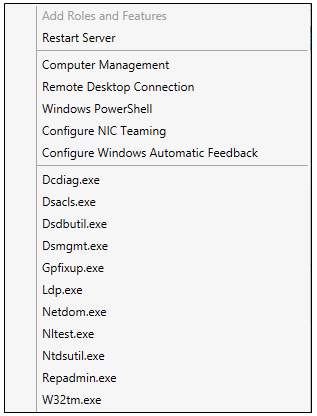
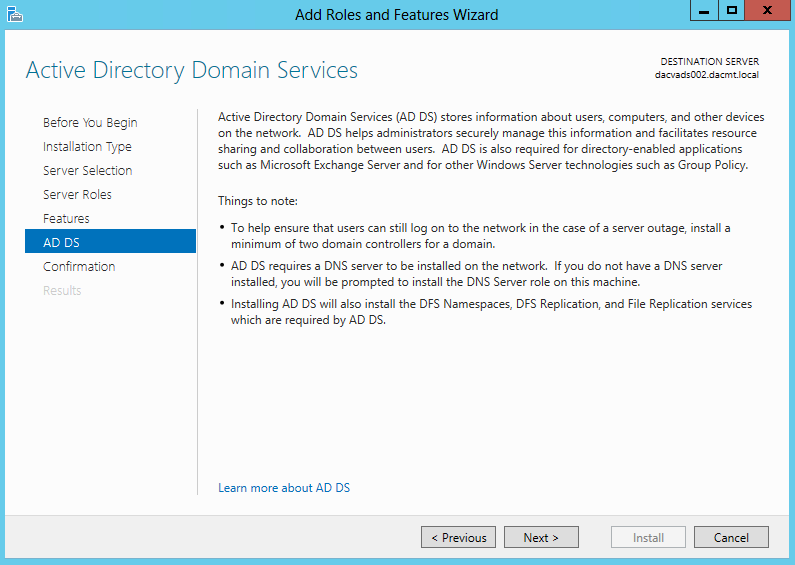
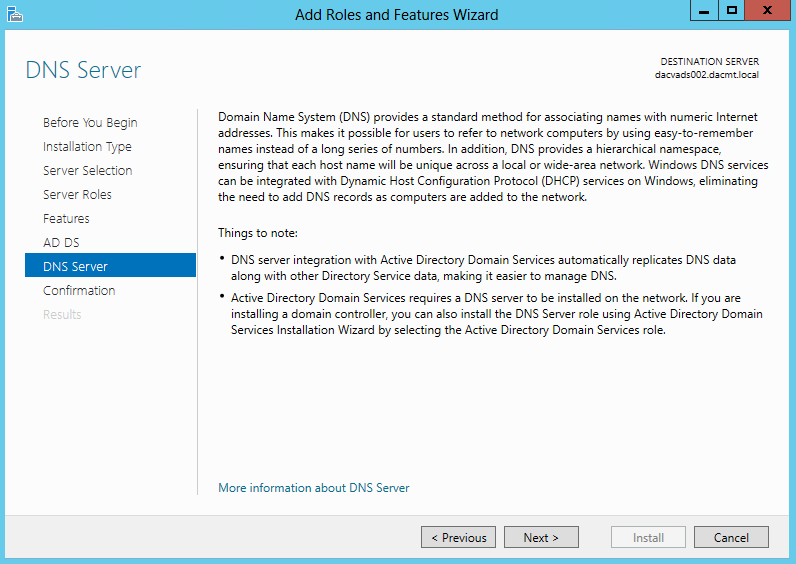
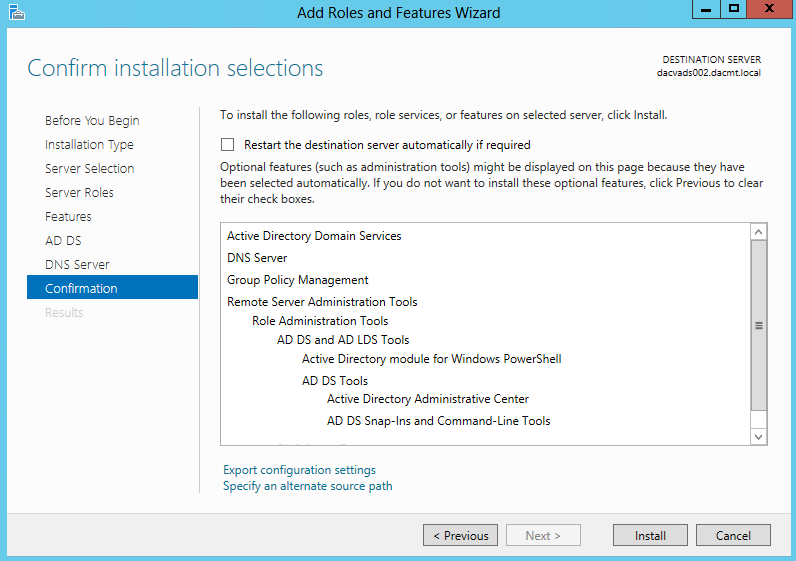
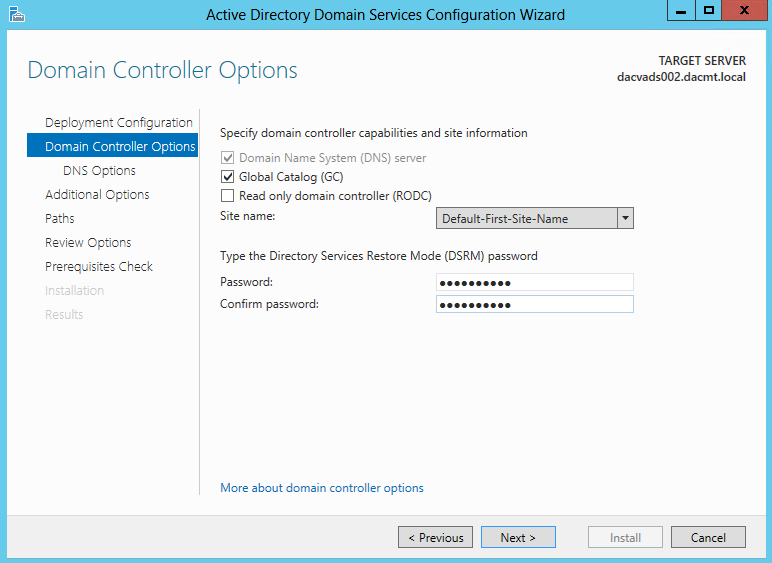
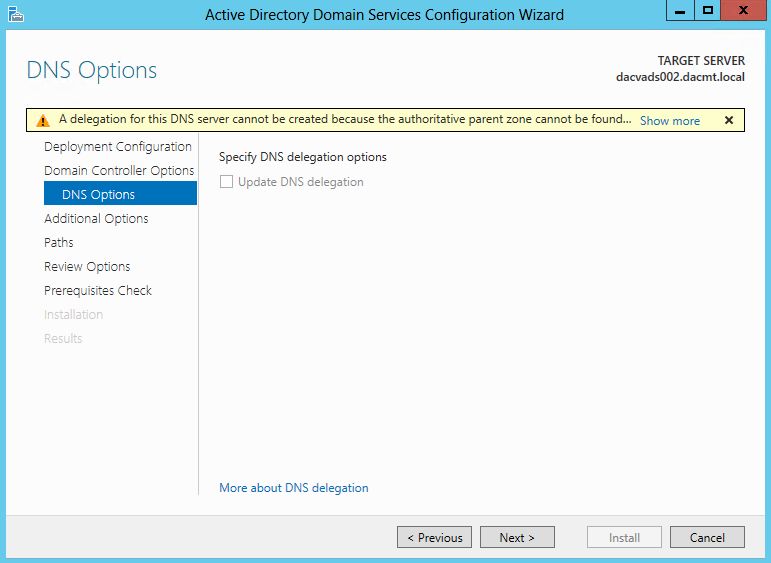
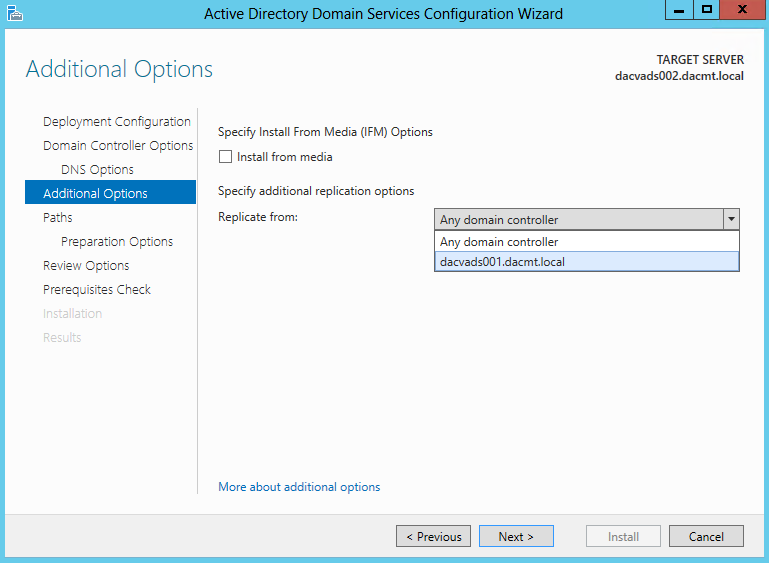
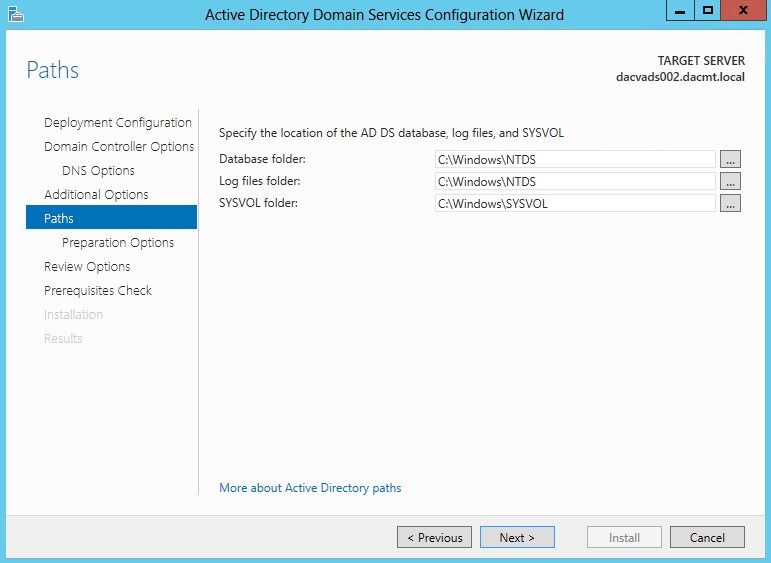
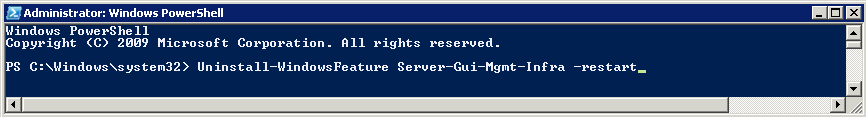
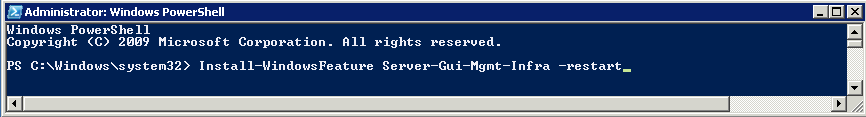
