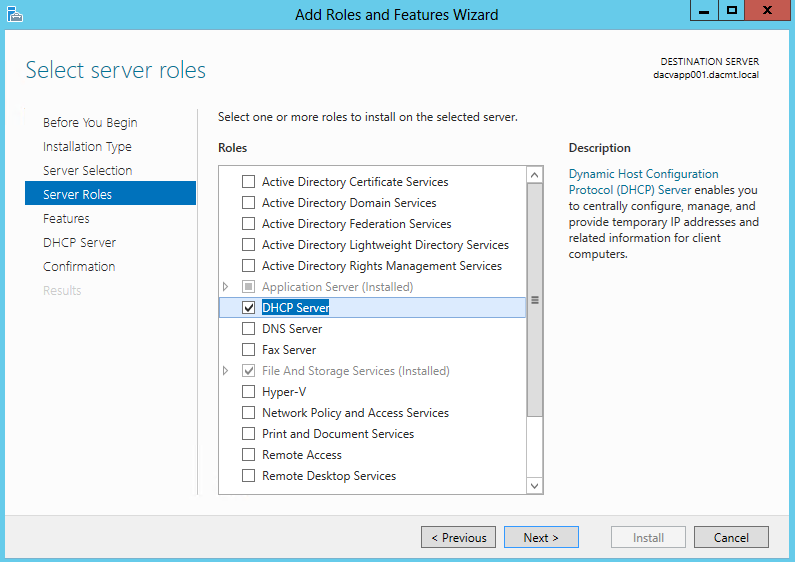
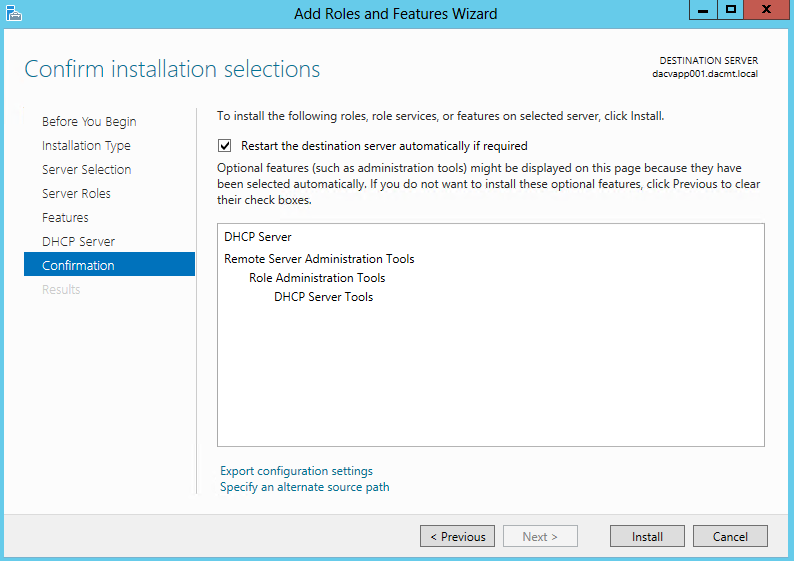
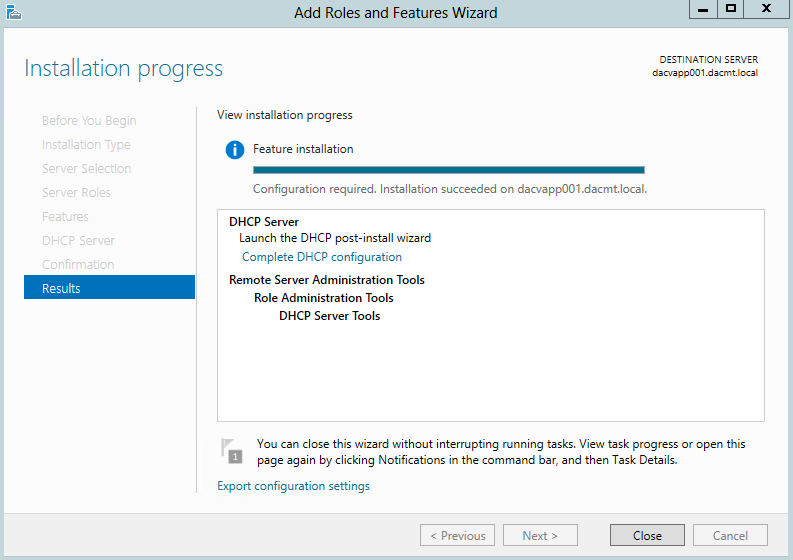
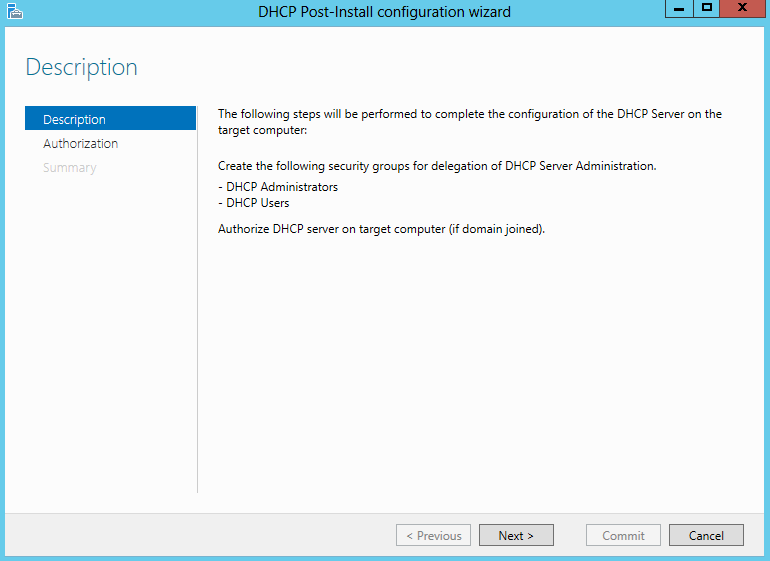
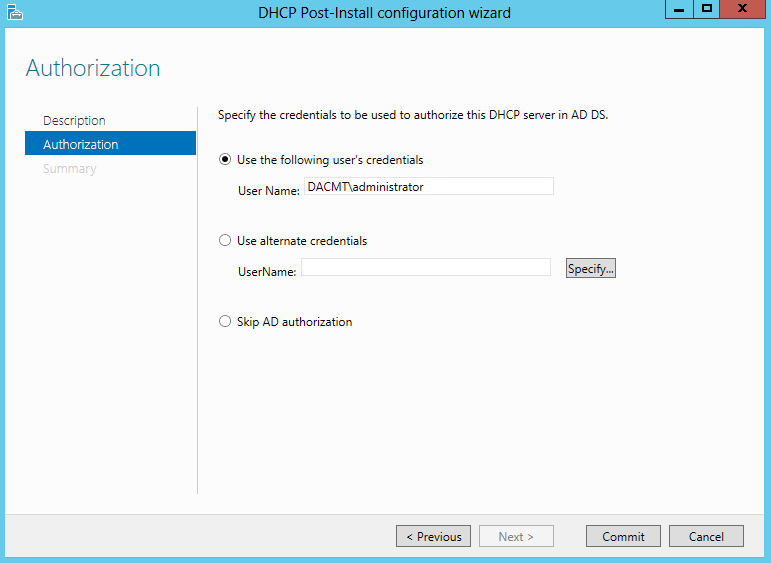
