Multipathing Considerations
Specific considerations apply when you manage storage multipathing plug-ins and claim rules. The following considerations help you with multipathing
- If no SATP is assigned to the device by the claim rules, the default SATP for iSCSI or FC devices is VMW_SATP_DEFAULT_AA. The default PSP is VMW_PSP_FIXED.
- When the system searches the SATP rules to locate a SATP for a given device, it searches the driver rules first. If there is no match, the vendor/model rules are searched, and finally the transport rules are searched. If no match occurs, NMP selects a default SATP for the device.
- If VMW_SATP_ALUA is assigned to a specific storage device, but the device is not ALUA-aware, no claim rule match occurs for this device. The device is claimed by the default SATP based on the device’s transport type.
- The default PSP for all devices claimed by VMW_SATP_ALUA is VMW_PSP_MRU. The VMW_PSP_MRU selects an active/optimized path as reported by the VMW_SATP_ALUA, or an active/unoptimized path if there is no active/optimized path. This path is used until a better path is available (MRU). For example, if the VMW_PSP_MRU is currently using an active/unoptimized path and an active/optimized path becomes available, the VMW_PSP_MRU will switch the current path to the active/optimized one.
- If you enable VMW_PSP_FIXED with VMW_SATP_ALUA, the host initially makes an arbitrary selection of the preferred path, regardless of whether the ALUA state is reported as optimized or unoptimized. As a result, VMware does not recommend to enable VMW_PSP_FIXED when VMW_SATP_ALUA is used for an ALUA-compliant storage array. The exception is when you assign the preferred path to be to one of the redundant storage processor (SP) nodes within an active-active storage array. The ALUA state is irrelevant.
- By default, the PSA claim rule 101 masks Dell array pseudo devices. Do not delete this rule, unless you want to unmask these devices.
What can we use to configure Multipath Options
- vCLI
- vMA
- Putty into DCUI console
What we can view and adjust
- You can display all multipathing plugins available on your host