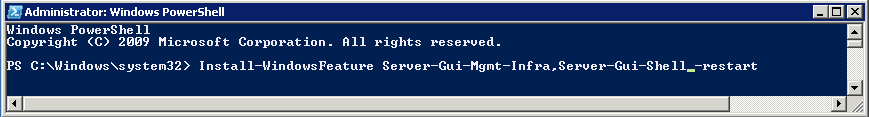
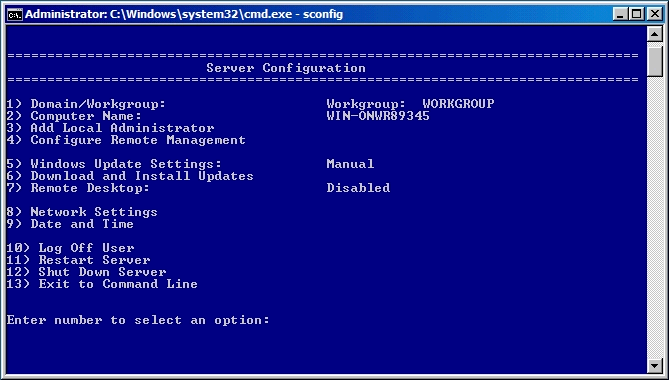
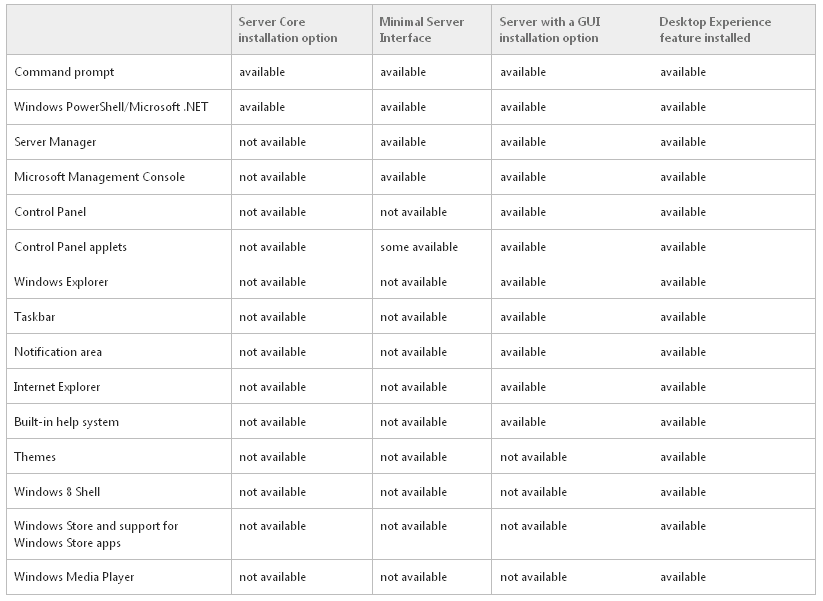
Once you install the Windows 2012 Domain Controller Role, you will find you are able to right click on the server in the console and a menu will appear showing that you are able to connect to several different command line tools. This looks like a very handy feature to have so lets have a deeper look at these tools