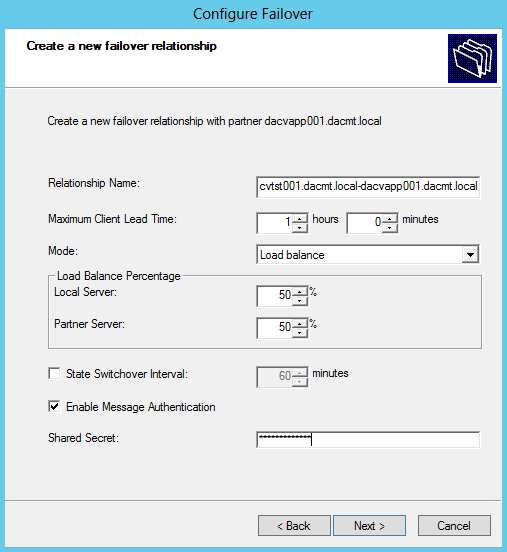
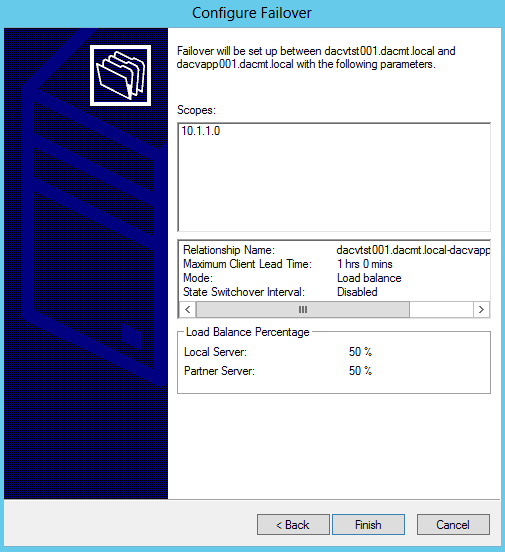
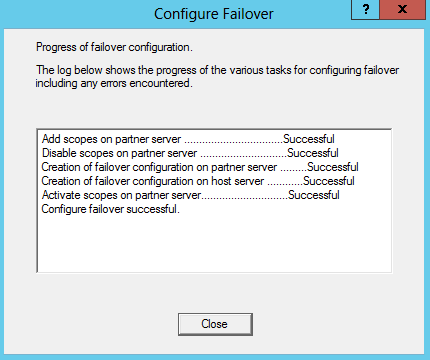
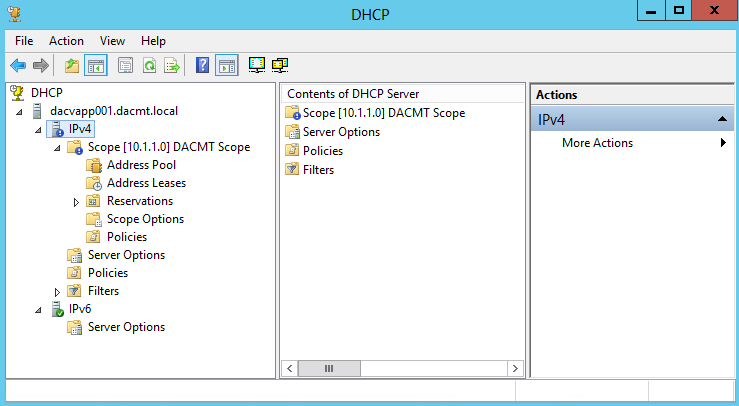
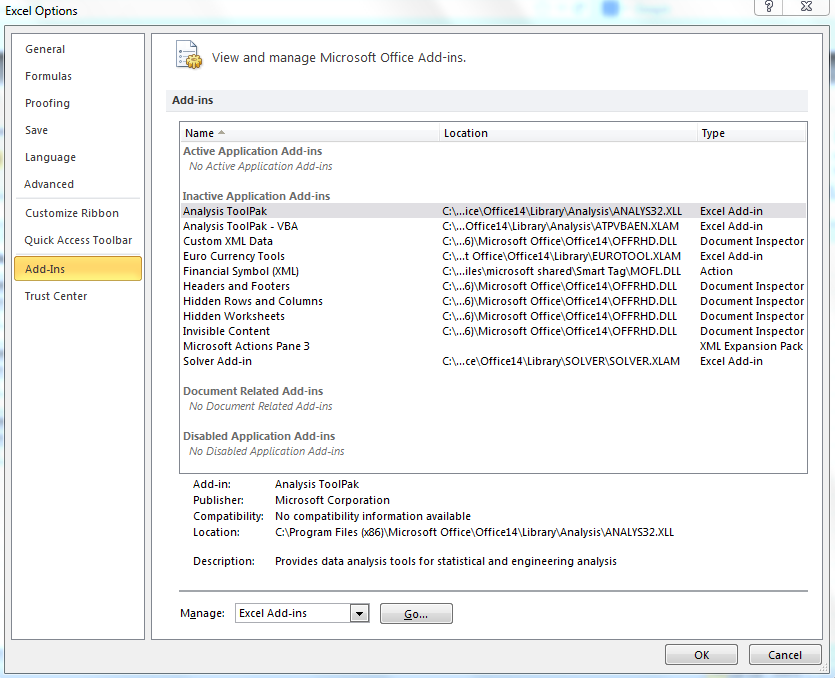
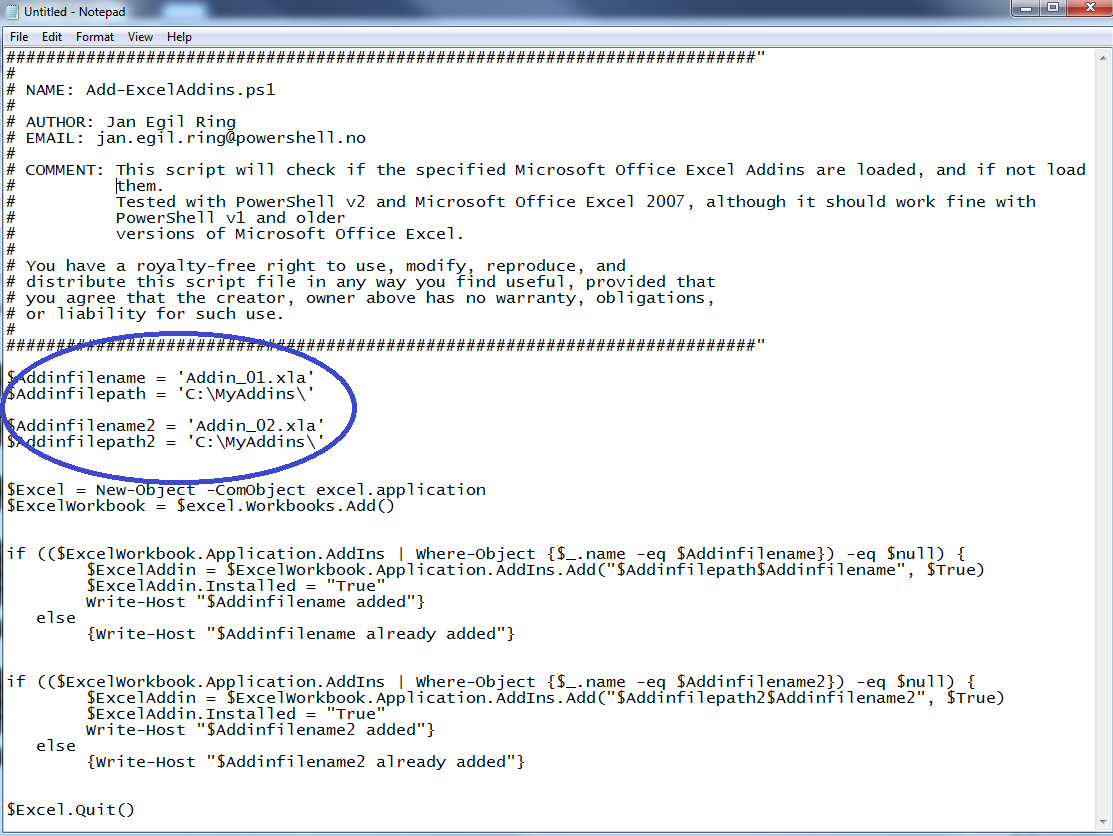
