
What’s slack space?
vSAN Slack Space is the free space in the vSAN Datastore reserved for vSAN’s internal operational and rebuild actions such as..
- Rebalancing operations and VM snapshots
- Component rebuilds – If you have a FTT=1 RAID1 vSAN storage Policy and you decide to change this to a FTT=1 RAID5 storage policy, vSAN will need to use extra space to perform this type of change.
- Host maintenance mode data evacuation
VMware used to recommend 25-30% of free space for Slack Space although from 7.0u1 there are a couple of new features under the Reservation and Alerts section of the vSAN Services on a cluster which can be used to control this space. You will hear it called Capacity Reserve to reflect the methodical and improved approach to compute reserve capacity.
- Operations reserve
- Host rebuild reserve
By default, these features are disabled, meaning all vSAN capacity is available for workloads.
Reserved capacity is not supported on stretched clusters, clusters with fault domains and nested fault domains, ROBO cluster or if the cluster has less than 4 hosts.
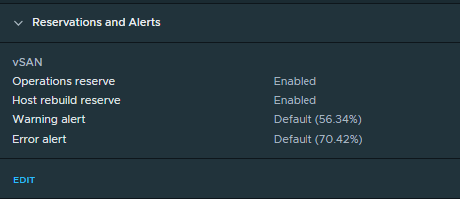
Reservations and Alerts
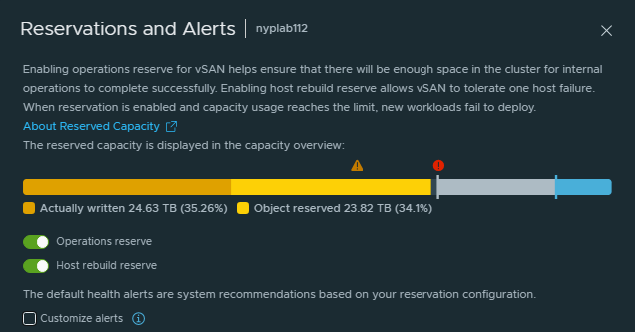
Enabling Operations Reserve for vSAN ensures that there will be enough space in the cluster for internal operations to complete successfully.
Enabling Host Rebuild Reserve allows vSAN to tolerate one host failure
When reservation is is enabled and capacity usage reaches the limit, new workloads fail to deploy or power on but existing VMs are fine.
Click Edit to view
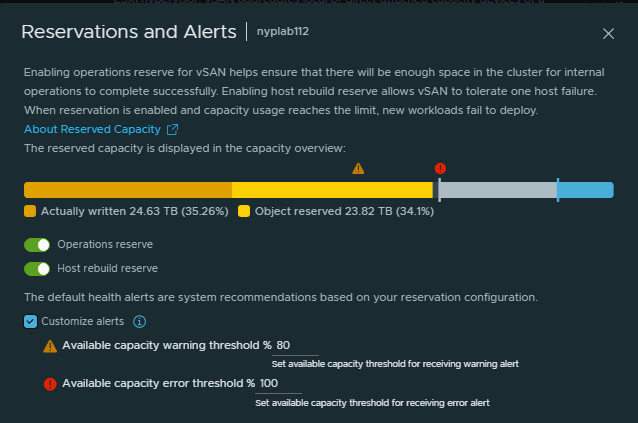
You can customise the thresholds of when to receive warning and error alerts. The threshold percentage is calculated based on available capacity which is the total capacity minus the reserved capacity. If you do not set customised values, vSAN will use the default thresholds to generate alerts.
Operation reserve
This is basically the capacity set aside for vSAN to run it’s internal operations as seen earlier – host maintenance mode data evacuation, component rebuilds, rebalancing operations, and VM snapshots. Activities such as rebuilds and rebalancing can temporarily consume additional raw capacity.
Host rebuild reserve
The first parameter is Host Rebuild Reserve. This reservation is set to one host worth of capacity. This means that if one host in the vSAN cluster fails and no longer contributes storage, there is still sufficient capacity remaining in the cluster to rebuild and re-protect all vSAN objects. This reservation is based on the N+1 host count recommendation. In small clusters, the percentage is high (e.g. 25% in a 4-node cluster), the percentage decreases significantly as the number of hosts in vSAN cluster increases (single digit 8% approx of capacity values for clusters > 12 nodes). For example, a 48-node cluster can improve capacity savings up to 18%, resulting in greater resource optimization at a lower cost.
Unfortunately you cannot simply enable Host rebuild reserve on its own when enabling Operation Reserve. You must enable Operations reserve and then you can choose to enable Host rebuild reserve as well, or leave it disabled. Be aware that the 10% overhead of the Operations threshold is taken into consideration before the Host rebuild reserve is taken into account. For example, in a small 4/6 node vSAN cluster, the 10% Operations Reserve is first calculated and accounted for, before the Host rebuild reserve threshold is taken into account.
Considerations for both Operations reserve and Host rebuild reserve enabled
When you enable Operations reserve with the Host rebuild reserve and a host is put into maintenance mode, the host may not come back online. In this case, vSAN continues to reserve capacity for another host failure. The host failure is in addition to the host that is already in maintenance mode. This might cause the failure of operations if the capacity usage is above the host rebuild threshold
When you enable reserved capacity with the Host rebuild enabled and a host fails, vSAN may not start repairing affected objects until the repair timer expires. During this time vSAN continues to reserve capacity for another host failure. This can cause failure of operations if the capacity usage is above the current host rebuild threshold. After any repairs are complete, you can deactivate the reserved capacity for the host rebuild if the cluster does not have the capacity for another host failure.

