
This release of VMware vSphere 7.0 includes VMware ESXi 7.0 and VMware vCenter Server 7.0. There are almost too many features to mention so I have summarized some of the new tools available below.
Deployment and Planning Tools
- vSphere Hardware and Guest Operating System Compatibility Guides. An online reference that shows what hardware, converged systems, operating systems, third-party applications, and VMware products are compatible with a specific version of a VMware software product.
- VMware Product Interoperability Matrices. Provides details about the compatibility of current and earlier versions of VMware vSphere components, including ESXi, vCenter Server, and other VMware products.
- VMware Configuration Maximums. When you configure, deploy, and operate your virtual and physical equipment, you must stay at or below the maximums supported by your product. The limits presented in the Configuration Maximums tool are tested limits supported by VMware.
Lifecycle management
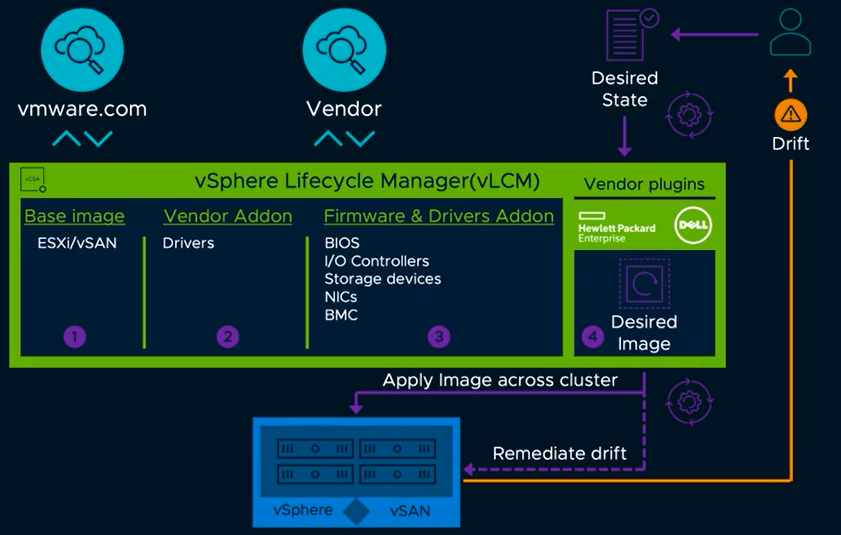
Lifecycle management for larger customers has proved tricky at times and VMware Update Manager is sometimes not the best tool for lifecycle management at scale. VMware is introducing vSphere Lifecycle Management (VLCM), which will replace the vSphere Update Manager (VUM) The new approach will be able to upgrade the hypervisor including firmware and drivers for physical hardware. The most important capabilities of vLCM are to achieve a desired state model, integration with hardware vendors for full-stack firmware updates and drivers, and simplified OEM image customizations, along with automatic compatibility checks.

vCenter Profiles
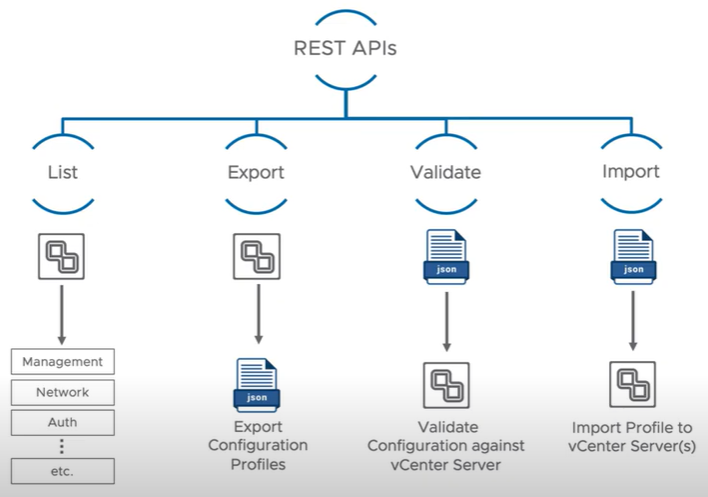
This is a brand new API feature allowing an administrator to export existing vCenter server configurations and import them them into another vCenter. vCenter Server profiles consist of 4 REST APIs. List Validate, Export and Import.
