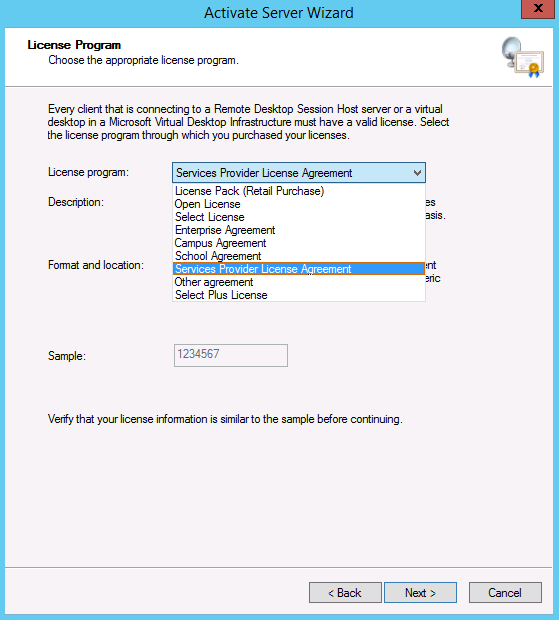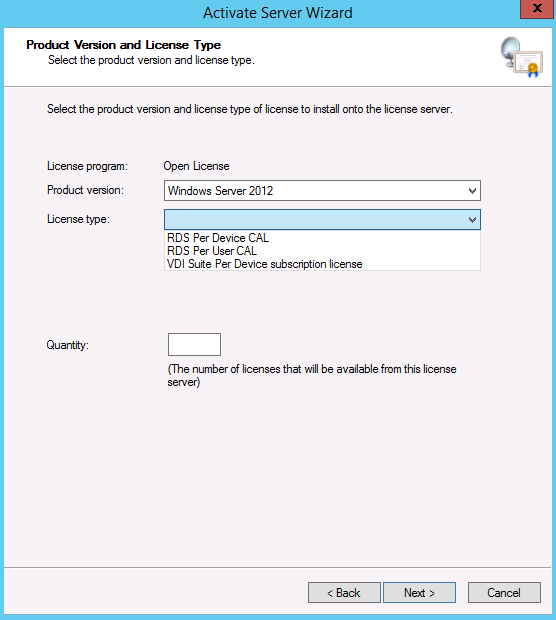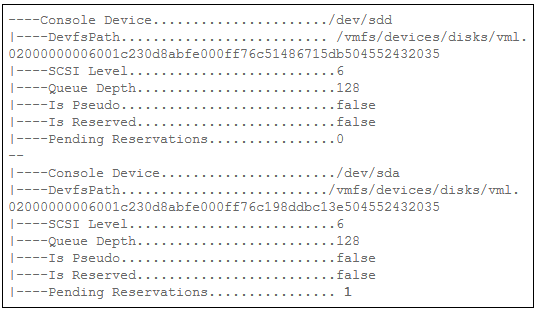
What are WMI Filters?
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) filters allow you to dynamically determine the scope of Group Policy objects (GPOs) based on attributes of the target computer. When a GPO that is linked to a WMI filter is applied on the target computer, the filter is evaluated on the target computer.
When a GPO that is linked to a WMI filter is applied on the target computer, the filter is evaluated on the target computer. If the WMI filter evaluates to false, the GPO is not applied (except if the client computer is running Windows 2000, in which case the filter is ignored and the GPO is always applied). If the WMI filter evaluates to true, the GPO is applied.
WMI makes data about a target computer available for administrative use. Such data can include hardware and software inventory, settings, and configuration information. For example, WMI exposes hardware configuration data such as CPU, memory, disk space, and manufacturer, as well as software configuration data from the registry, drivers, file system, Active Directory, the Windows Installer service, networking configuration, and application data.
GPOs are processed in the following order
The WMI filter is a separate object from the GPO in the directory.
To apply a WMI filter to a GPO, you link the filter to the GPO. This is shown in the WMI filtering section on the Scope tab of a GPO. Each GPO can have only one WMI filter, however the same WMI filter can be linked to multiple GPOs.
WMI filters, like GPOs, are stored on a per-domain basis. A WMI filter and the GPO it is linked to must be in the same domain.
- The local GPO is applied.
- GPOs linked to sites are applied.
- GPOs linked to domains are applied.
- GPOs linked to organizational units are applied. For nested organizational units, GPOs linked to parent organizational units are applied before GPOs linked to child organizational units are applied
A practical GPO and WMI example.
