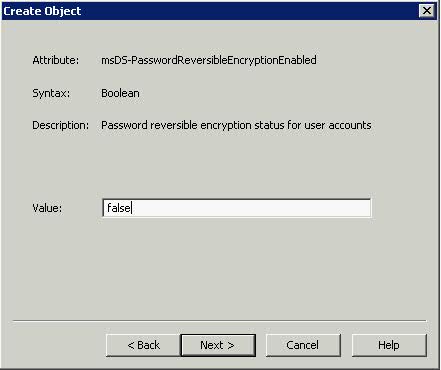
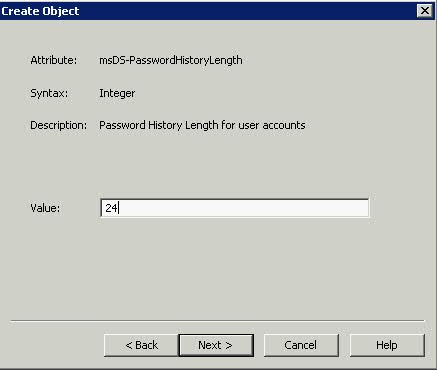
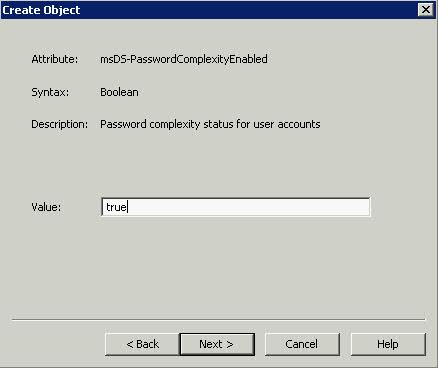
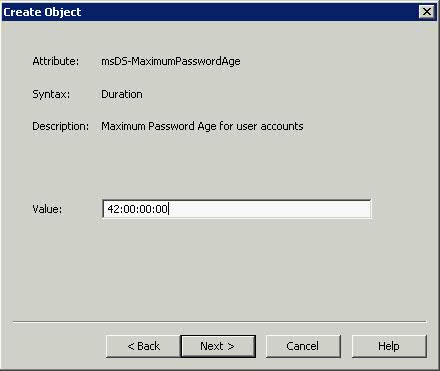
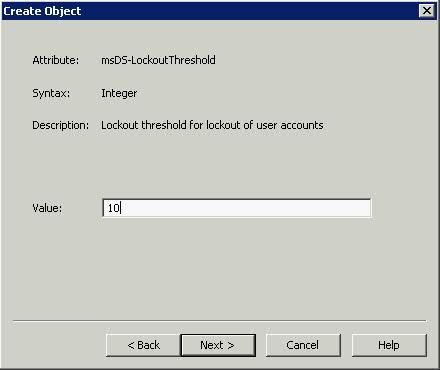
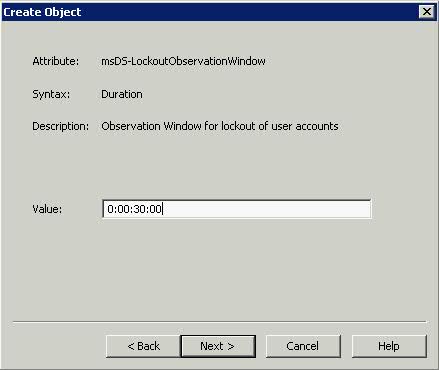
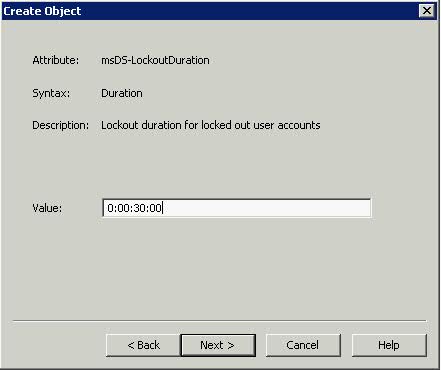
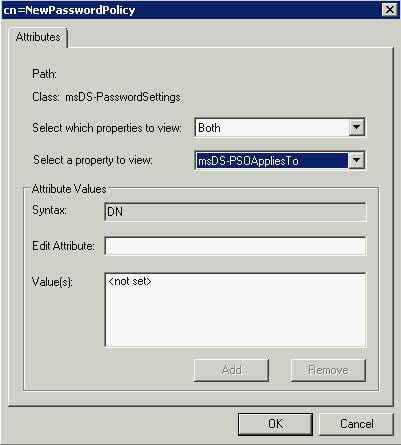
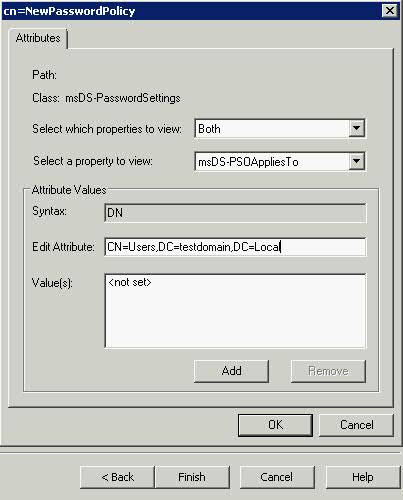
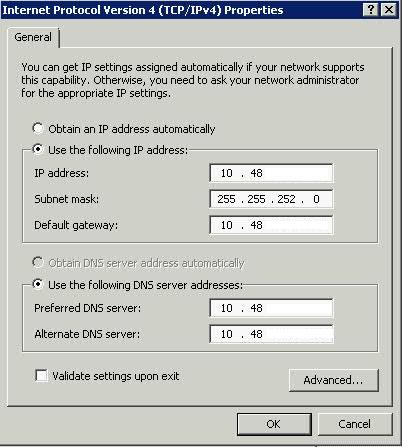
What is the VMware vSphere vMA?
The vSphere Management Assistant (vMA) is a SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11‐based virtual machine that includes prepackaged software such as the vSphere command‐line interface, and the vSphere SDK for Perl.
Why use vMA?
- vMA allows administrators to run scripts or agents that interact with ESXi hosts and vCenter Server systems without having to authenticate each time.
- Used to remotely manage ESXi hosts
- Central location to execute system management scripts
vMA Capabilities
- vMA provides a flexible and authenticated platform for running scripts and programs.
- As administrator, you can add vCenter Server systems and ESXi hosts as targets and run scripts and programs on these targets. Once you have authenticated while adding a target, you need not login again while running a vSphere CLI command or agent on any target.
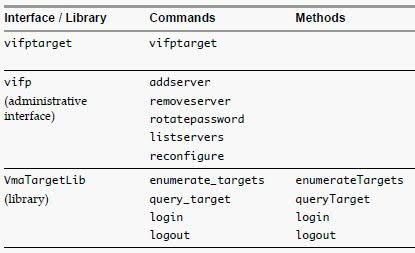
- As a developer, you can use the APIs provided with the VmaTargetLib library to programmatically connect to vMA targets by using Perl or Java.
- vMA enables reuse of service console scripts that are currently used for ESXi administration, though minor modifications to the scripts are usually necessary.
- vMA comes preconfigured with two user accounts, namely, vi‐admin and vi‐user.
- As vi‐admin, you can perform administrative operations such as addition and removal of targets. You can also run vSphere CLI commands and agents with administrative privileges on the added targets.
- As vi‐user, you can run the vSphere CLI commands and agents with read‐only privileges on the target.
- You can make vMA join an Active Directory domain and log in as an Active Directory user. When you run commands from such a user account, the appropriate privileges given to the user on the vCenter Server system or the ESXi host would be applicable.
- vMA can run agent code that make proprietary hardware or software components compatible with VMware ESX. These code currently run in the service console of existing ESX hosts. You can modify most of these agent code to run in vMA, by calling the vSphere API, if necessary. Developers must move any agent code that directly interfaces with hardware into a provider.
vMA Component Overview
When you install vMA, you are licensed to use the virtual machine that includes all vMA components.
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP1 – vMA runs SUSE Linux Enterprise Server on the virtual machine. You can move files between the ESXi host and the vMA console by using the vifs vSphere CLI command.
- VMware Tools – Interface to the hypervisor.
- vSphere CLI – Commands for managing vSphere from the command line. See the vSphere Command‐Line Interface Installation and Reference Guide.