- You can list any 3rd Party MPPs as well as your hosts PSP and SATPs and review the paths they claim
- You can also define new paths and specify which multipathing plugin should claim the path
The ESXCLI Commands
Click the link to take you to the vSphere 5 Documentation Center for each command
These are the 2 commands you need to use to perform configuration of multipathing
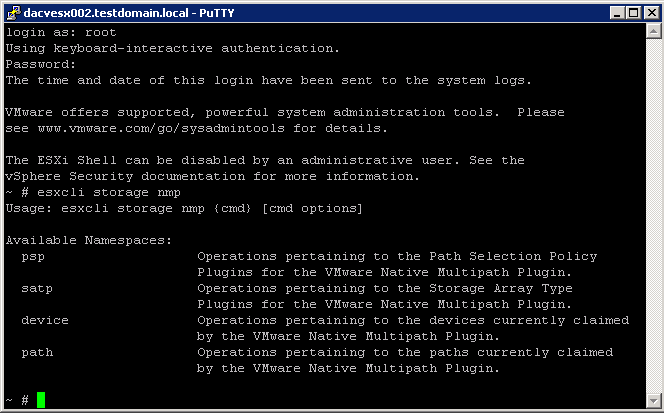
esxcli storage nmp psp Namespaces
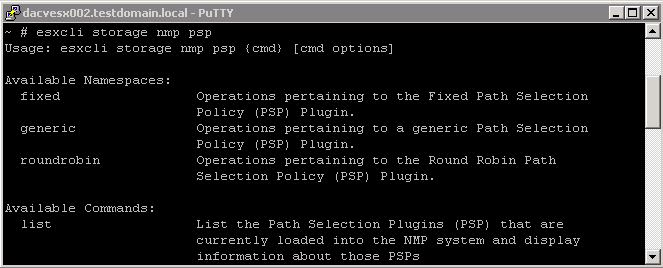
Display NMP PSPs
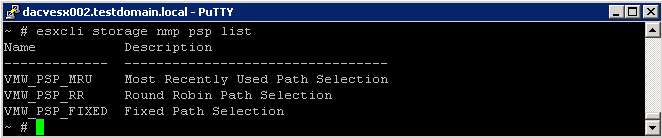
- esxcli storage nmp psp list
This command list all the PSPs controlled by the VMware NMP
More complicated commands with esxcli storage nmp psp namespace
- esxcli storage nmp psp fixed deviceconfig set - -device naa.xxx –path vmhba3:C0:T5:L3
The command sets the preferred path to vmhba3:C0:T5:L3. Run the command with – -default to clear the preferred path selection
esxcli storage nmp satp Namespaces
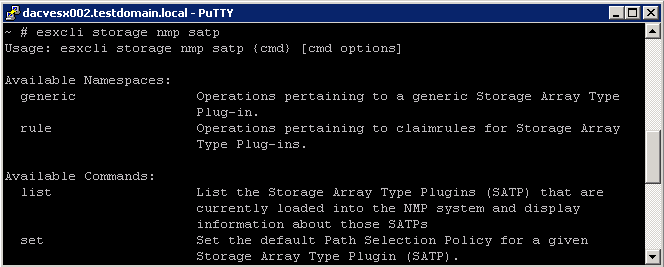
Display SATPs for the Host
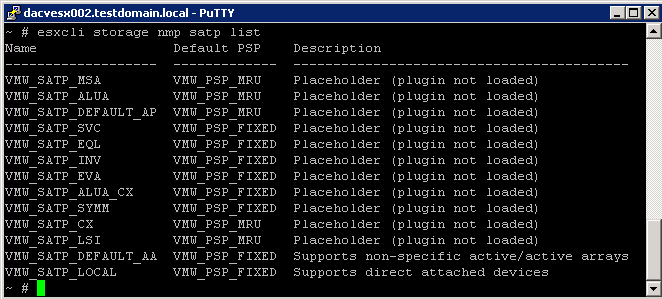
- esxcli storage nmp satp list
For each SATP, the output displays information that shows the type of storage array or system this SATP supports and the default PSP for any LUNs using this SATP. Placeholder (plugin not loaded) in the Description column indicates that the SATP is not loaded.
More complicated commands with esxcli storage nmp satp namespaces
- esxcli storage nmp satp rule add -V NewVend -M NewMod -s VMW_SATP_INV
The command assigns the VMW_SATP_INV plug-in to manage storage arrays with vendor string NewVend and model string NewMod.
esxcli storage nmp device NameSpaces
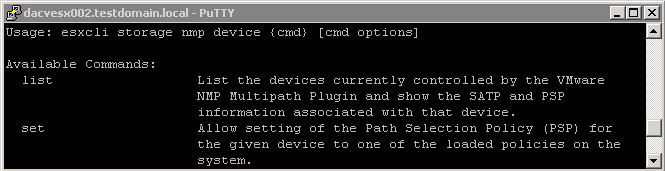
Display NMP Storage Devices
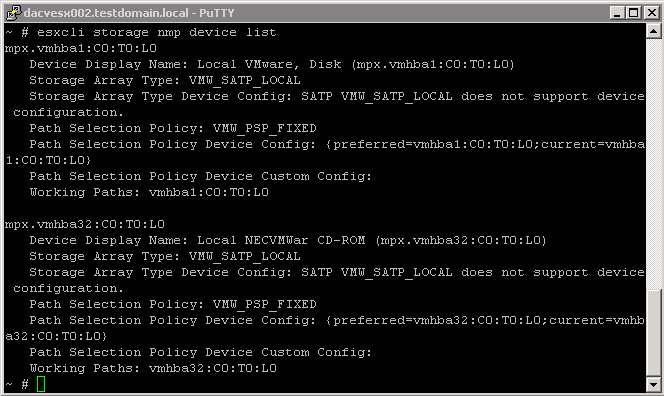
- esxcli storage nmp device list
This command list all storage devices controlled by the VMware NMP and displays SATP and PSP information associated with each device
More complicated commands with esxcli storage nmp device namespaces
- esxcli storage nmp device set - -device naa.xxx - -psp VMW_PSP_FIXED
This command sets the path policy for the specified device to VMW_PSP_FIXED
esxcli storage nmp path Namespaces