We had a requirement to have separate GPOs for Windows 7 Internet Explorer 10 users than Windows XP Internet Explorer 8 users. This is where we can have a policy which is filtered by Windows 7.
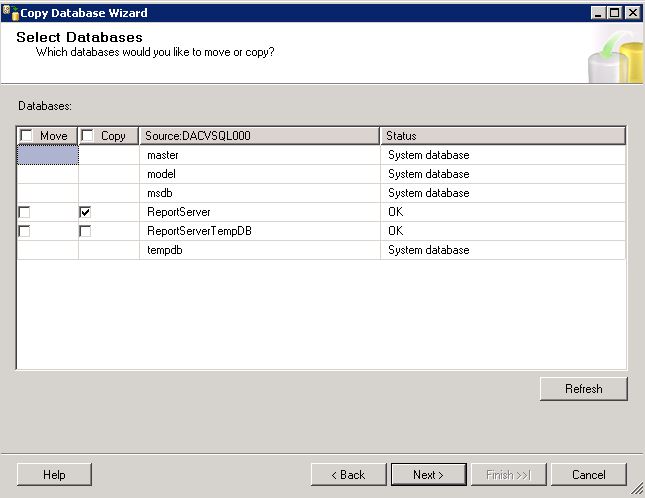
- First of all log into your Group Policy Management Console
- Create a new Group policy which will need to be assigned at the domain level, OU level or sub OU level depending on your design.
- Modify the Group Policy with the settings you require
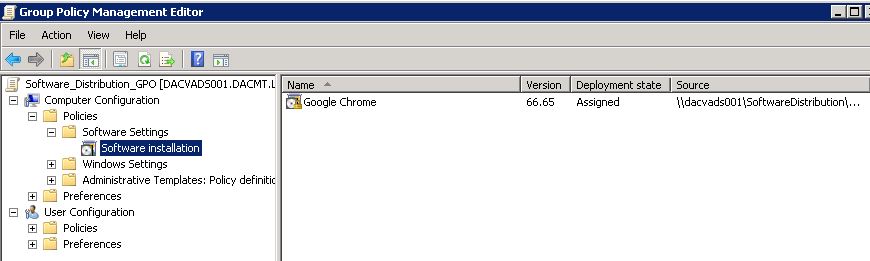
- Now have a look at where WMI Filters are located by scrolling down to the bottom of the GPMC
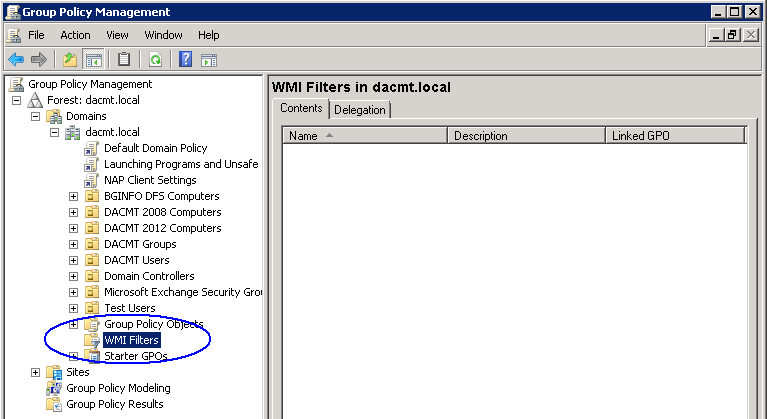
- Right click and select New
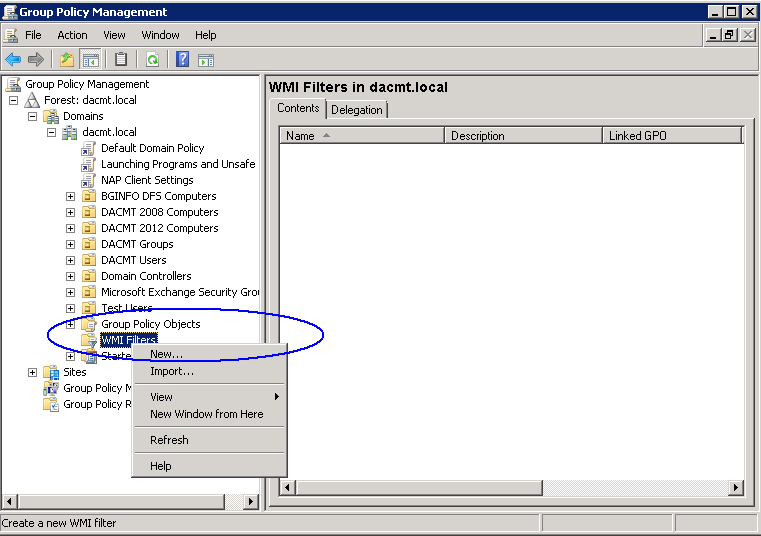
- Put in a name and description
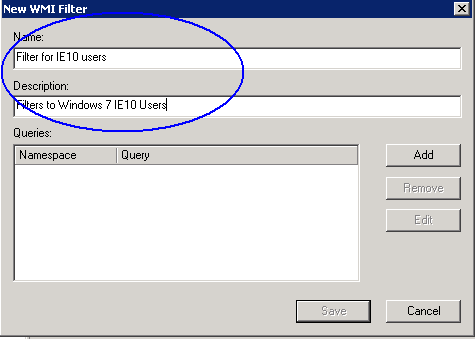
- Next Click Add and you will get a new box where we can then add our WMI filter code
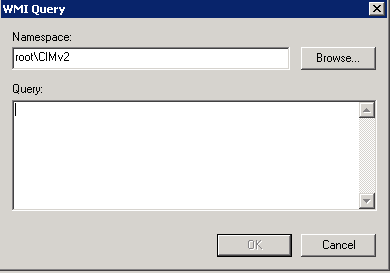
It is probably worth talking a little about the Namespace and WMI language at this point. The queries are written using the WMI Query Language (WQL), a SQL-like language. Queries can be combined with AND and OR logical operators to achieve whatever effect the administrator wants. Each query is executed against a particular WMI namespace. When you create a query, you must specify the namespace. The default is root\CIMv2, which is appropriate for most WMI queries.
