Installing DNS
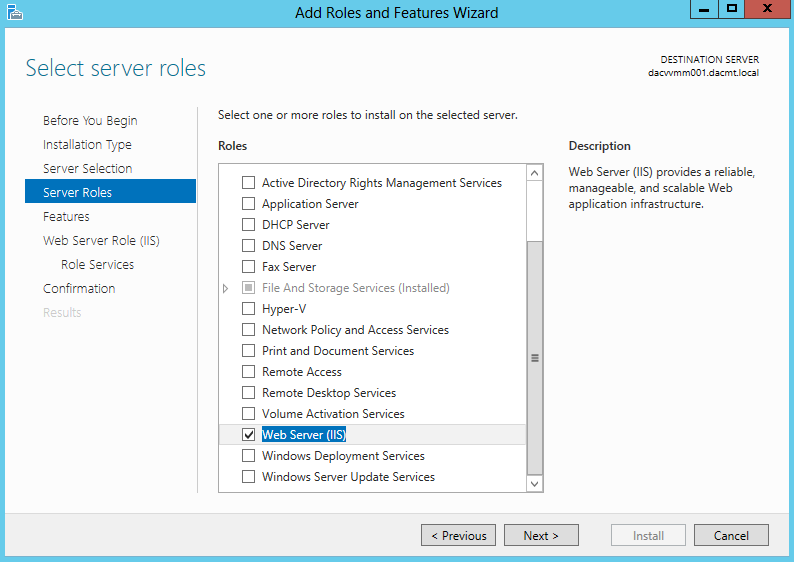
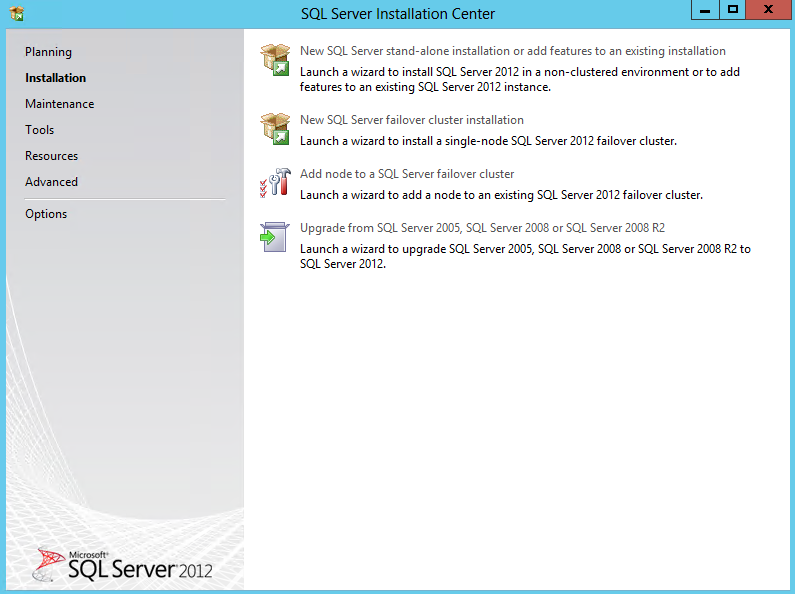
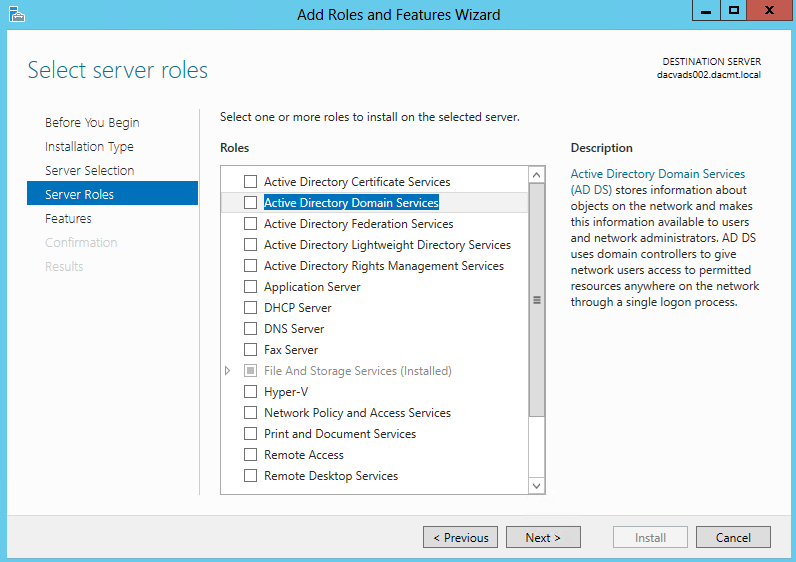
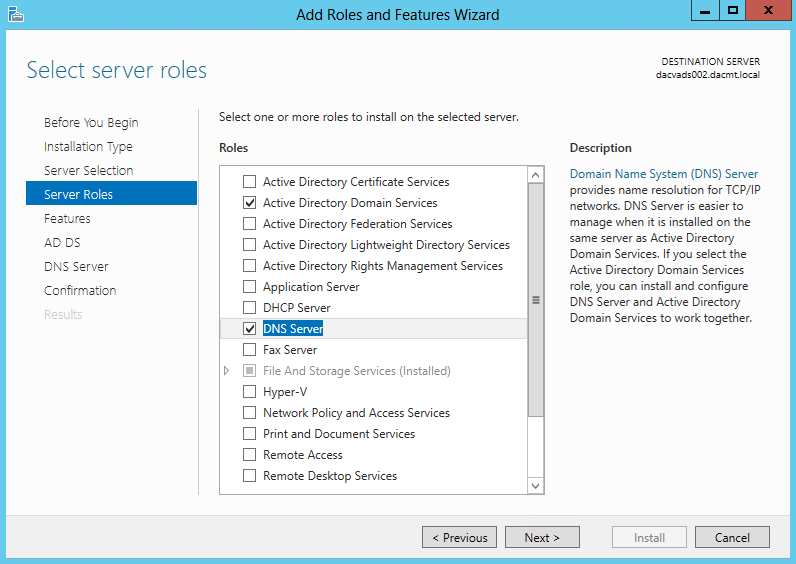
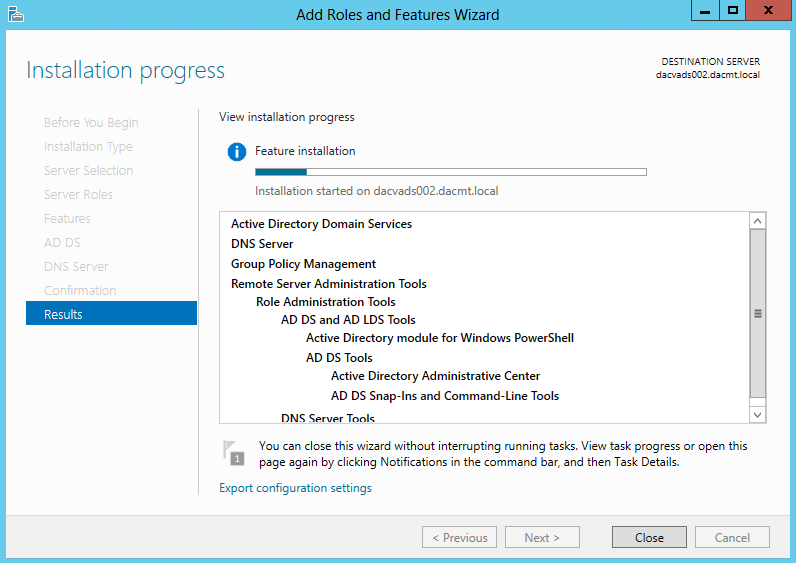
The process of deploying a DNS server on a Windows Server 2012 computer involves installing the DNS Server role by using the Add Roles and Features Wizard in Server Manager. The actual installation requires no additional input; there are no additional pages in the wizard and no role services to select. Once you install the DNS Server role, the computer is ready to perform caching-only name resolution services for any clients that have access to it. The role also installs the DNS Manager console, which you use to configure the DNS server’s other capabilities
DNS Queries