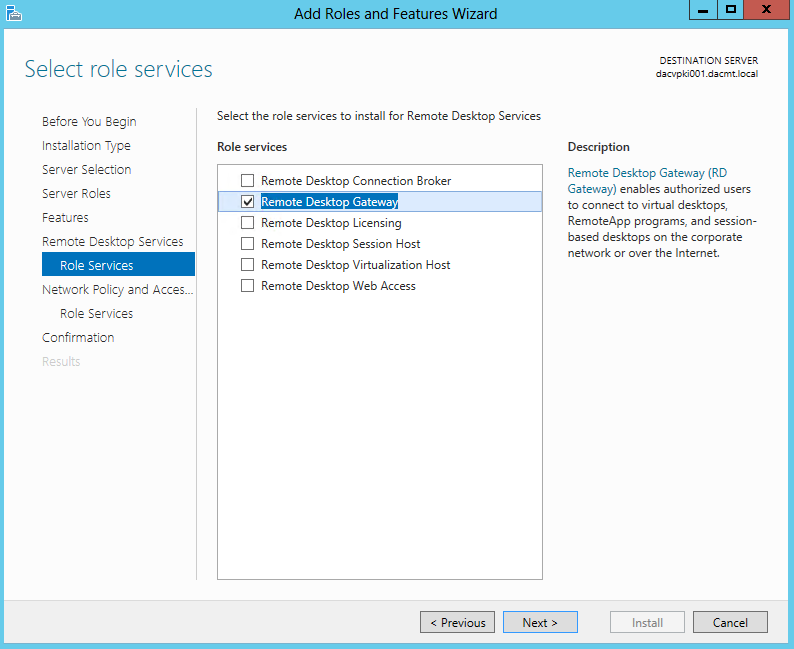
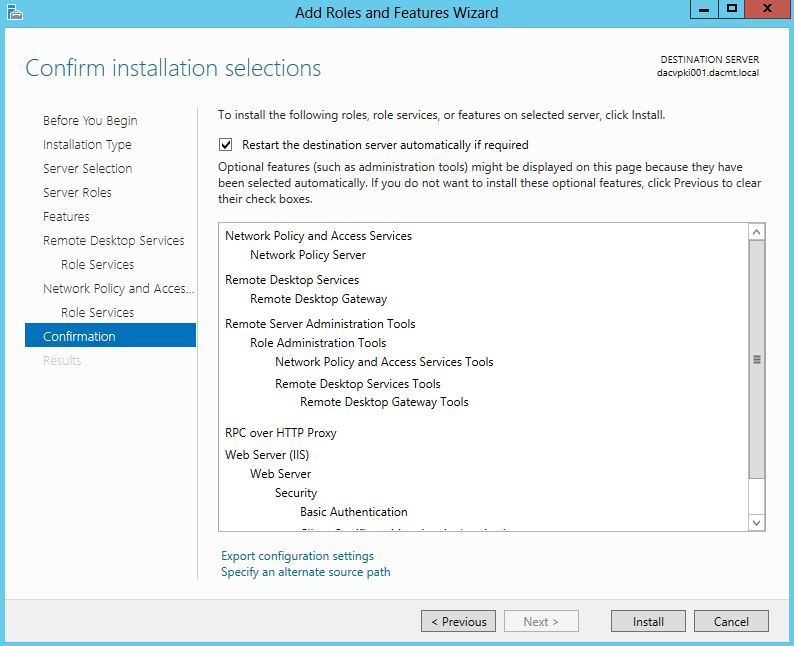
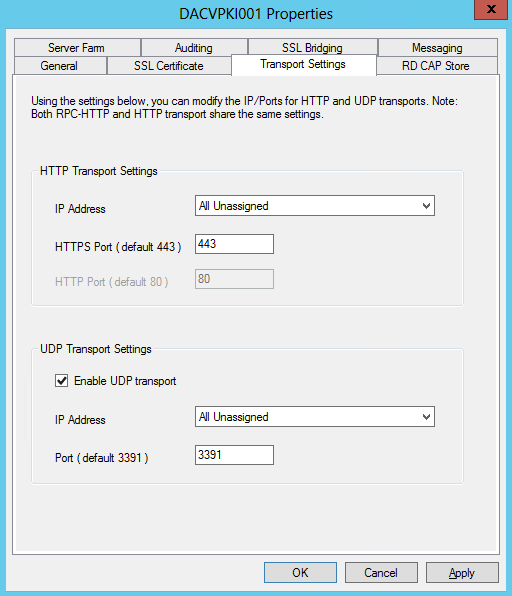
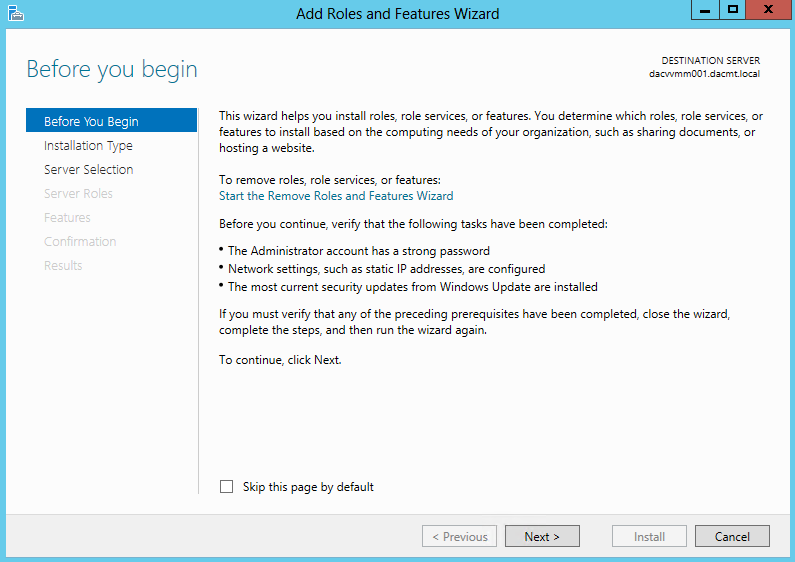
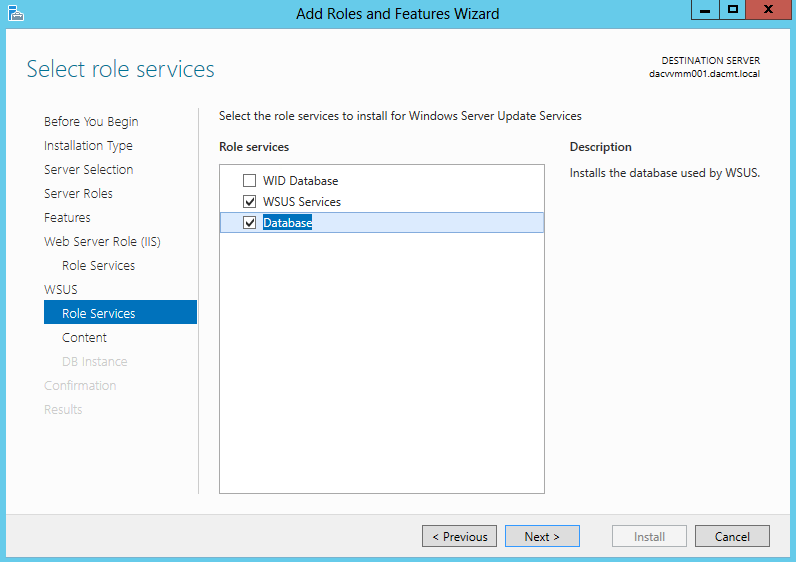