I downloaded a small free program from Microsoft called WMI Code Creator. The tool also allows you to browse through the available WMI namespaces and classes on the local computer to find their descriptions, properties, methods, and qualifiers.
As an example below, I can look at the Operation System properties and find the version and also the name if I look at the Caption Properties
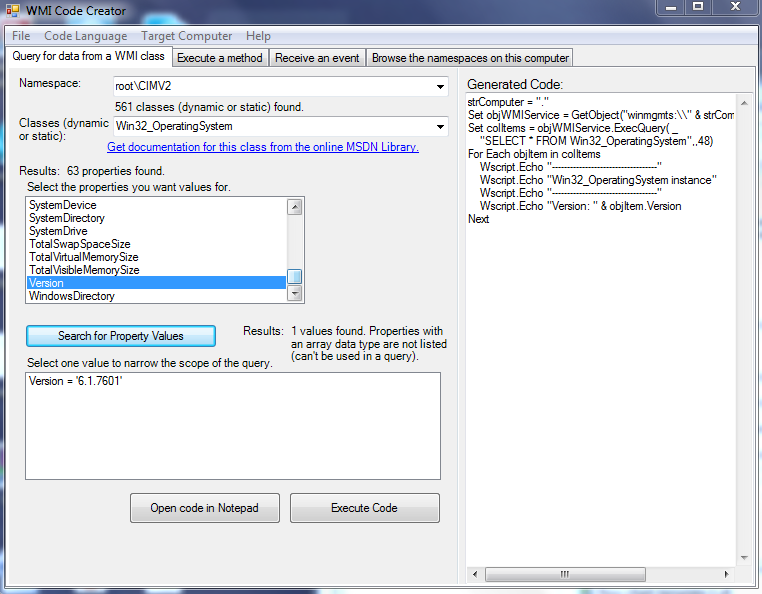
Note: This piece of software is useful for delving into the WMI information but you need to be able to use the WMI query in a way Active Directory understands.
SELECT [property] from [wmi class]
- Have a look at the table below. Both Windows Server 2012 and Windows 8 return version numbers that begin with 6.2. To differentiate between the client and server versions, include the clause to check the ProductType field. This value returns 1 for client versions of Windows such as Windows 8, 2 for server versions of Windows operating as domain controllers, and 3 for server versions of Windows that are not operating as domain controllers.