List returns a listing of the configurations that can be imported or exported. Export can export the vCenter configuration as a JSON file for editing. Validate can be used by administrators to validate the configuration which will be implemented on the target vCenter server. Import can then be run to pass the desired configuration changes to the target vCenter Server. These changes do not require a reboot.
With vCenter Server 7.0 profiles you can easily revert to the last known good configuration by importing a valid vCenter server profile.
vCenter Server Update Planner
vCenter Server Update Planner helps to plan, discover, and upgrade customer environments successfully. You will receive notifications when an upgrade or update is available directly in the vSphere Client. With vCenter Server 7, you can run what if scenarios with pre-checks which will show whether your environment would be affected by the Upgrade and also shows which applications need to upgraded first and to which version.
- You must join the VMware Customer Experience Improvement Program (CEIP) to use Update Planner.
- vCenter Server must have access to the internet to participate in CEIP either directly or via proxy
- Update Planner (along with; Skyline Health for vSphere, vSAN Performance Analytics, vSAN Support Insight, Host Hardware Compatibility, etc.) uses this path to query VMware Product Interoperability Matrices online and report findings via the vSphere Client
vCenter Server Planner is accessed from the Updates tab
Content Library
The updates to Content Library include added administrative control and versioning support. It provides centralized management for virtual machine templates, virtual appliances, ISO images, and scripts. You can now use Check-In and Check-Out actions, as well as template versioning, allowing an administrator to make changes and keep track of VM Template versions
Multihomed vCenter
vCenter Server NIC multihoming is now supported with vCenter Server 7. This will allow more options and flexibility for management networks and network segmentation
Upgrade and converge PSCs in one operation
External PSCs are converged during the upgrade operation.
vMotion enhancements
In previous versions the vMotion process installs Page Tracers on all vCPUs to monitor changed memory pages. Leveraging all vCPUs on large VMs takes up a huge amount of resources. vSphere 7 installs the Page Tracer on just one vCPU which reduces the impact and resource utilization. vSphere 7 also makes changes to the way the memory bitmap is transferred during the switch-over phase. Previously the entire bitmap was copied, but now it’s only transfers a compacted bitmap which takes significantly less time.

Assignable hardware
VMware has included Bitfusion in vSphere 7. Bitfusion, a company VMware acquired in 2019, is able to take advantage of GPU virtualization for the purposes of AI/ML use cases. vSphere 7 now allows you to assign hardware that you used to be locked to a specific host for. NVIDIA vGPU and Dynamic DirectPath I/O devices can now be set on a VM and are fully supported across the cluster with DRS and HA

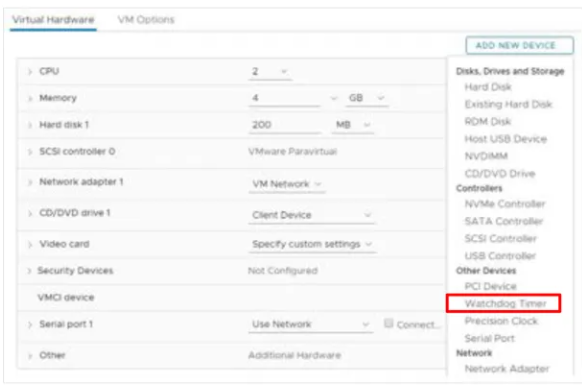
Watchdog timer
Hardware version 17 introduces the Watchdog Timer to monitor your VM’s guest OS. If it detects that the VM is hung or down, it will take an action to restart the VM. The feature is based on the following Microsoft specifications: Watchdog Resource Table (WDRT) and Watchdog Action Table (WDAT). It’s supported on Windows Servers and Linux guests.