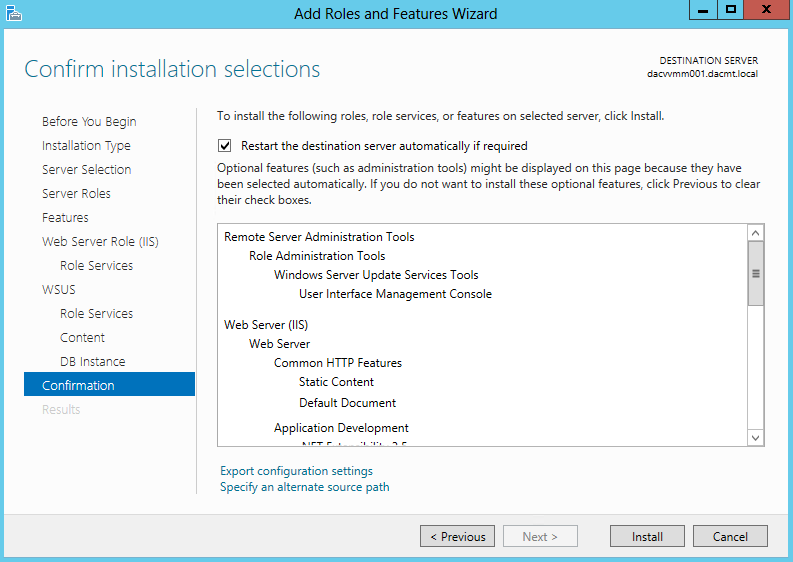
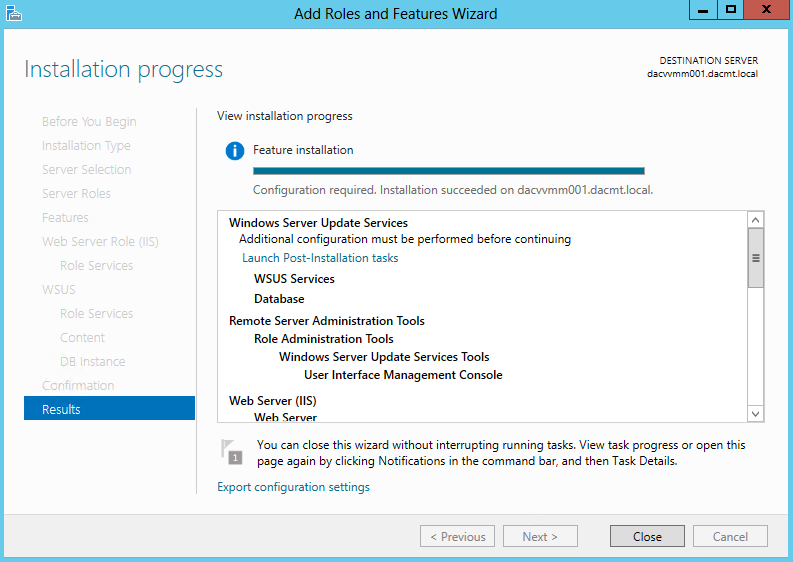
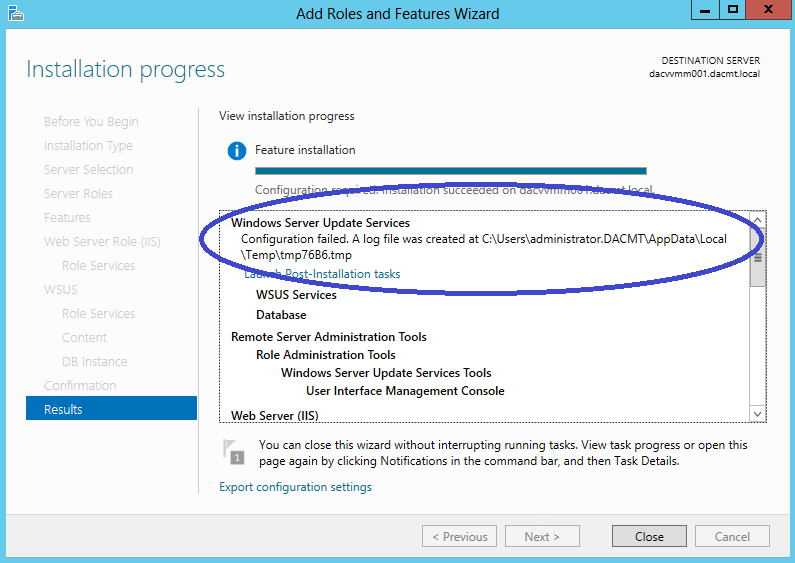
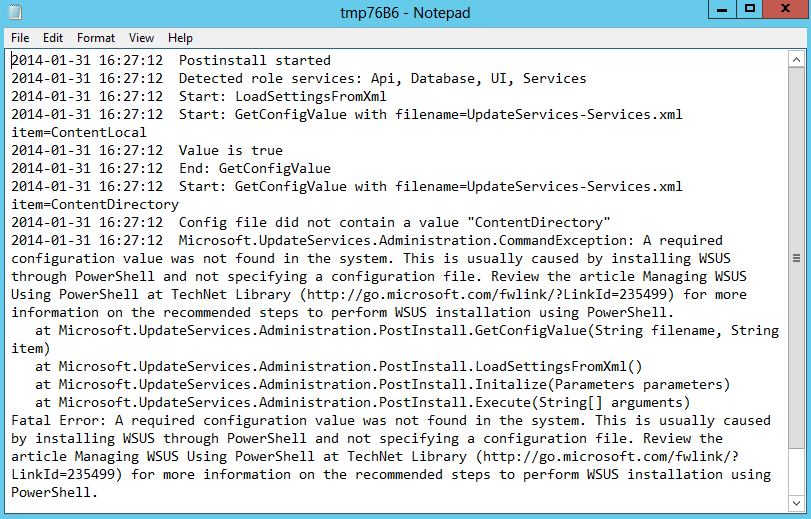
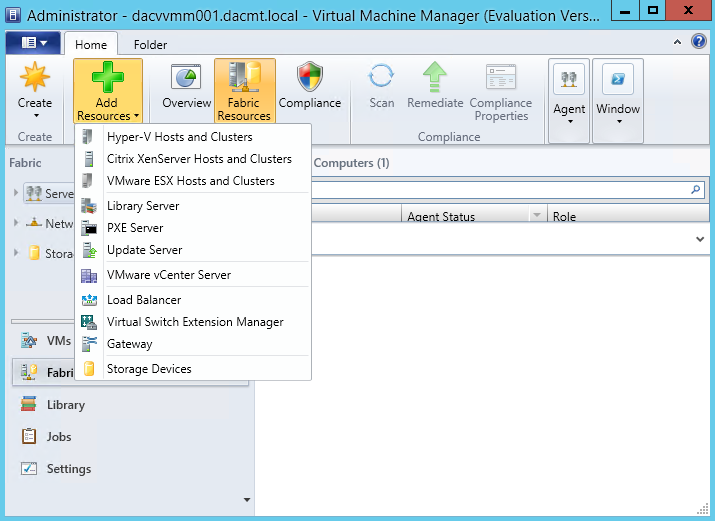
What are Functional Levels?