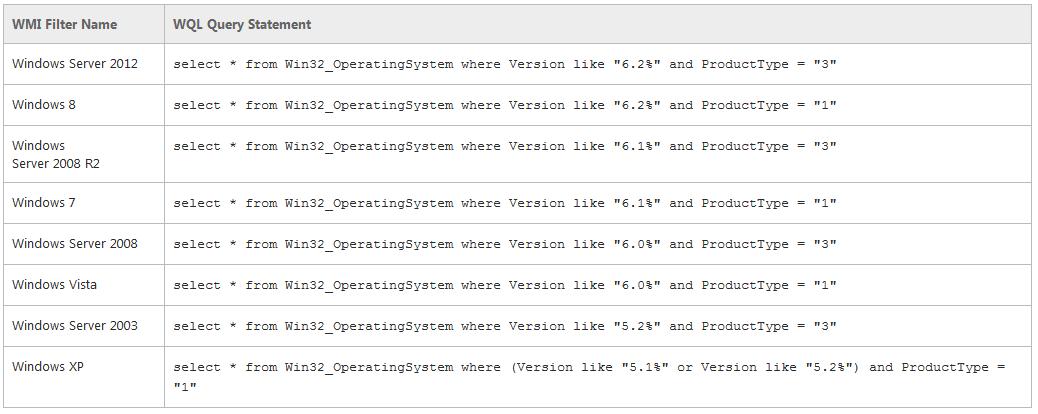
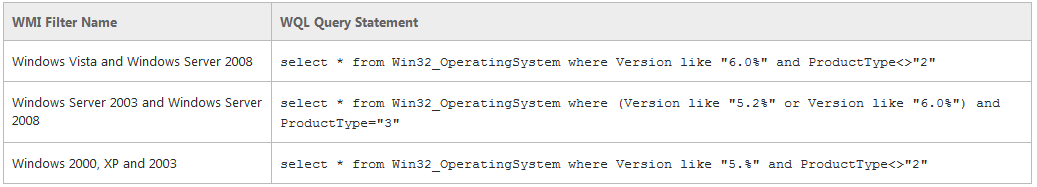
- You can also create combination filters when required by your design. The following table shows query statements for common operating system combinations.
- As an example we wanted our policy to apply to Windows 7, Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 so this was our filter
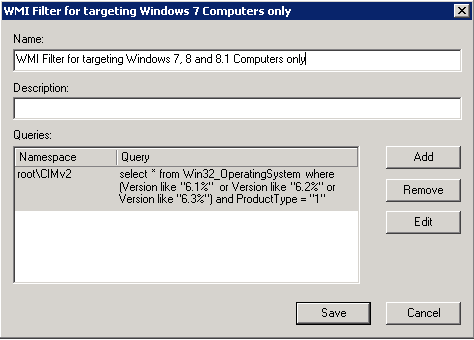
- Click Save and go back to your Group Policy
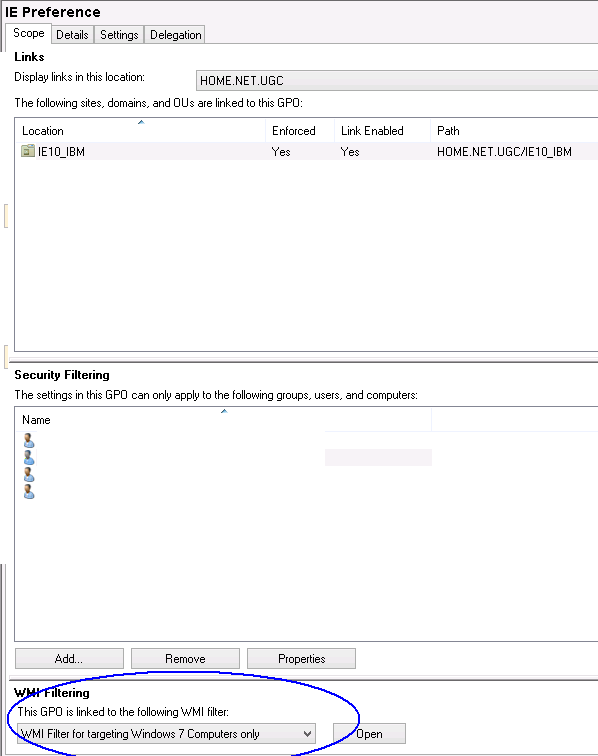
- Click on Scope and look at the bottom of the Scope Page where you will see WMI Filters
- Here you will need to select your WMI Filter and apply it
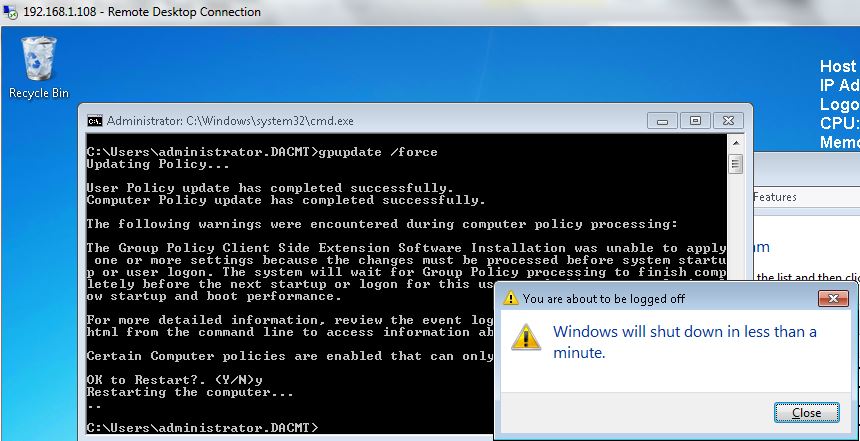
- Next click start run and type gpupdate /force on your DC to push out the settings.