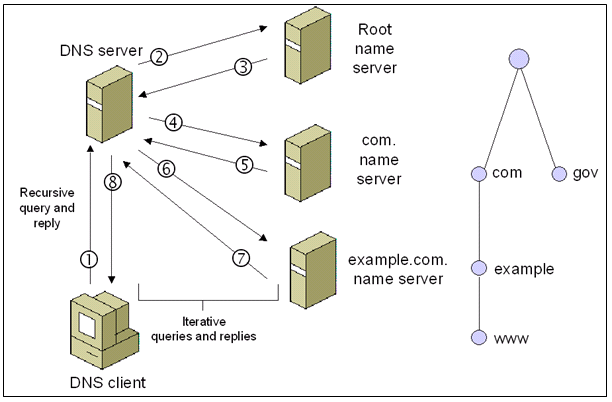
- An iterative query is one where the DNS server may provide a partial answer to the query (or give an error). DNS servers must support non-recursive queries.
- A recursive query is one where the DNS server will fully answer the query (or give an error). DNS servers are not required to support recursive queries and both the resolver (or another DNS acting recursively on behalf of another resolver) negotiate use of recursive service using bits in the query headers
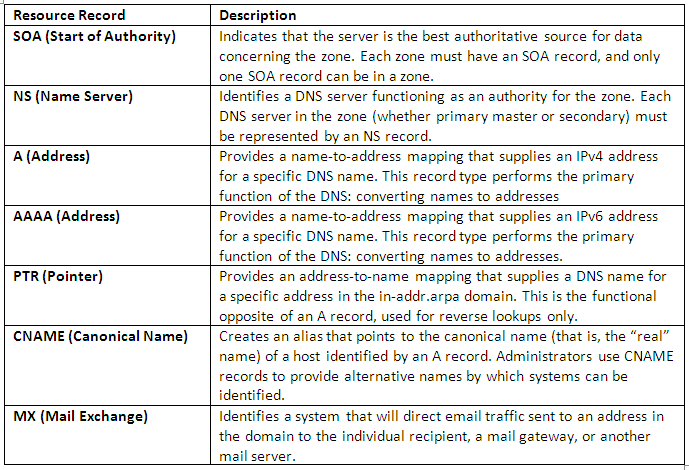
Types of DNS Record
Creating zones
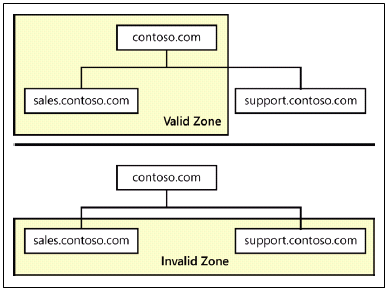
A zone is an administrative entity you create on a DNS server to represent a discrete portion of the DNS namespace. Administrators typically divide the DNS namespace into zones to store them on different servers and to delegate their administration to different people. Zones always consist of entire domains or subdomains. You can create a zone that contains multiple domains as long as those domains are contiguous in the DNS namespace. For example, you can create a zone containing a parent domain and its child, because they are directly connected, but you cannot create a zone containing two child domains without their common parent, because the two children are not directly connected.
The DNS server in Windows Server 2012 can support as many as 200,000 zones on a single server, although it is hard to imagine a scenario that would require that many. In most cases, an administrator creates multiple zones on a server and then delegates most of them to other servers, which then become responsible for hosting them.