- vSphere SDK for Perl – Client‐side Perl framework that provides a scripting interface to the vSphere API. The SDK includes utility applications and samples for many common tasks.
- Java JRE version 1.6 – Runtime engine for Java‐based applications built with vSphere Web Services SDK.
- vi‐fastpass ‐ Authentication component.
Requirements
- AMD Opteron, rev E or later
- Intel processors with EM64T support with VT enabled.
- vSphere 5.0
- vSphere 4.1 or later
- vSphere 4.0 Update 2 or later
- vCenter Application 5.0
vSphere Authentication Mechanism
vMA’s authentication interface allows users and applications to authenticate with the target servers using vi‐fastpass or Active Directory. While adding a server as a target, the Administrator can determine if the target needs to use vi‐fastpass or Active Directory authentication. For vi‐fastpass authentication, the credentials that a user has on the vCenter Server system or ESXi host are stored in a local credential store. For Active Directory authentication, the user is authenticated with an Active Directory server.
When you add an ESXi host as a fastpass target server, vi‐fastpass creates two users with obfuscated passwords on the target server and stores the password information on vMA:
- vi‐admin with administrator privileges
- vi‐user with read‐only privileges
The creation of vi‐admin and vi‐user does not apply for Active Directory authentication targets. When you add a system as an Active Directory target, vMA does not store any information about the credentials. To use the Active Directory authentication, the administrator must configure vMA for Active Directory.
After adding a target server, you must initialize vi‐fastpass so that you do not have to authenticate each time you run vSphere CLI commands. If you run a vSphere CLI command without initializing vi‐fastpass, you will be asked for username and password. You can initialize vi‐fastpass by using one of the following methods:
- Run vifptarget -s esx1.testdomain.local
- Call the Login method in a Perl or Java program
Installing vMA
Download the vMA from the following location
https://my.vmware.com/web/vmware/details?productId=229&downloadGroup=VMA50
- Use a vSphere Client to connect to a system that is running the supported version of ESXi or vCenter Server.
- If connected to a vCenter Server system, select the host to which you want to deploy vMA in the inventory pane.
- Select File > Deploy OVF Template. The Deploy OVF Template wizard appears.
- Select Deploy from a file or URL if you have already downloaded and unzipped the vMA virtual appliance package.
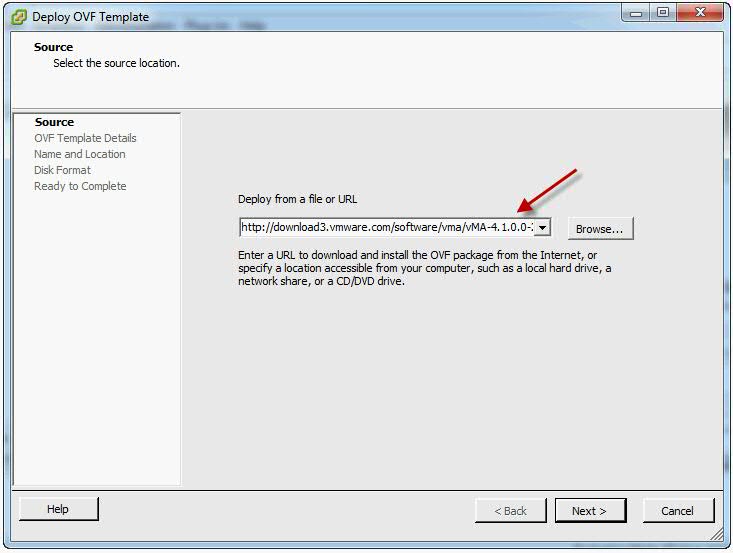
- Click Browse, select the OVF, and click Next.