- If you want to test that your GPO and WMI filters work then you can go back to your Group policy management console and look right down the bottom again where you have an option – Group Policy Results
- Right click and select Group Policy Results wizard and you can run through this and select a target computer and user to test whether then WMI works.
- At the end you will get a Summary, Details and Policy Events and you want to scroll down and check Details where it will say whether the WMI Filter came out as True or False!
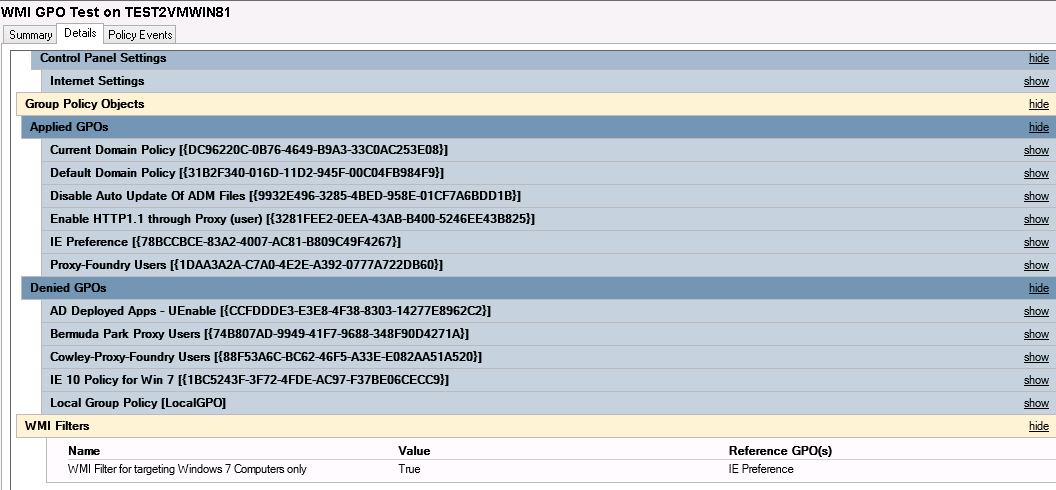
- And that’s it. It’s worth having a look through the many ways you can filter and write queries.
An interesting point to finish
What takes precedence when multiple, conflicting GPOs apply to the same OU?
“Links to a specific site, domain, or organizational unit are applied in reverse sequence based on link order. For example, a GPO with Link Order 1 has highest precedence over other GPOs linked to that container.”
What takes precedence when multiple, conflicting enforced GPOs apply to the same OU?
Standard GPO Inheritance Rules in Organizational Units
Any unconfigured settings anywhere in a GPO are ignored, and only configured settings are inherited. There are three possible scenarios:
- A higher-level GPO has a value for a setting, and a lower-level GPO does not.
- A GPO linked to a parent OU has a value for a setting, and a GPO linked to a child OU has a non-conflicting value for the same setting.
- A GPO linked to a parent OU has a value for a setting, and a GPO linked to a child OU has a conflicting value for the same setting.
If a GPO has settings configured for a parent organizational unit and the same policy settings are unconfigured for a child organizational unit, the child inherits the parent’s GPO settings. That makes sense.
If a GPO has settings configured for a parent organizational unit that do not conflict with the settings in a GPO configured for a child organizational unit, the child organizational unit inherits the parent GPO settings and applies its own GPOs as well. A good example of this is two logon scripts; these scripts don’t conflict, so both are run
If a GPO has settings configured for a parent organizational unit that conflict with the same settings in another GPO configured for a child organizational unit, the child organizational unit does not inherit those specific GPO settings from the parent organizational unit. The settings in the GPO child policy take priority