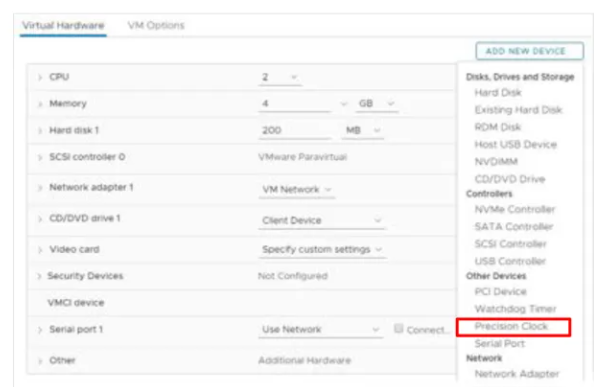
Precision time control
This is a feature which is enabled on the host and VM. and it will keep sub-millisecond accuracy on the VM based on the host time. it is useful for financial and scientific virtual machines and requires hardware version 17. You can choose between NTP and PTP
vCenter certificates
vSphere 7 has now changed the way we renew and replace certificates which will make it far easier to manage. You can now renew a VMware CA-signed certificate, replace a VMware CA-signed certificate, replace the current certificate with a third-party CA-signed certificate and you can create a new Certificate Signing Request all through the vCenter GUI. Previously this was done via the certificate management tool in the CLI.
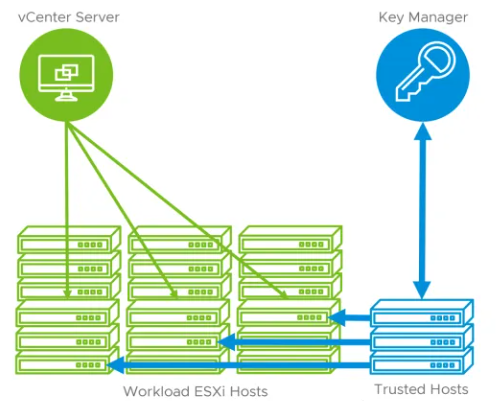
vSphere Trust Authority
The vSphere Trust Authority creates a hardware root of trust to secure the environment using a hardware Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and a separate Trust Authority Cluster which involves having extra hosts to do this. You will also need an external Key Management Server. The Trust Authority Cluster becomes the Trusted Key Provider over the cluster and in the Workload ESXi hosts. This approach allows the Trust Authority Cluster to attest the entire workload cluster and the vCenter managing it
Improved DRS
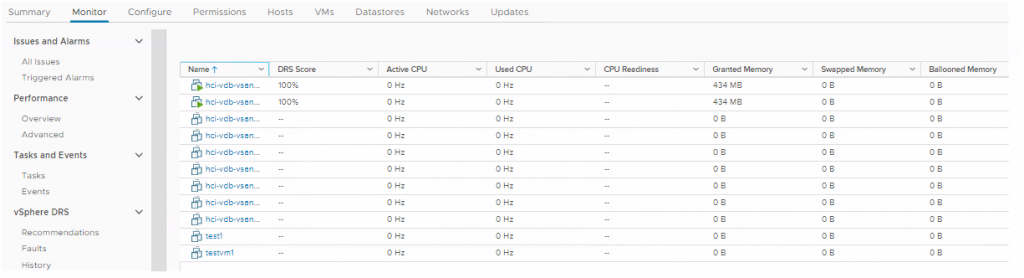
The Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) now runs every minute and bases the decision to move a VM by looking at the actual workload inside the VM and checking if it would run better on another host. It does not base the score on the relative load on the hosts, it bases it on the workload of the VM. Performance and capacity metrics are used in the algorithm Obtaining a VM DRS score of 80-100% shows that there is mild to no resource contention.
You can view the scores at the Cluster summary level
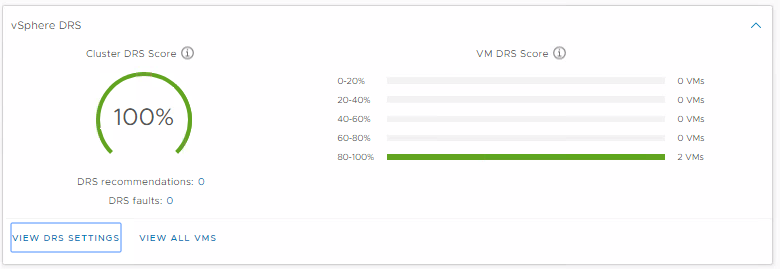
And at the Monitor > VM DRS Score level when the cluster is selected.