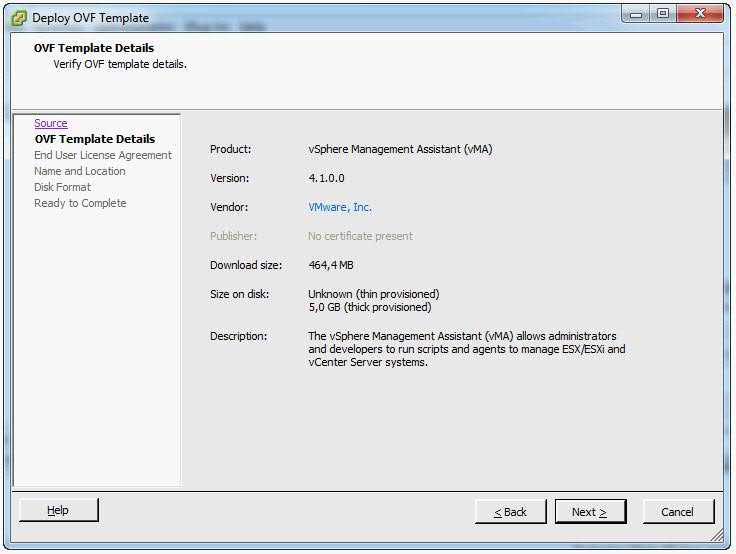
- Click Next when the OVF template details are displayed.
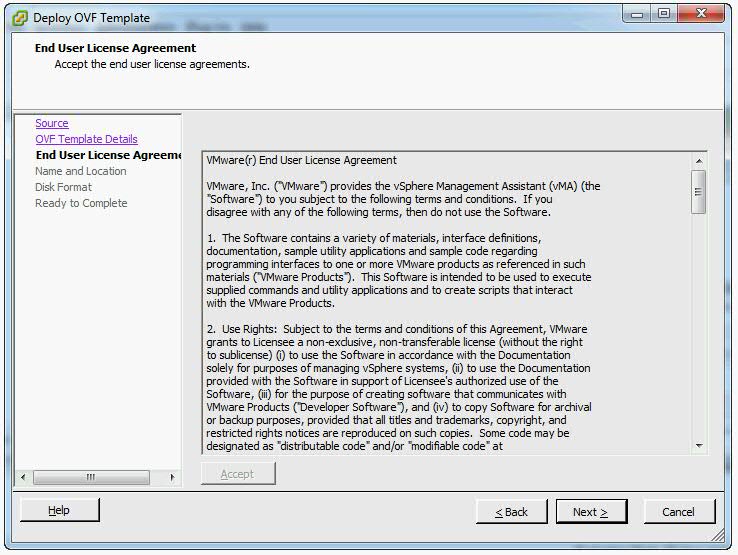
- Accept the license agreement and click Next.
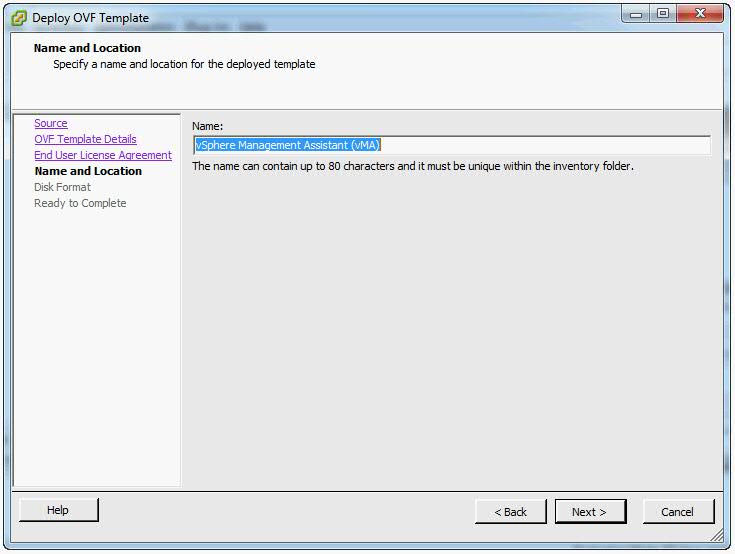
- Specify a name for the virtual machine. You can also accept the default virtual machine name. Select an inventory location for the virtual machine when prompted. If you are connected to a vCenter Server system, you can select a folder.
- If connected to a vCenter Server system, select the resource pool for the virtual machine. By default, the top‐level root resource pool is selected.
- If prompted, select the datastore to store the virtual machine on and click Next.
- Select the required disk format option and click Next.