Display NMP Paths
- esxcli storage nmp path list
This command list all the paths controlled by the VMware NMP and displays SATP and PSP information associated with each device
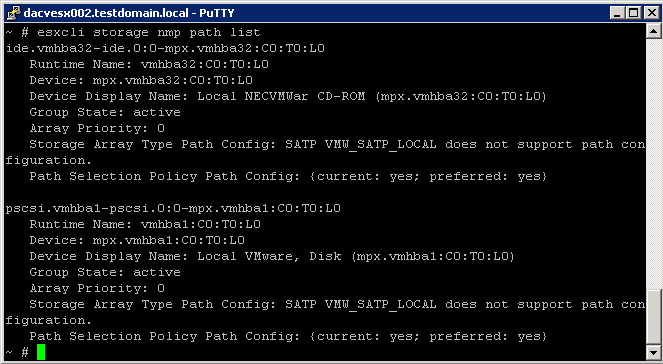
More complicated commands with esxcli storage nmp path namespaces
There is only really the list command associated with this command
esxcli storage core Command Namespaces
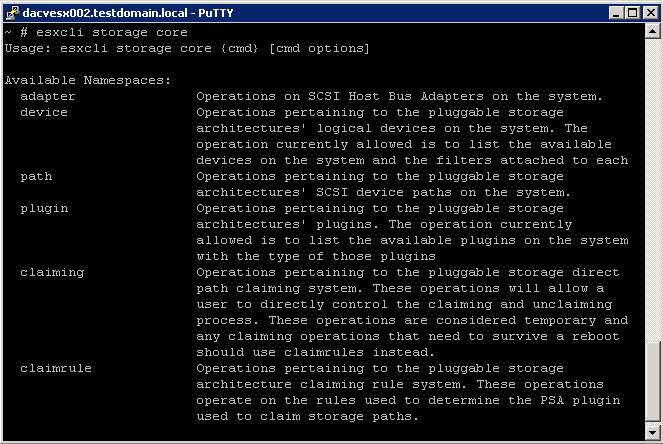
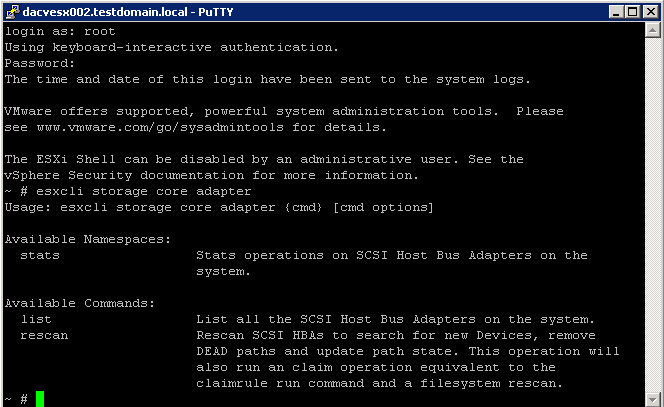
esxcli storage core adapter Command Namespaces
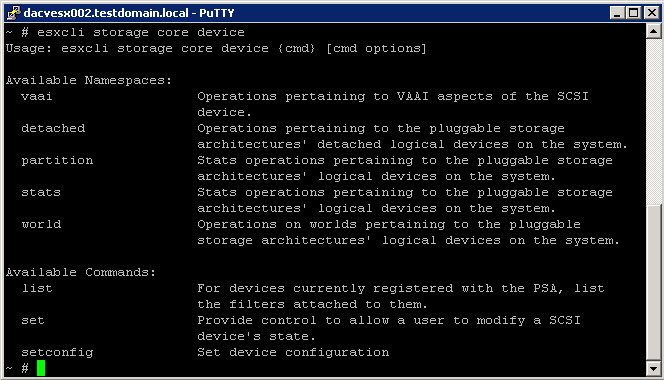
esxcli storage core device Command Namespaces
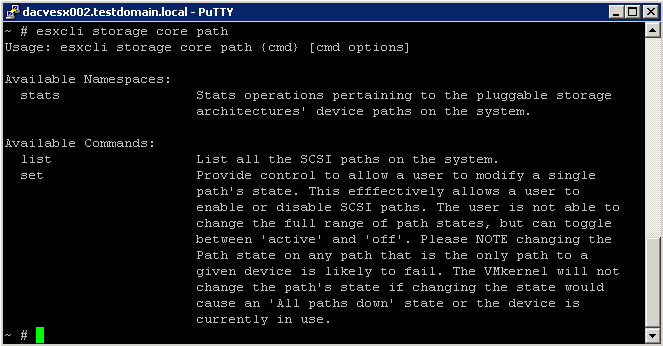
esxcli storage core path Command Namespaces
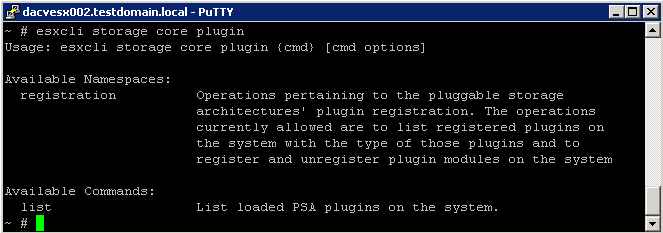
esxcli storage core plugin Command Namespaces
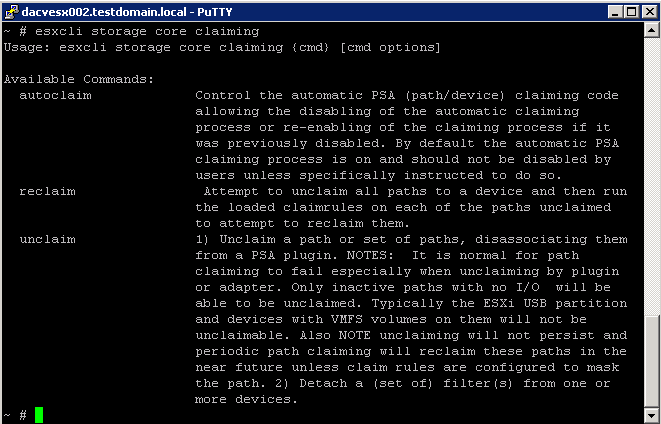
esxcli storage core claiming Command Namespaces
The esxcli storage core claiming namespace includes a number of troubleshooting commands. These commands are not persistent and are useful only to developers who are writing PSA plugins or troubleshooting a system. If I/O is active on the path, unclaim and reclaim actions fail
The help for esxcli storage core claiming includes the autoclaim command. Do not use this command unless instructed to do so by VMware support staff
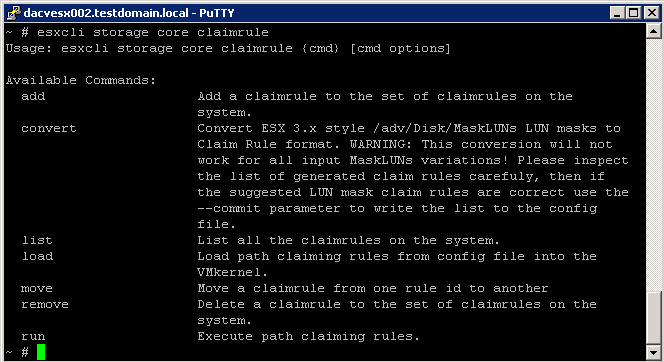
esxcli storage core claimrule Command Namespaces
The PSA uses claim rules to determine which multipathing module should claim the paths to a particular device and to manage the device. esxcli storage core claimrule manages claim rules.
Claim rule modification commands do not operate on the VMkernel directly. Instead they operate on the configuration file by adding and removing rules
To change the current claim rules in the VMkernel
|
1
|
Run one or more of the esxcli storage core claimrule modification commands (add, remove, or move).
|
|
2
|
Run esxcli storage core claimrule load to replace the current rules in the VMkernel with the modified rules from the configuration file.
|
Claim rules are numbered as follows.
- Rules 0–100 are reserved for internal use by VMware.