vSphere 7 with Kubenetes
vSphere 7 is available in two editions
- vSphere 7 – The next generation of vSphere for non-container apps
- vSphere 7 with Kubernetes – The new generation of vSphere for containerized applications. This is available through VMware Cloud Foundation
With vSphere 7 with Kubernetes, VMware delivers embedded Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service for fully compliant and conformant Kubernetes capabilities for containerized applications. This approach provides Kubernetes APIs to developers, enabling CI/CD processes across a global infrastructure including on-premises data centers, hyperscalers, and Managed Service Providers (MSP) infrastructure
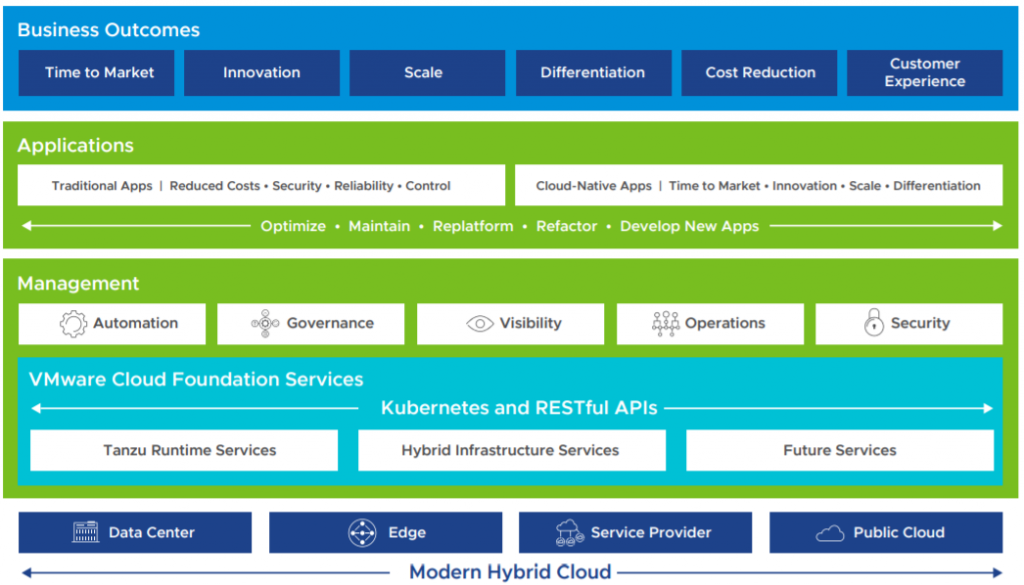
VMware Cloud Foundation Services consists of two families of services: Tanzu Runtime Services and Hybrid Infrastructure Services.
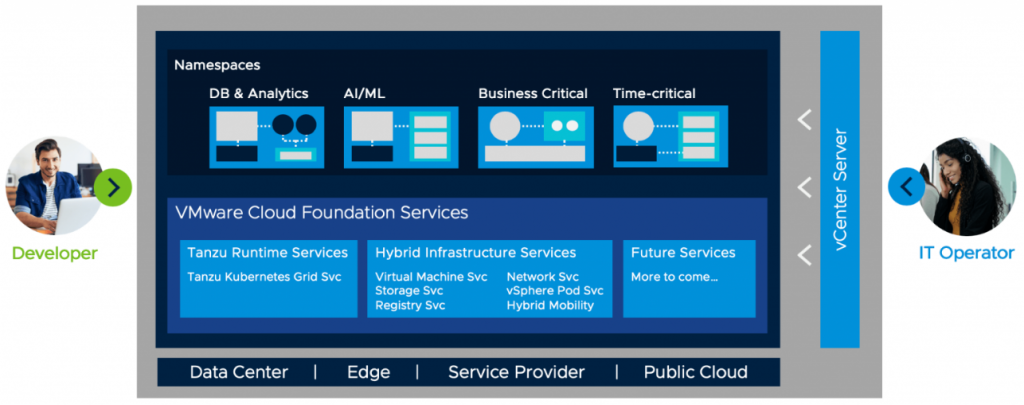
Tanzu Runtime Services allow developers to build applications using the upstream Kubernetes distributions.
- Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service The Tanzu Kubernetes Grid Service allows developers to manage consistent, compliant and conformant Kubernetes clusters
Hybrid Infrastructure Services allow developers to provision and work with infrastructures such as compute, storage, and networking.
- vSphere Pod Service The vSphere Pod Service lets developers run containers directly on the hypervisor for improved security, performance, and manageability.
- Storage Service The Volume Service allows developers to manage persistent disks for use with containers, Kubernetes and virtual machines.
- Network Service The Network Service allows developers to manage Virtual Routers, Load Balancers and Firewall Rules.
- Registry Service The Registry Service allows developers to store, manage and secure Docker and OCI images.
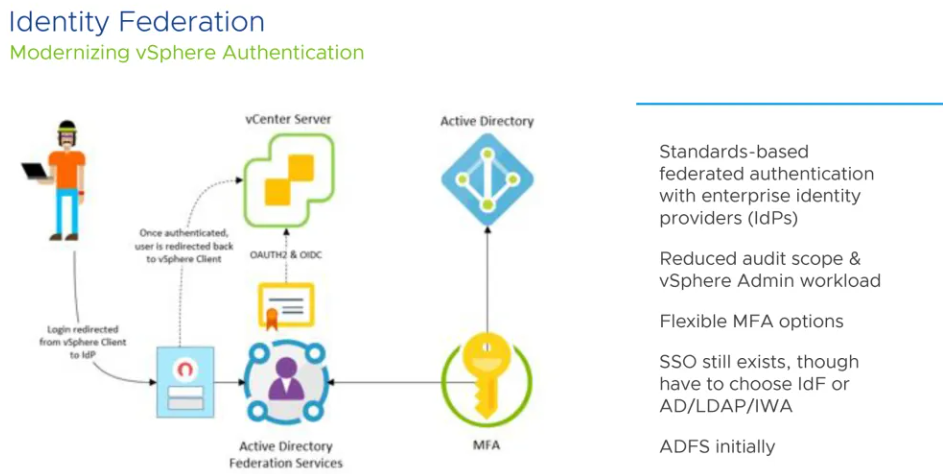
Identity Federation
vCenter Server supports identity provider federation for Microsoft Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) It also acts as an identity provider to manage identity information for users. It also provides authentication services that can be leveraged by applications.
vSGX / Secure Enclaves
When an application has something it needs to keep secret such as an encryption key or personally identifying information then that the secret is visible to a lot of layers. the secret is stored in system memory and in the CPUs. Next, the hypervisor can see it followed by the guest OS and the application. Intel’s Software Guard Extensions (SGX) are used to keep secrets from the guest OS and the hypervisor. This functionality is now exposed to VMs runing hardware version 17 where you can enable it in the VM settings. While there are various processes in place that protect one application from another, and the OS from an unprivileged user, an application has virtually no protection from processes running with higher privileges, including the OS itself. Malware which gains administrative privileges has unrestricted access to all system resources and all applications running on the system. Sophisticated malware can target an application’s protection schemes to extract encryption keys and even the secret data itself directly from memory.