Every zone consists of a zone database, which contains the resource records for the domains in that zone. The DNS server in Windows Server 2012 supports three zone types, which specify where the server stores the zone database and what kind of information it contains. These zone types are as follows
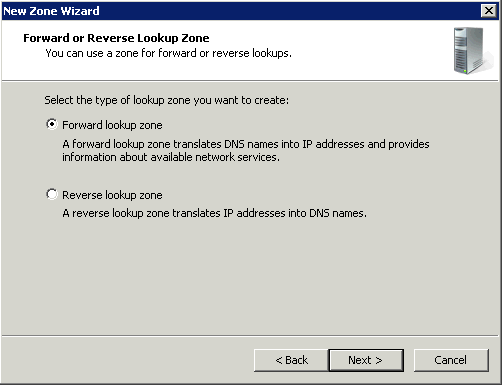
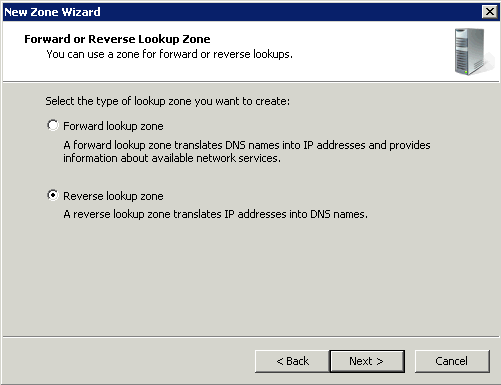
Forward Lookup Zone
A forward lookup zone is a DNS zone in which hostname to IP address relations are stored. When a computer requests the IP address of a specific hostname, the forward lookup zone is queried and the result is returned.
Reverse Lookup Zone
A reverse lookup zone does just the opposite. When a computer requests the hostname of an IP address, the reverse lookup zone is queried and the result is returned.
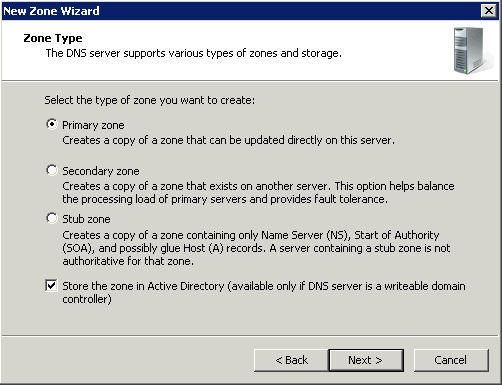
Primary/Active Directory Integrated Zone
Zones that are integrated with Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) use directory replication to transfer zone data between DNS servers. Zones that are not integrated with AD DS (that is, that store zone data in files) use conventional zone transfer to propagate zone changes among primary and secondary DNS server. Zones that are integrated with AD DS usually require little or no management apart from the management of the corresponding AD DS forests and domains. Active Directory–integrated zones do not ordinarily employ secondary DNS servers.
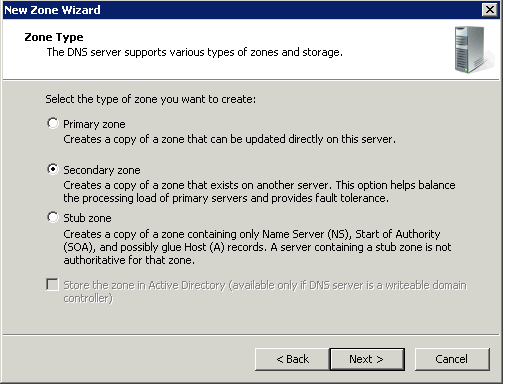
Secondary Zones
Secondary servers can be used as backups for DNS clients. This allows you to use secondary servers as a means to create fault tolerant and load balanced DNS query traffic on your network and reserve your DNS-enabled primary servers for use only by those clients that need them to perform dynamic registration and updates of their A and PTR RRs. Secondary DNS servers maintain a read-only copy of zone data that is transferred periodically from the primary DNS server for the zone. You can configure DNS clients to query secondary DNS servers instead of (or in addition to) the primary DNS server for a zone, reducing demand on the primary server and ensuring that DNS queries for the zone will be answered even if the primary server is not available.