Functional levels determine the available Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain or forest capabilities. They also determine which Windows Server operating systems you can run on domain controllers in the domain or forest. However, functional levels do not affect which operating systems you can run on workstations and member servers that are joined to the domain or forest.
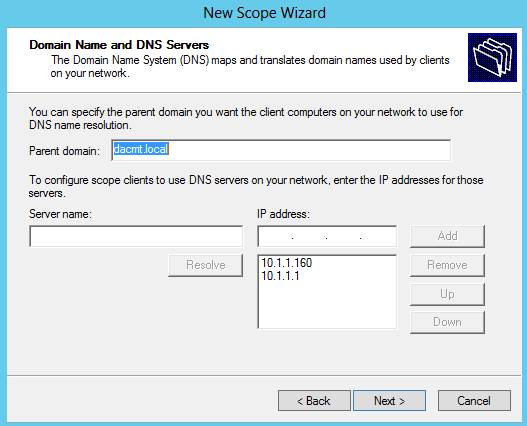
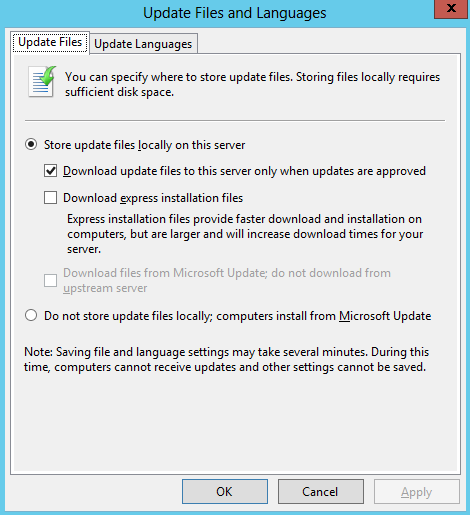
When you deploy AD DS, you need to set the domain and forest functional levels to the highest value that your environment can support. This way, you can use as many AD DS features as possible. For example, if you are sure that you will never add domain controllers that run Windows Server 2003 to the domain or forest, select the Windows Server 2008 functional level during the deployment process. However, if you might retain or add domain controllers that run Windows Server 2003, select the Windows Server 2003 functional level.
When you deploy a new forest, you are prompted to set the forest functional level and then set the domain functional level. You cannot set the domain functional level to a value that is lower than the forest functional level. For example, if you set the forest functional level to Windows Server 2008, you can set the domain functional level only to Windows Server 2008. In this case, the Windows 2000 native and Windows Server 2003 domain functional level values are not available. In addition, all domains that you subsequently add to that forest have the Windows Server 2008 domain functional level by default.
You can set the domain functional level to a value that is higher than the forest functional level. For example, if the forest functional level is Windows Server 2003, you can set the domain functional level to Windows Server 2003or higher.
Guidelines for raising domain and forest functional levels
- You must be a member of the Domain Admins group to raise the domain functional level.
- You must be a member of the Enterprise Admins group to raise the forest functional level.
- You can raise the domain functional level on the primary domain controller (PDC) emulator operations master only. The AD DS administrative tools that you use to raise the domain functional level (the Active Directory Domains and Trusts snap-in and the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in) automatically target the PDC emulator when you raise the domain functional level.
- You can raise the forest functional level on the schema operations master only. Active Directory Domains and Trusts automatically targets the schema operations master when you raise the forest functional level.
- You can raise the functional level of a domain only if all domain controllers in the domain run the version or versions of Windows Server that the new functional level supports.
- You can raise the functional level of a forest only if all domain controllers in the forest run the version or versions of Windows Server that the new functional level supports.
- You cannot set the domain functional level to a value that is lower than the forest functional level, but you can set it to a value that is equal to or higher than the forest functional level.
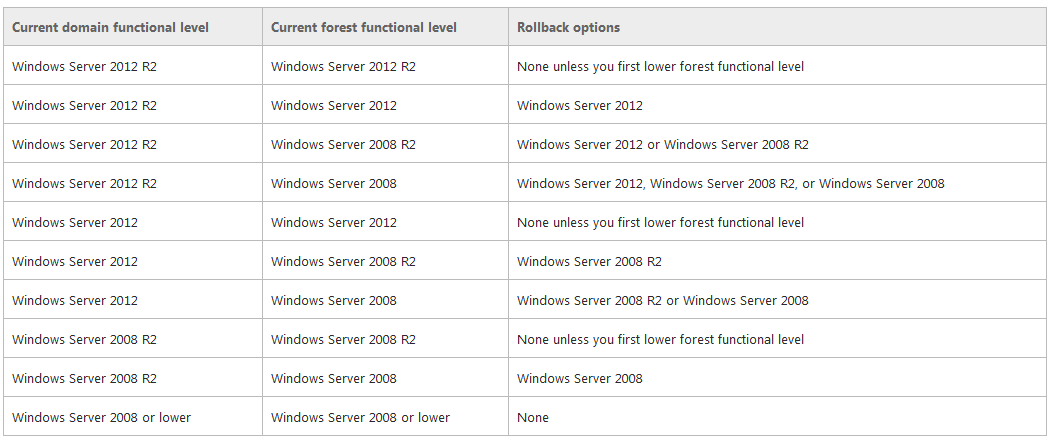
- With versions of Windows Server that are earlier than Windows Server 2008 R2, you cannot roll back or lower a functional level under any circumstances. If you have to revert to a lower functional level with a version of Windows Server that is earlier than Windows Server 2008 R2, you must rebuild the domain or forest or restore it from a backup copy.