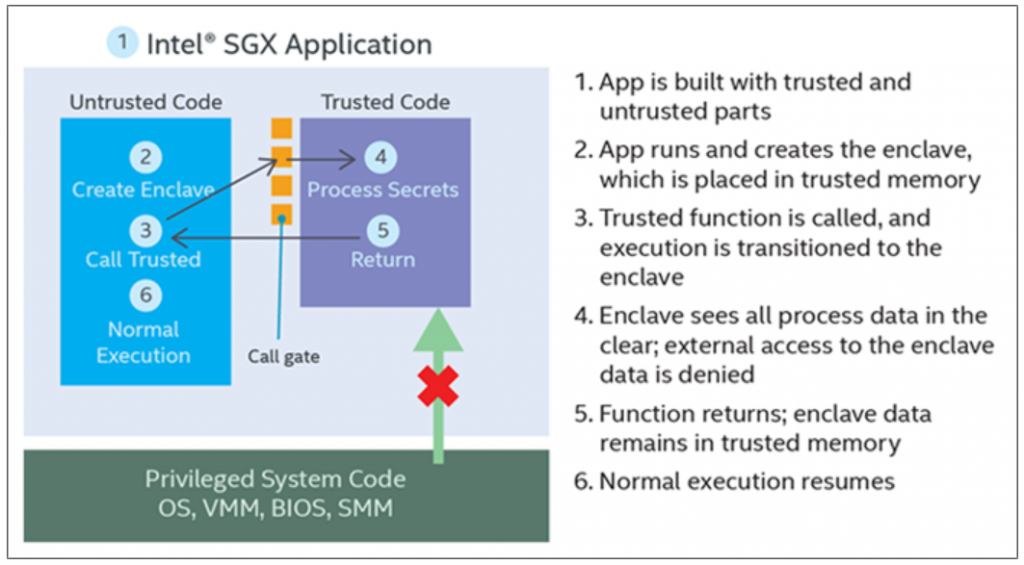
There are restrictions to using this feature though as listed below

vSAN enhancements
vSphere Lifecycle Manager
VMware vSAN 7.0 benefits from the new vSphere Lifecycle Manager functionality. vLCM delivers a single lifecycle workflow for the full HCI server stack: vSphere, vSAN, drivers and OEM server firmware.
Native File services
vSAN 7 now offers file and block persistent volumes. This allows vSphere administrators to enable NFS 3 and 4.1 shares, vVols. These can support encryption and snapshots. VMware vSAN 7.0 will also provide file-level persistent storage for containers
Increased Visibility into vSAN Used Capacity.
Replication objects are now visible in vSAN monitoring for customers using SRM and vSphere Replication. The objects are labelled “vSphere Replicas” in the “Replication” category.
Uninterrupted Application Run Time.
vSAN 7 provides improvements to the uptime in stretched clusters by introducing the ability to redirect VM I/O from one site to another in the event of a capacity imbalance. Once the disks at the first site have freed up capacity, customers can redirect I/O back to the original site without disruption.
VM Encryption cloning enhancements
In vSphere 7, encryption is now supported when cloning a VM or creating a VM from a template. When cloning an unencrypted VM, you can encrypt the destination VM and when cloning an encrypted VM, you can decrypt the destination VM. Also when cloning an encrypted VM, you can recrypt the destination VM by shallow rekeying. Note that the VM to be cloned must be powered off.
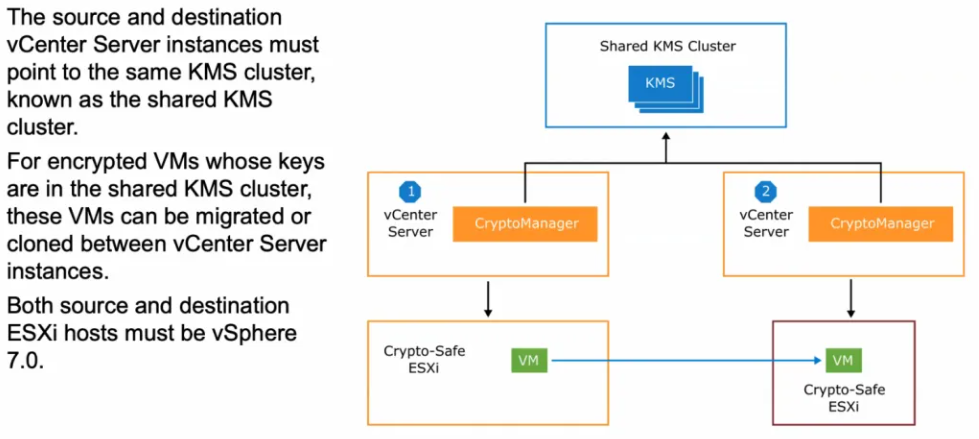
Encrypted VM cross vCenter migration
Cross vCenter server migrations of an encrypted VM is now possible as long as both vCenters can see the same KMS Server and are all vSphere 7.0 hosts. VMs can be powered on or off to migrate.


Leave a Reply