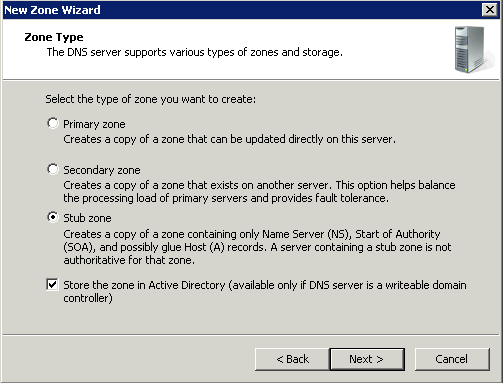
Stub zones
Stub zones are used when you want a DNS server hosting a parent zone to remain aware of the authoritative DNS servers for one of its child zones. If the stub zone for a child zone is hosted on the same DNS server as the parent zone, the DNS server hosting the stub zone will receive a list of all new authoritative DNS servers for the child zone when it requests an update from the stub zone’s master server . This method of updating the DNS server hosting the parent zone maintains a current list of the authoritative DNS servers for the child zone as they are added and removed.
A conditional forwarder is not an efficient method of keeping a DNS server hosting a parent zone aware of the authoritative DNS servers for a child zone. If you used this method, whenever the authoritative DNS servers for the child zone changed, the conditional forwarder setting on the DNS server hosting the parent zone would have to be manually configured with the IP address for each new authoritative DNS server for the child zone.
Caching Server
Caching servers can also be arranged in a hierarchy. This makes sense in cases where the network capacity is limited and/or network latency between the DNS client and the rest of the Internet is high. When connecting a laptop to the Internet through a slow dial-up connection it makes sense to run a caching server right on the laptop. This way each click on a hyperlink on the same web-site will not cause DNS related traffic over the dial-up link. Such a local caching server is often configured to send all queries for which it does not have cached answers to the ISPs caching server in turn. Sometimes corporate networks have local caching servers that in turn send queries to a corporate caching server before they are sent out to the Internet. This way the corporate caching server can build a large cache based on queries from the whole enterprise.
Types of DNS Configuration
Interfaces
Use this tab to select the IP Addresses that the DNS Server will use to listen to queries
Forwarder
A forwarder is a Domain Name System (DNS) server on a network that you can use to forward DNS queries for external DNS names to DNS servers outside that network. You can also use conditional forwarders to forward queries according to specific domain names.
A DNS server on a network is designated as a forwarder when you configure the other DNS servers in the network to forward the queries that they cannot resolve locally to that DNS server. By using a forwarder, you can manage name resolution for names outside your network, such as names on the Internet
To use forwarders to manage the DNS traffic between your network and the Internet, configure your network’s firewall to allow only a dedicated set of DNS servers to communicate with the Internet. When you configure other DNS servers in your network to forward queries that they cannot resolve locally to these designated DNS servers, they act as your forwarders. DNS servers that forward queries to the Internet should not host zones to avoid exposing your internal network namespace to external attackers.
Advanced
Use this tab to set Advanced Settings
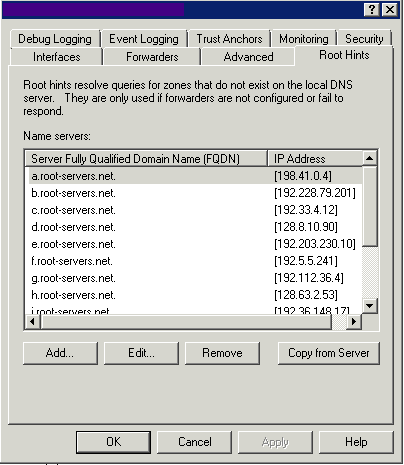
Root Hints
Use this tab to specify the servers to be used for root hints when forwarders are not configured or do not respond. The 13 root name server names are located in a domain called root-servers.net and are named using letters of the alphabet. The servers are scattered around the world on different subnets to provide fault tolerance.