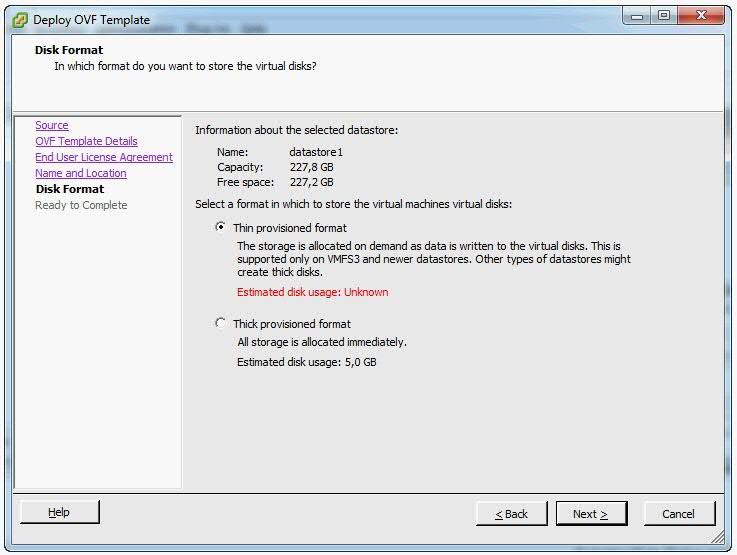
- Finish
- IMPORTANT. Enure that vMA is connected to the management network on which the vCenter Server system and the ESXi hosts that are intended vMA targets are located.
- Review the information and click Finish.
- The wizard deploys the vMA virtual machine to the host that you selected. The deploy process can take several minutes.
- In the vSphere Client, right‐click the virtual machine, and click Power On.
- You may encounter a network IP Pool error message. If you do follow the link below and make sure you set up your IP pools like the example below
- http://kb.vmware.com.Id=2007012
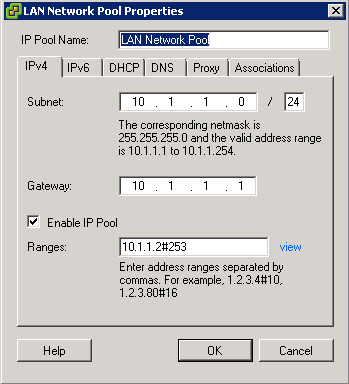
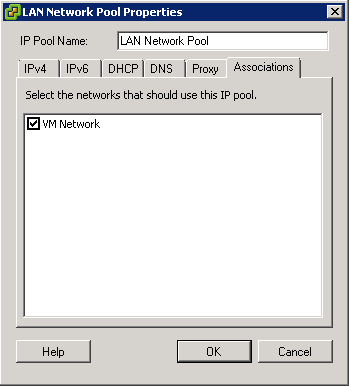
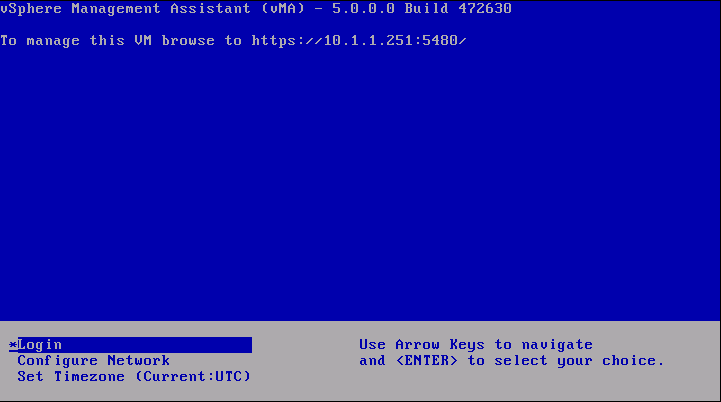
- Select the Console tab and answer the network configuration prompts
- When prompted, specify a password for the vi‐admin user. You will first have to enter the old password which is vmware. The system will then only accept a strong password for the change
- vMA is now configured and the vMA console appears. The console displays the URL from which you can access the Web UI.
Upgrading or Updating
Upgrading
IMPORTANT: You cannot upgrade a previous version of vMA to vMA 5.0. You must install a fresh vMA 5.0 instance.
Updating
You can download software updates including security fixes from VMware and components included in vMA, such as the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server updates and JRE.
- Access the Web UI on Port 5480
- Log in as vi‐admin.
- Click the Update tab and then the Status tab.
- Open the Settings tab and then from the Update Repository section, select a repository.
- Click Check Updates.
- Click Install Updates.