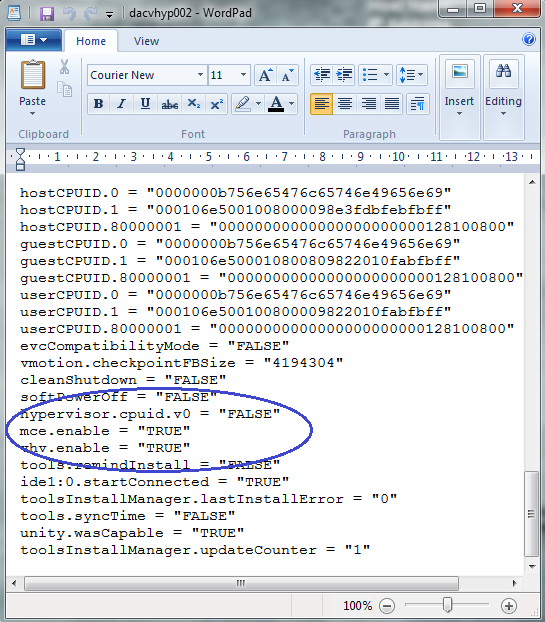
- After you set the domain functional level, you cannot roll back or lower the domain functional level except in the cases listed in the following table. The domain functional level can be lowered only by using Windows PowerShell
- Make sure replication is working properly
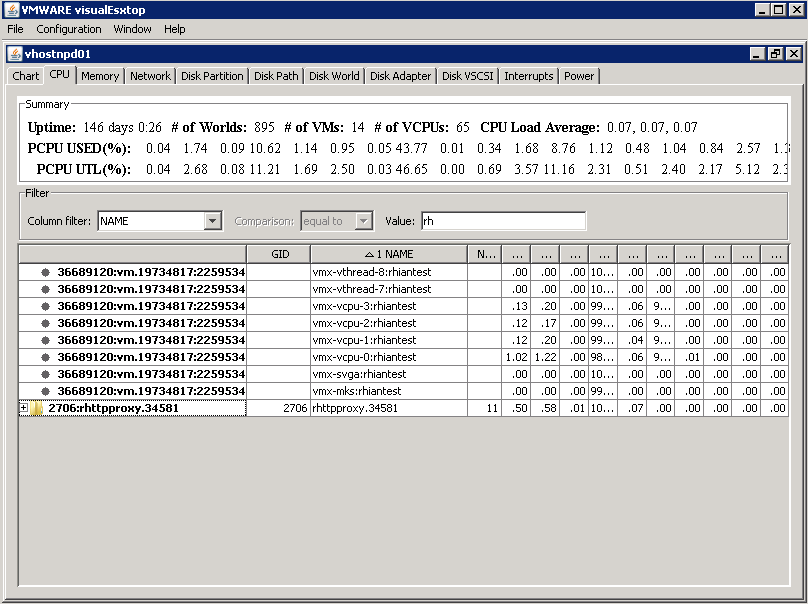
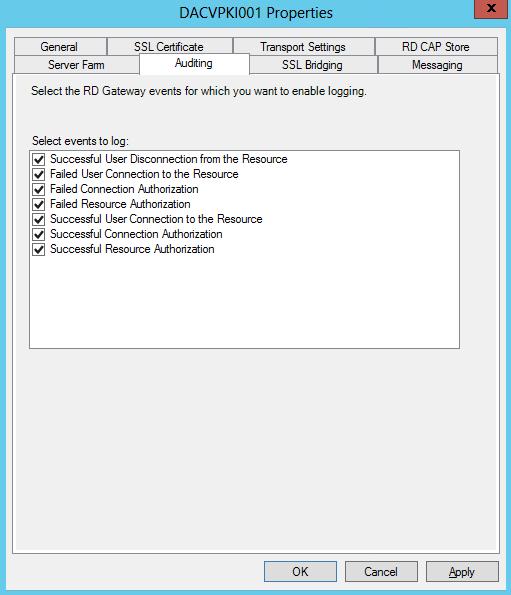
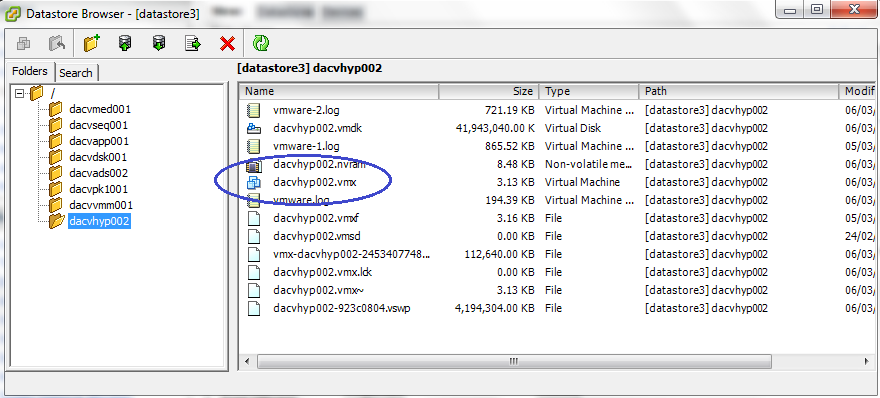
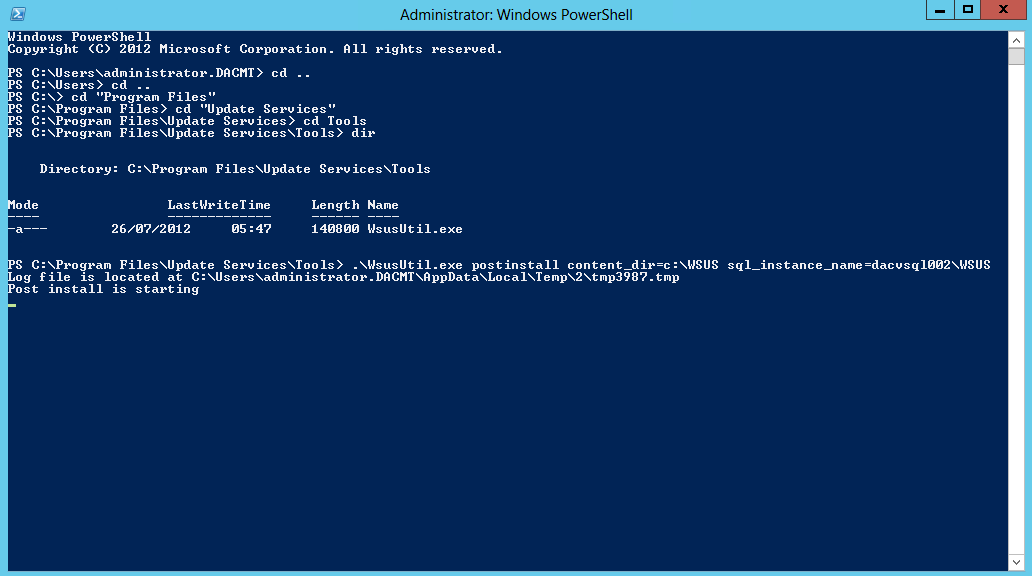
Checking Replication
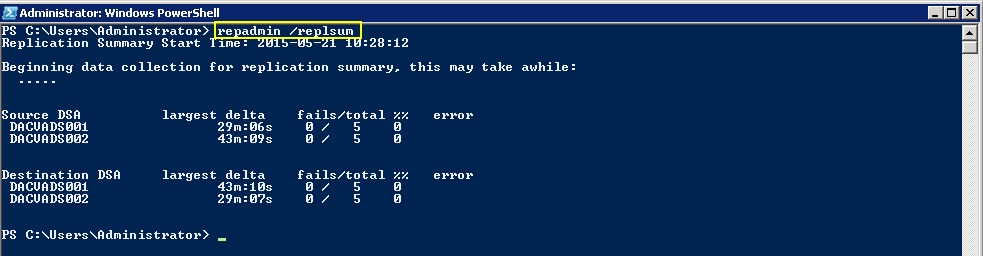
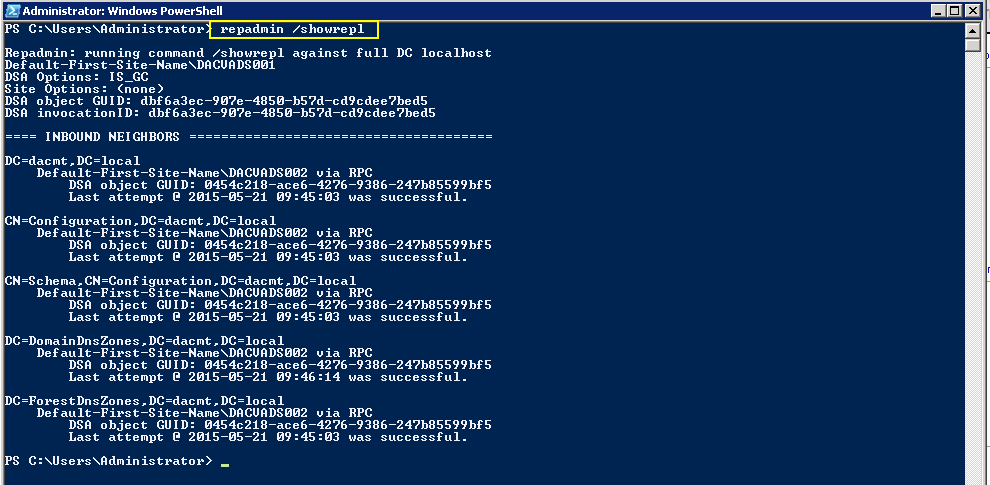
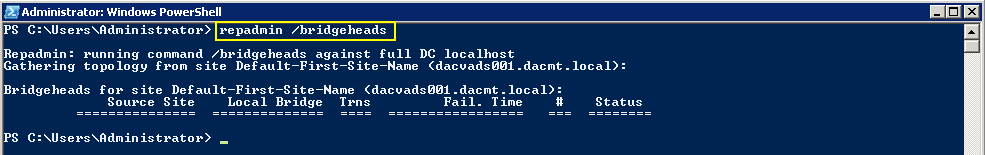
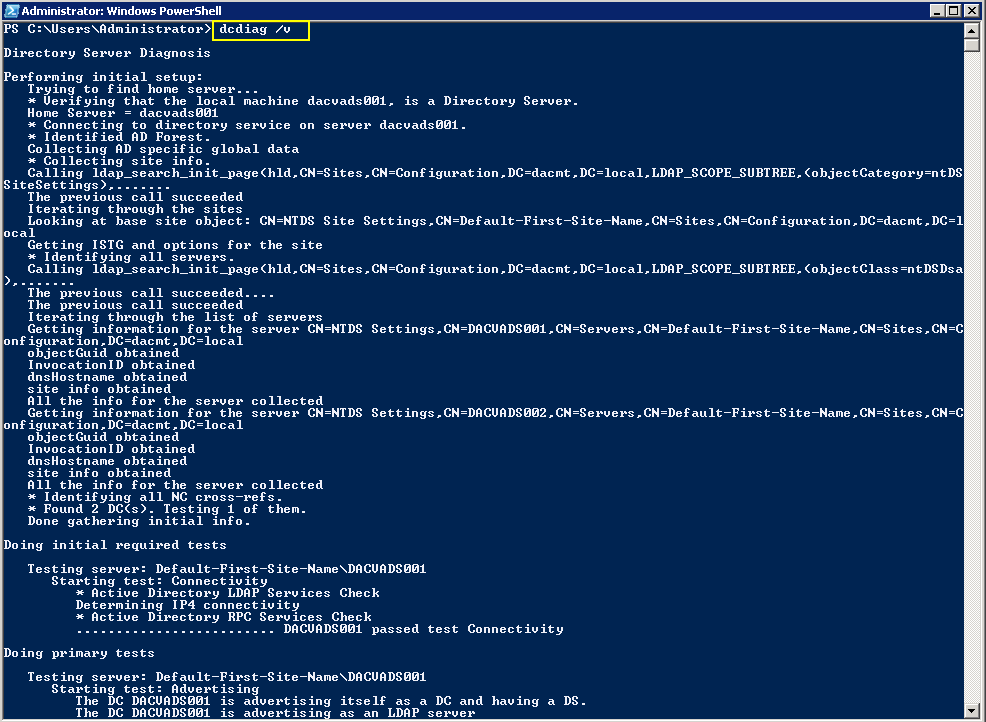
- dcdiag /v (checking overall health of the domain)
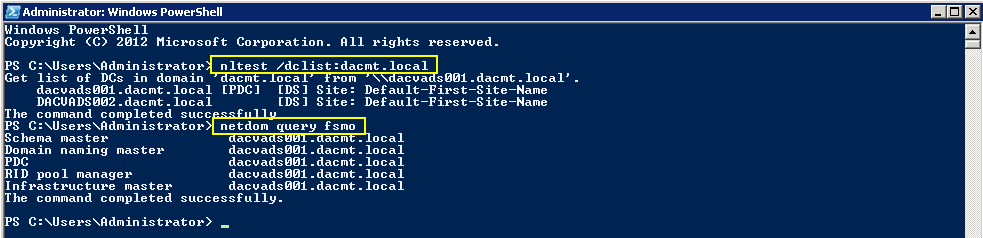
Checking what Domain Controllers and FSMO roles you have
Features available at Forest Function Levels
Windows 2003
- Domain rename
- Linked-value replication. Linked-value replication makes it possible for you to change group membership to store and replicate values for individual members instead of replicating the entire membership as a single unit. Storing and replicating the values of individual members uses less network bandwidth and fewer processor cycles during replication, and prevents you from losing updates when you add or remove multiple members concurrently at different domain controllers.
- The ability to deploy a read-only domain controller (RODC)
- Improved Knowledge Consistency Checker (KCC) algorithms and scalability. The intersite topology generator (ISTG) uses improved algorithms that scale to support forests with a greater number of sites than AD DS can support at the Windows 2000 forest functional level. The improved ISTG election algorithm is a less-intrusive mechanism for choosing the ISTG at the Windows 2000 forest functional level.
- The ability to create instances of the dynamic auxiliary class named dynamicObject in a domain directory partition
- The ability to convert an inetOrgPerson object instance into a User object instance, and to complete the conversion in the opposite direction
- The ability to create instances of new group types to support role-based authorization.
These types are called application basic groups and LDAP query groups.
