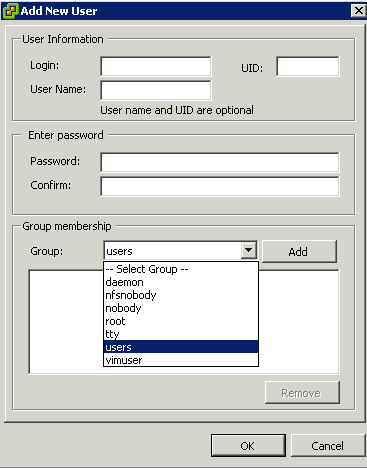
Security Options
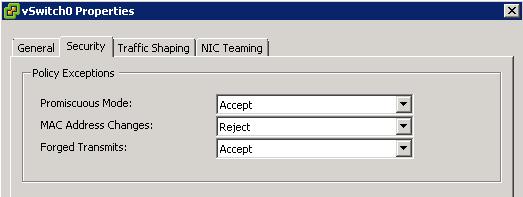
Promiscuous Mode
Promiscuous mode eliminates any reception filtering that the virtual network adapter would perform so that the guest operating system receives all traffic observed on the wire. By default, the virtual network adapter cannot operate in promiscuous mode.
Although promiscuous mode can be useful for tracking network activity, it is an insecure mode of operation, because any adapter in promiscuous mode has access to the packets regardless of whether some of the packets are received only by a particular network adapter. This means that an administrator or root user within a virtual machine can potentially view traffic destined for other guest or host operating system
Note
In some situations, you might have a legitimate reason to configure a standard switch to operate in promiscuous mode (for example, if you are running network intrusion detection software or a packet sniffer
MAC Address Changes
The setting for the MAC Address Changes option affects traffic that a virtual machine receives.
When the option is set to Accept, ESXi accepts requests to change the effective MAC address to other than the initial MAC address.
When the option is set to Reject, ESXi does not honor requests to change the effective MAC address to anything other than the initial MAC address, which protects the host against MAC impersonation. The port that the virtual adapter used to send the request is disabled and the virtual adapter does not receive any more frames until it changes the effective MAC address to match the initial MAC address. The guest operating system does not detect that the MAC address change was not honored.
Note
The iSCSI initiator relies on being able to get MAC address changes from certain types of storage. If you are using ESXi iSCSI and have iSCSI storage, set the MAC Address Changes option to Accept.
In some situations, you might have a legitimate need for more than one adapter to have the same MAC address on a network—for example, if you are using Microsoft Network Load Balancing in unicast mode. When Microsoft Network Load Balancing is used in the standard multicast mode, adapters do not share MAC addresses.
MAC address changes settings affect traffic leaving a virtual machine. MAC address changes will occur if the sender is permitted to make them, even if standard switches or a receiving virtual machine does not permit MAC address chan
Forged Transmits
The setting for the Forged Transmits option affects traffic that is transmitted from a virtual machine.
When the option is set to Accept, ESXi does not compare source and effective MAC addresses.
To protect against MAC impersonation, you can set this option to Reject. If you do, the host compares the source MAC address being transmitted by the operating system with the effective MAC address for its adapter to see if they match. If the addresses do not match, ESXi drops the packet.
The guest operating system does not detect that its virtual network adapter cannot send packets by using the impersonated MAC address. The ESXi host intercepts any packets with impersonated addresses before they are delivered, and the guest operating system might assume that the packets are dropped
Note
This option is enabled by default, because it is occasionally needed to avoid software licensing problems. For example, if software on a physical machine is licensed to a specific MAC address, it will not work in a virtual machine because the VM’s MAC address is different. In this case, allowing forged transmits enables you to use the software by forging the VM’s MAC address.
However, allowing forged transmits poses a security risk.If an administrator has only authorized specific MAC addresses to enter the network, an intruder may be able to change his unauthorized MAC address to an authorized one