Debug Logging
Use this tab to configure packet-level logging for debugging purposes.
Event Logging
Use this tab to specify the types of events that will be recorded in the DNS event log.
Trust Anchors
Trust Anchors is the new feature in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7. We can now sign and host DNSSEC-signed (Domain Name System Security Extension) zones to provide more security in our DNS infrastructure.
Monitoring
Use this tab to perform tests to verify the correct server configuration.
Security
Use this tab to set permissions for the DNS Server
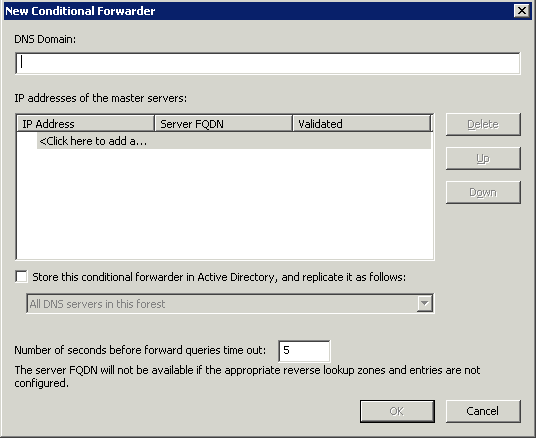
Conditional forwarders
A conditional forwarder setting configures the DNS server to forward a query it receives to a DNS server depending on the DNS name contained in the query. In situations where you want DNS clients in separate networks to resolve each others’ names without having to query DNS servers on the Internet, such as in the case of a company merger, you should configure the DNS servers in each network to forward queries for names in the other network. DNS servers in one network will forward names for clients in the other network to a specific DNS server that will build up a large cache of information about the other network. When forwarding in this way, you create a direct point of contact between two networks’ DNS servers, reducing the need for recursion.
Stub zones do not provide the same server-to-server benefit because a DNS server hosting a stub zone in one network will reply to queries for names in the other network with a list of all authoritative DNS servers for the zone with that name, instead of the specific DNS servers you have designated to handle this traffic. This configuration complicates any type of security settings that you want to establish between specific DNS servers running in each of the networks.
Zone Delegation
Domain Name System (DNS) provides the option of dividing up the namespace into one or more zones, which can then be stored, distributed, and replicated to other DNS servers. When you are deciding whether to divide your DNS namespace to make additional zones, consider the following reasons to use additional zones:
- You want to delegate management of part of your DNS namespace to another location or department in your organization.
- You want to divide one large zone into smaller zones to distribute traffic loads among multiple servers, improve DNS name resolution performance, or create a more-fault-tolerant DNS environment.
- You want to extend the namespace by adding numerous subdomains at once, for example, to accommodate the opening of a new branch or site.
If, for any of these reasons, you can benefit from delegating zones, it might make sense to restructure your namespace by adding additional zones. When you are deciding how to structure zones, use a plan that reflects the structure of your organization.
When you delegate zones within your namespace, remember that for each new zone that you create, you need delegation records in other zones that point to the authoritative DNS servers for the new zone. This is necessary both to transfer authority and to provide correct referral to other DNS servers and clients of the new servers that are being made authoritative for the new zone.
When a standard primary zone is first created, all the resource record information is stored as a text file on a single DNS server. This server acts as the primary master for the zone. Zone information can be replicated to other DNS servers to improve fault tolerance and server performance.
When you are structuring your zones, there are several good reasons to use additional DNS servers for zone replication:
- Added DNS servers provide zone redundancy, which makes it possible for DNS names in the zone to be resolved for clients if a primary server for the zone stops responding.
- Added DNS servers can be placed so as to reduce DNS network traffic. For example, adding a DNS server to the opposing side of a low-speed, wide area network (WAN) link can be useful in managing and reducing network traffic.
- Additional secondary servers can be used to reduce loads on a primary server for a zone.