- Deactivation and redefinition of attributes and classes in the schema. The following attributes can be reused: ldapDisplayName, schemaIdGuid, OID, and mapiID.
- Domain-based DFS namespaces running in Windows Server 2008 Mode, which includes support for access-based enumeration and increased scalability.
Windows 2008
All of the features that are available at the Windows Server 2003 forest functional level, but no additional features are available. All domains that are subsequently added to the forest, however, operate at the Windows Server 2008 domain functional level by default.
Windows 2008 R2
- All of the features that are available at the Windows Server 2003 forest functional level, plus the following features:
- Active Directory Recycle Bin, which provides the ability to restore deleted objects in their entirety while AD DS is running.
- All domains that are subsequently added to the forest will operate at the Windows Server 2008 R2 domain functional level by default.
- If you plan to include only domain controllers that run Windows Server 2008 R2 in the entire forest, you might choose this forest functional level for administrative convenience. If you do, you will never have to raise the domain functional level for each domain that you create in the forest.
Windows 2012
- All of the features that are available at the Windows Server 2008 R2 forest functional level, but no additional features.
- All domains that are subsequently added to the forest will operate at the Windows Server 2012 domain functional level by default
Windows 2012 R2
- All of the features that are available at the Windows Server 2008 R2 forest functional level, but no additional features.
- All domains that are subsequently added to the forest will operate at the Windows Server 2012 domain functional level by default
Features available at Domain Function Levels
Windows Server 2003
- Universal groups for both distribution and security groups.
- Group nesting
- Group conversion, which allows conversion between security and distribution groups
- Security identifier (SID) history
- The domain management tool, Netdom.exe, which makes it possible for you to rename domain controllers
- Logon time stamp updates
The lastLogonTimestamp attribute is updated with the last logon time of the user or computer. This attribute is replicated within the domain.