- Rules 101–65435 are available for general use. Any third party multipathing plugins installed on your system use claim rules in this range. By default, the PSA claim rule 101 masks Dell array pseudo devices. Do not remove this rule, unless you want to unmask these devices.
- Rules 65436–65535 are reserved for internal use by VMware.
When claiming a path, the PSA runs through the rules starting from the lowest number and determines is a path matches the claim rule specification. If the PSA finds a match, it gives the path to the corresponding plugin. This is worth noticing because a given path might match several claim rules.
The following examples illustrate adding claim rules.
- Add rule 321, which claims the path on adapter vmhba0, channel 0, target 0, LUN 0 for the NMP plugin.
- esxcli storage core claimrule add -r 321 -t location -A vmhba0 -C 0 -T 0 -L 0 -P NMP
- Add rule 429, which claims all paths provided by an adapter with the mptscsi driver for the MASK_PATH plugin.
- esxcli storage core claimrule add -r 429 -t driver -D mptscsi -P MASK_PATH
- Add rule 914, which claims all paths with vendor string VMWARE and model string Virtual for the NMP plugin.
- esxcli storage core claimrule add -r 914 -t vendor -V VMWARE -M Virtual -P NMP
- Add rule 1015, which claims all paths provided by FC adapters for the NMP plugin.
- esxcli storage core claimrule add -r 1015 -t transport -R fc -P NMP
Example: Masking a LUN
In this example, you mask the LUN 20 on targets T1 and T2 accessed through storage adapters vmhba2 and vmhba3.
- esxcli storage core claimrule list
- esxcli storage core claimrule add -P MASK_PATH -r 109 -t location -A
vmhba2 -C 0 -T 1 -L 20
- esxcli storage core claimrule add -P MASK_PATH -r 110 -t location -A
vmhba3 -C 0 -T 1 -L 20
- esxcli storage core claimrule add -P MASK_PATH -r 111 -t location -A
vmhba2 -C 0 -T 2 -L 20
- esxcli storage core claimrule add -P MASK_PATH -r 112 -t location -A
vmhba3 -C 0 -T 2 -L 20
- esxcli storage core claimrule load
- esxcli storage core claimrule list
- esxcli storage core claiming unclaim -t location -A vmhba2
- esxcli storage core claiming unclaim -t location -A vmhba3
- esxcli storage core claimrule run