- You can also set an automatic download schedule for updates
Configure vMA for Active Directory Authentication
Configure vMA for Active Directory authentication so that ESXi hosts and vCenter Server systems added to Active Directory can be added to vMA without having to store the passwords in vMA’s credential store. This is a more secure way of adding targets to vMA.
- Ensure that the DNS server configured for vMA is the same as the DNS server of the domain. You can change the DNS server by using the vMA Console or the Web UI
- Ensure that the domain is accessible from vMA.
- Ensure that you can ping the ESXi and vCenter server systems that you want to add to vMA and that pinging resolves the IP address to , where domainname is the domain to which vMA is to be added.
- From the vMA console, run the following command
- sudo domainjoin-cli join dacmt.local administrator
- When prompted, provide the Active Directory administratorʹs password.
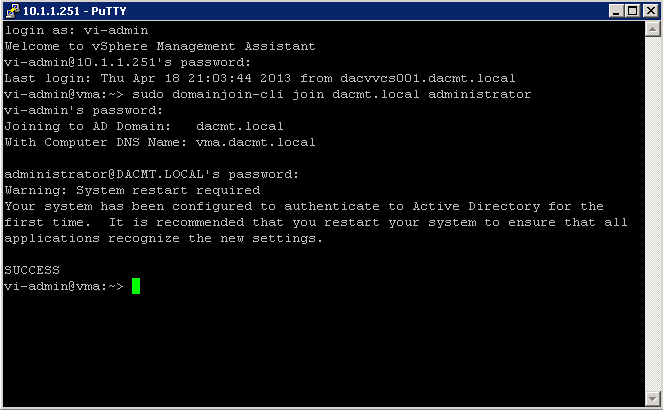
- On successful authentication, the command adds vMA as a member of the domain. The command also adds entries in the /etc/hosts file with vmaHostname.domainname.
- Restart vMA
- Now, you can add an Active Directory target to vMA
- Note: You can also access the Web UI
Add Target Servers to vMA
After you configure vMA, you can add target servers that run the supported vCenter Server or ESXi version. For vCenter Server, and ESXi system targets, you must have the name and password of a user who can connect to that system
To add a vCenter Server system as a vMA target for Active Directory Authentication
- Log in to vMA as vi‐admin.
- Add a server as a vMA target by running the following command
vifp addserver vc1.mycomp.com –authpolicy adauth –username ADDOMAIN\user1
Here, –authpolicy adauth indicates that the target needs to use the Active Directory authentication. If you run this command without the –username option, vMA prompts for the name of the user that can connect to the vCenter Server system. You can specify this user name as shown in the following example:
If –authpolicy is not specified in the command, then fpauth is taken as the default authentication policy.
- Verify that the target server has been added by typing
vifp listservers –long
- Set the target as the default for the current session:
vifptarget –set | -s
- Verify that you can run a vSphere CLI command without authentication by running a command on one of the ESXi hosts, for example:
esxcli –server –vihost network nic list
- The command runs without prompting for authentication information.
IMPORTANT: If the name of a target server changes, you must remove the target server by using vifp removeserver with the old name, then add the server using vifp addserver with the new name
To add a vCenter Server system as a vMA target for fastpass Authentication
- Log in to vMA as vi‐admin
- Add a server as a vMA target by running the following command:
vifp addserver vc2.mycomp.com –authpolicy fpauth
Here, –authpolicy fpauth indicates that the target needs to use the fastpass authentication.
- Specify the username when prompted: MYDOMAIN\user1Specify the password for that user when prompted.
- Review and accept the security risk information.
- Verify that the target server has been added.
vifp listservers –long
- Set the target as the default for the current session.
vifptarget –set | -s
- Verify that you can run a vSphere CLI command without authentication by running a command on one of the ESXi hosts, for example:
esxcli –server –vihost network nic list
IMPORTANT: If the name of a target server changes, you must remove the target server by using vifp removeserver with the old name, then add the server using vifp addserver with the new name
To add an ESXi host as a vMA target
- Log in to vMA as vi‐admin.
- Run addserver to add a server as a vMA target.
vifp addserver Serverxyz
- You are prompted for the target server’s root user password.Specify the root password for the ESXi host that you want to add.
- vMA does not retain the root password. Instead, vMA adds vi‐admin and vi‐user to the ESXi host, and stores the obfuscated passwords that it generates for those users in the VMware credential store.
