. This can consume a lot of memory. Normally your scroll area controlled by the scroll bars is very small. However, sometimes Excel thinks there are cells well below your used range. One way is to check where Excel thinks the last cell is located. Do this by pressing CTRL+SHIFT+END. If it well below your used range, then select all “unused” columns in this range and delete them. Then select all unused rows in this range and delete them . Then close and re-open Excel
- Install the latest upgrades to your version of Office.
- You can try deleting temp files. There is a nice piece of software called Temp File Deleter https://www.add-ins.com/temp_file_deleter.htm
- If you are using Google Desktop Search, un-install it. Google Desktop Search appears to be a memory hog and has been reported to interfere with Microsoft Excel. Specifically, it installs a COM add-in that monitors every action in Excel so that it can index it which can slow everything down
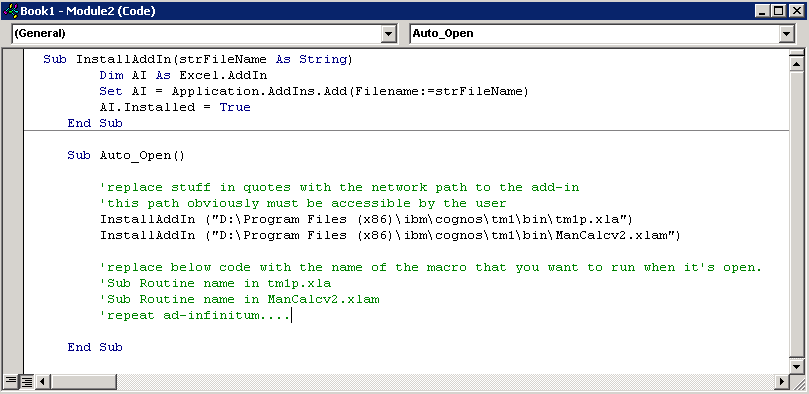
- If you are using Excel 2010-2013, click File, Options, Advanced, and go to the General section. Check if you have an alternate startup folder and check its content, and remove anything you do not need
- Check and see if you have an un-needed add-in or workbook in your XLSTART folder. This folder may vary location wise depending on local and roaming profiles
- Delete your XLB file. (Search for *.XLB) It can become corrupt but cause no visible problems. If corrupt it can consume lots of memory. Excel will recreate, but button customization will be lost. This is a file where Excel stores its toolbar settings. To delete it, use the XLB File Deleter which is a free product. There have been reports that doing this will solve problems.
- Your printer or its driver may be causing the problem. HP printers have a history of causing a memory problem with Excel. We do not know if HP fixed the problem and it may still be around or surfacing again. Change your default printer if you have other printers available as a test
- Use of macros that do very extensive file creating, data manipulation, and graphing have been known to cause memory leak problems. Such macros are ones that typically run for 30 minutes or longer.
- If you have Track Changes turned on in Excel, turn off Track Changes as it uses a fair amount of memory. The default is Off.
- Turn off AutoRecovery, as this takes up Excel memory. However, have a backup if you do. To turn off AuoRecovery go to File,Options, Save. Uncheck Auto Recovery
- Problems in your application data folder for Excel can be the cause. The folder is typically “c:\documents and settings\%username%\application data\microsoft\excel”. This is a hidden folder, so set your Explorer options to show hidden folders. After backing up, rename or delete this folder and its subfolders. Reboot the machine and open Excel. Excel will recreate the folder and needed contents.
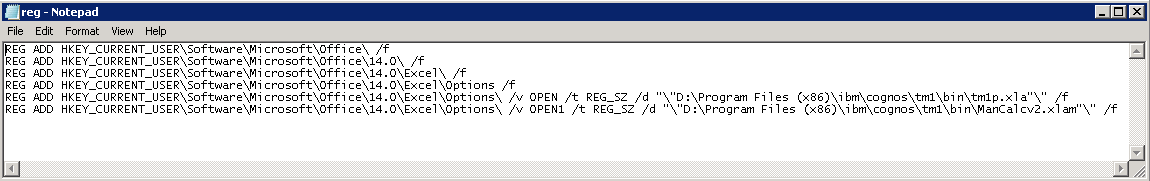
- Run the following 2 commands. “C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\OFFICE11\excel.exe” /unregserver and “C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\OFFICE11\excel.exe” /regserver. (Change the number 11 to 12 for Excel 2007, 14 for Excel 2010 and 15 for Excel 2013) These commands remove most of the Excel registry entries and then resets them. However, they do leave some residual settings.