- The ability to set the userPassword attribute as the effective password on inetOrgPerson and user objects
- The ability to redirect Users and Computers containers
By default, two well-known containers are provided for housing computer and user accounts, namely, cn=Computers,<domain root> and cn=Users,<domain root>. This feature allows the definition of a new, well-known location for these accounts.
- The ability for Authorization Manager to store its authorization policies in AD DS
- Constrained delegation
Constrained delegation makes it possible for applications to take advantage of the secure delegation of user credentials by means of Kerberos-based authentication.
You can restrict delegation to specific destination services only.
- Selective authentication
Selective authentication makes it is possible for you to specify the users and groups from a trusted forest who are allowed to authenticate to resource servers in a trusting forest
Windows Server 2008
- All of the default AD DS features, all of the features from the Windows Server 2003 domain functional level, and the following features are available:
- Distributed File System (DFS) replication support for the Windows Server 2003 System Volume (SYSVOL)
DFS replication support provides more robust and detailed replication of SYSVOL contents.
- Beginning with Windows Server 2012 R2, File Replication Service (FRS) is deprecated. A new domain that is created on a domain controller that runs at least Windows Server 2012 R2 must be set to the Windows Server 2008 domain functional level or higher
- Domain-based DFS namespaces running in Windows Server 2008 Mode, which includes support for access-based enumeration and increased scalability. Domain-based namespaces in Windows Server 2008 mode also require the forest to use the Windows Server 2003 forest functional level.
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES 128 and AES 256) support for the Kerberos protocol. In order for TGTs to be issued using AES, the domain functional level must be Windows Server 2008 or higher and the domain password needs to be changed.
- Last Interactive Logon Information
- Fine-grained password policies make it possible for you to specify password and account lockout policies for users and global security groups in a domain
- Personal Virtual Desktops
Windows Server 2008 R2
- All default Active Directory features, all features from the Windows Server 2008 domain functional level, plus the following features:
- Authentication mechanism assurance, which packages information about the type of logon method (smart card or user name/password) that is used to authenticate domain users inside each user’s Kerberos token. When this feature is enabled in a network environment that has deployed a federated identity management infrastructure, such as Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS), the information in the token can then be extracted whenever a user attempts to access any claims-aware application that has been developed to determine authorization based on a user’s logon method.
- Automatic SPN management for services running on a particular computer under the context of a Managed Service Account when the name or DNS host name of the machine account changes
Windows Server 2012
- The KDC support for claims, compound authentication, and Kerberos armoring KDC administrative template policy has two settings (Always provide claims and Fail unarmored authentication requests) that require Windows Server 2012 domain functional level.
Windows Server 2012 R2
- DC-side protections for Protected Users. Protected Users authenticating to a Windows Server 2012 R2 domain can no longer: Authenticate with NTLM authentication, Use DES or RC4 cipher suites in Kerberos pre-authentication, Be delegated with unconstrained or constrained delegation, Renew user tickets (TGTs) beyond the initial 4 hour lifetime
- Authentication Policies: New forest-based Active Directory policies which can be applied to accounts in Windows Server 2012 R2 domains to control which hosts an account can sign-on from and apply access control conditions for authentication to services running as an account.
- Authentication Policy Silos: New forest-based Active Directory object, which can create a relationship between user, managed service and computer, accounts to be used to classify accounts for authentication policies or for authentication isolation.
NTDSUTIL
This tool can remove old AD DC metadata which can stop the raising of Functional Levels
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc728068%28WS.10%29.aspx
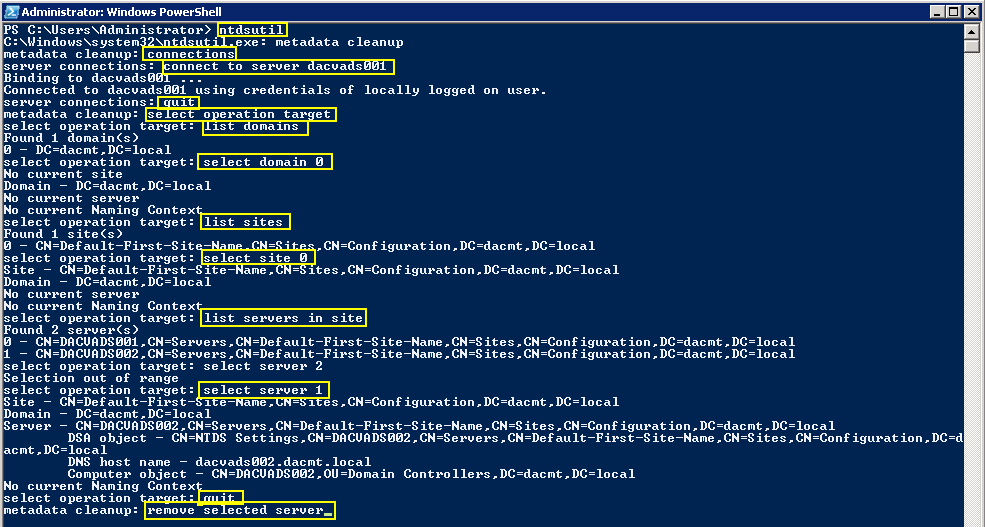
The GUI Metadata Cleanup Utility
The GUI Metadata Cleanup Utility removes Active Directory domain controller metadata left behind after a domain controller is removed improperly or unsuccessfully
https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/d31f091f-2642-4ede-9f97-0e1cc4d577f3
Forest Recovery Information
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/8e3e4377-ef54-4a70-9215-a5d2ba4d0eb9%28v=ws.10%29#BKMK_ResetTrustPassword
http://blogs.technet.com/b/askds/archive/2011/06/14/what-is-the-impact-of-upgrading-the-domain-or-forest-functional-level.aspx
Useful Microsoft Link
https://technet.microsoft.com/library/understanding-active-directory-functional-levels%28WS.10%29.aspx
Questions?
- Once you have upgraded the Domain functional level, how long should you wait before upgrading the forest functional level?
The change should take effect immediately as soon as the operation completes on the server. if you have multiple DC’s or domain, it may take longer. If you have plenty of time and want to play it safe, wait 24 hours but normally 15 minutes is fine. if you have multiple DC’s, you can log into each DC and verify the functional level.
- By raising the root domain functional level, will this automatically raise any child domains or do we need to raise the level on the PDC of the root domain then raise the level on the PDC in the child domain? Or do we do the child first then the root domain?
Each individual domain PDCe is responsible for maintaining it’s domain functional level. Because of this, where you raise the domain functional level first, does not matter (parent domain or child domain). Each domain’s DC’s will operate at the domain functional level of it’s PDCe (so long as it is supported). The Forest Functional Level affects all domains. As such all domains must be operating at or above the proposed Forest Functional Level.
- What is the best way to recover if things don’t go to plan? For e.g With a root domain with 2 DCs and a child domain with 5 DCs?
Before Windows Server 2008 R2, the only ways to recover are rebuild or restore from backup.
As the PDCe is responsible for the Domain Functional Level and the Schema Operations Master is responsible for the Forest Functional Level, first, you would have to restore the server that holds the Schema Operations Master in the Parent domain (if you will be reverting to a Domain Functional Level less than allowed by the Forest Functional Level). Then you would restore the server that holds the PDCe FSMO role for each child domain.
- If we are running at Windows 2000 native domain level with all Windows 2008 R2 servers, can we raise the domain functional level straight to Windows Server 2008 R2?
If all of your DC’s are running Windows Server 2008 R2 then yes.