In a vSphere client connected to the target server, the Recent Tasks panel displays information about the users that vMA adds. The target server’s Users and Groups panel displays the users if you select it.
- Verify that the target server has been added:
vifp listservers
- Set the target as the default for the current session.
vifptarget –set | -s Serverxyz
- Verify that you can run a vSphere CLI command without authentication by running a command, for example:
esxcli network nic list
Running vSphere CLI for the Targets
If you have added multiple target servers, by default, vMA executes commands on the first server that you added. You should specify the server explicitly when running commands.
To run vSphere CLI for the targets
- Add servers as vMA targets.
vifp addserver vCenterserver
vifp addserver serverxyz
- Verify that the target server has been added:
vifp listservers
vifptarget -s serverxyz
- The command initializes the specified target server. Now, this server will be taken as the default target forthe vSphere CLI or vSphere SDK for Perl scripts.
- Run vSphere CLI or vSphere SDK for Perl scripts, by specifying the target server. For example:
esxcli –server serverxyz network nic list
Target Management Example Sequence
The following sequence of commands adds an ESXi host, lists servers, runs vifptarget to enable vi‐fastpass, runs a vSphere CLI command, and removes the ESXi host.
- vifp addserver serverxyz.company.com
- Type password: <password, not echoed to screen>
- vifp listservers
- serverxyz.company.com ESX
- vifptarget –set serverxyz.company.com
- esxcli storage core path list
cdrom vmhba0:1:0 (0MB has 1 paths and policy of fixed
Local 0:7:1 vmhba0:1:0 On active preferred
- vifp removeserver server1.company.com
- <password, not echoed to screen>
Enable the vi-user for the first time
- Log into vMA as vi-admin
- Set a password for the vi-user account
- sudo passwd vi-user
Note: The vi-admin is not “root” and receives all its privileges from the configuration of sudo. Sudo is a delegation system that allows “root” to allow other users privileges above and beyond merely being a “user.”
Adding another user alongside vi-admin and vi-user
‘sudo useradd username -p password’
Use vmkfstools to manage VMFS Datastores
Useful Command Ref
http://vmetc.com/wp-content/uploads/2007/11/man-vmkfstools.txt

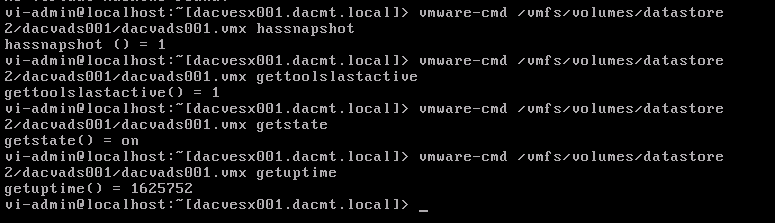
Use vmware-cmd to manage VMs
Useful Command Ref
http://www.vmware.com/support/developer/vcli/vcli41/doc/reference/vmware-cmd.html
Example showing 4 different commands
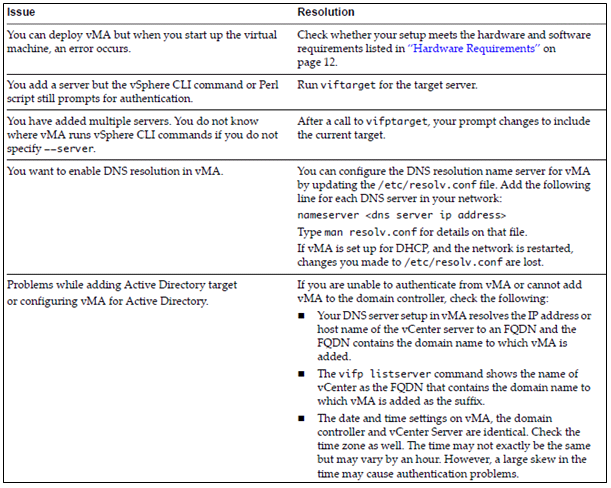
Troubleshoot common vMA errors and conditions
VMware TV
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cIh4QT0-hdY
Changing the IP Address or Hostname of vMA
https://communities.vmware.com/people/ravinder1982/blog/2012/06/15/changing-ip-address-or-hostname-of-vma