- A more extensive way to clean the registry is to rename the Excel registry key and let Excel recreate it. It depends on the version of Excel. First, close Excel. Then do Run, Regedit and go to the Excel registry key. It will be “HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Office\%version_number%\Excel”
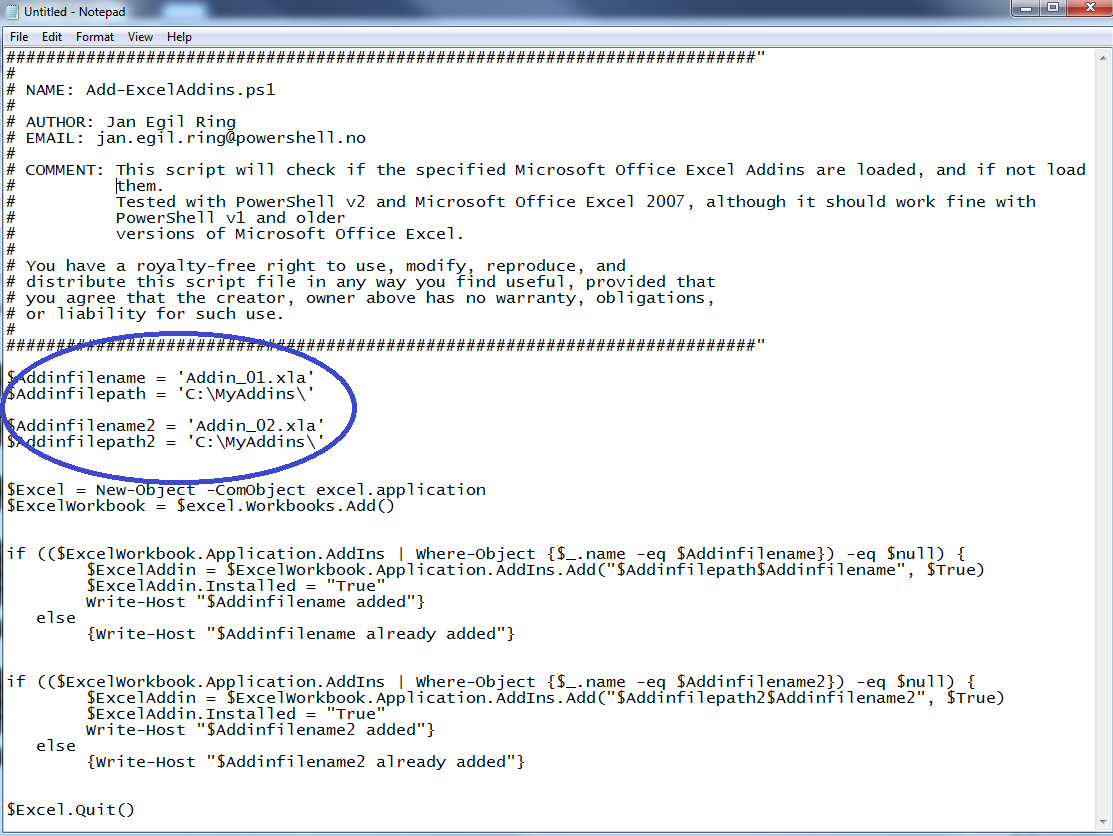
where %version_number% is 11 for Excel 2003, 12 for Excel 2007, 14 for Excel 2010 and 15 for Excel 2013. Rename this to OldExcel (this will back it up). Then re-open Excel. Excel will rebuild the registry entry. You will need to manually install any needed add-ins - It may be the case that the Server or PC that Excel is running on needs more memory or that you need to close other running apps which may be interfering with Excel or taking up more memory that Excel needs
- Try opening Excel in Safe Mode. For example C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office\Excel.exe /s
- Try opening Excel whilst holding the shift key down to stop any macros from executing or type Click Start, Run, “C:\Program Files\Microsoft Office\Office\Excel.exe” /Automation