I couldn’t have written it better myself so here’s a link to a blog on Kerberos and IIS and cross domain trusts.
How Kerberos Works
The current version of Kerberos is v5, which was developed in 1993. This is the version on which Microsoft’s implementation in Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003 is based. Windows 2000 and Server 2003 native mode domains use Kerberos by default. Domains that must authenticate NT systems along with the newer operating systems must use NT LAN Manager (NTLM) authentication.
Kerberos was named after Cerberus, the three-headed dog of Greek mythology, because of its three components
- A Key Distribution Center (KDC), which is a server that has two components: an Authentication Server and a Ticket Granting Service.
- The client (user)
- The server that the client wants to access
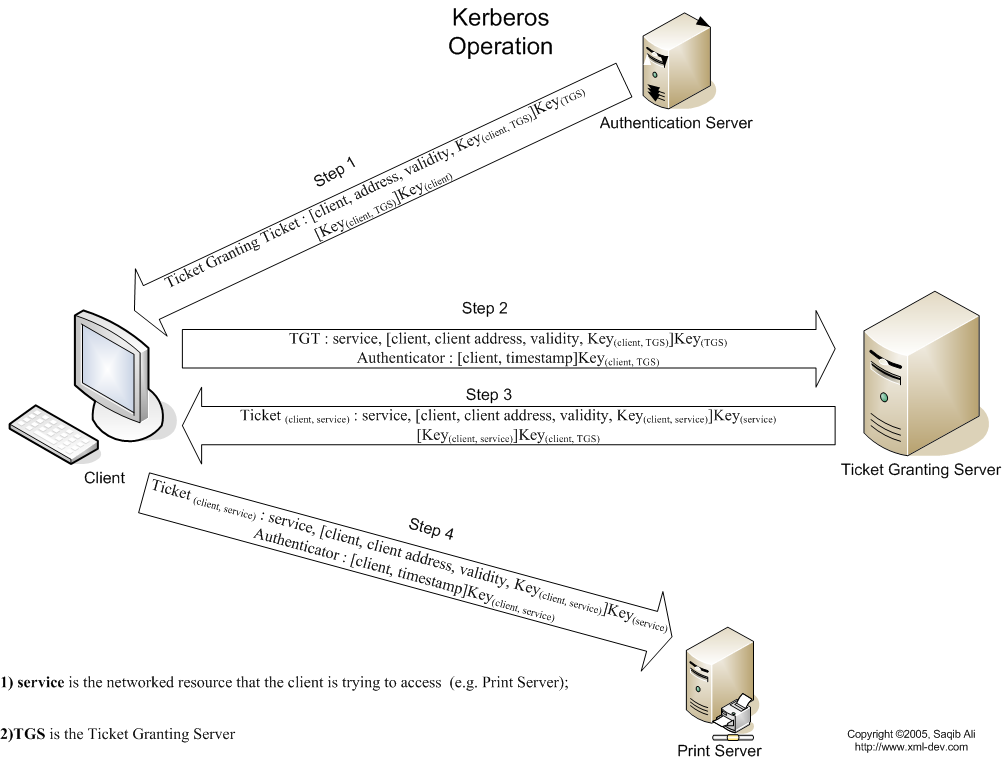
Logon process works with Kerberos as the authentication method
- To log on to the network, the user provides an account name and password.
- The Authentication Server (AS) component of the KDC accesses Active Directory user account information to verify the credentials.
- The KDC grants a Ticket Getting Ticket (TGT) that allows the user to get session tickets to access servers in the domain, without having to enter the credentials again (the TGT is good for 10 hours by default; this expiration period can be configured by the administrator).
- When the user attempts to access resources on a server in the domain, the TGT is used to make the request. The client presents the TGT to the KDC to obtain a service ticket.
- The Ticket Granting Service (TGS) component of the KDC authenticates the TGT and then grants a service ticket. The service ticket consists of a ticket and a session key. A service ticket is created for the client and the server that the client wants to access.
- The client presents the service ticket to create a session with the service on the server. The server uses its key to decrypt the information from the TGS, and the client is authenticated to the server.
- If mutual authentication is enabled, the server also authenticates to the client