You can run these commands in the Active Directory Module for Windows PowerShell or cmd.exe
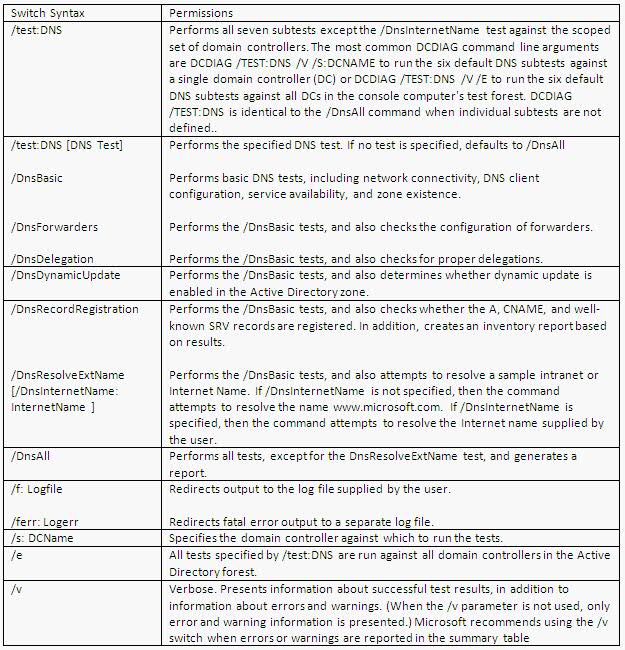
What does Dcdiag.exe do?
This command-line tool analyzes the state of one or all domain controllers in a forest and reports any problems to assist in troubleshooting. DCDiag.exe consists of a variety of tests that can be run individually or as part of a suite to verify domain controller health and DNS Health
What does Dsacls.exe do?
Dsacls.exe is a command-line tool that you can use to query the security attributes and to change permissions and security attributes of Active Directory objects. It is the command-line equivalent of the Security tab in the Windows Active Directory snap-in tools such as Active Directory Users and Computers and Active Directory Sites and Services.
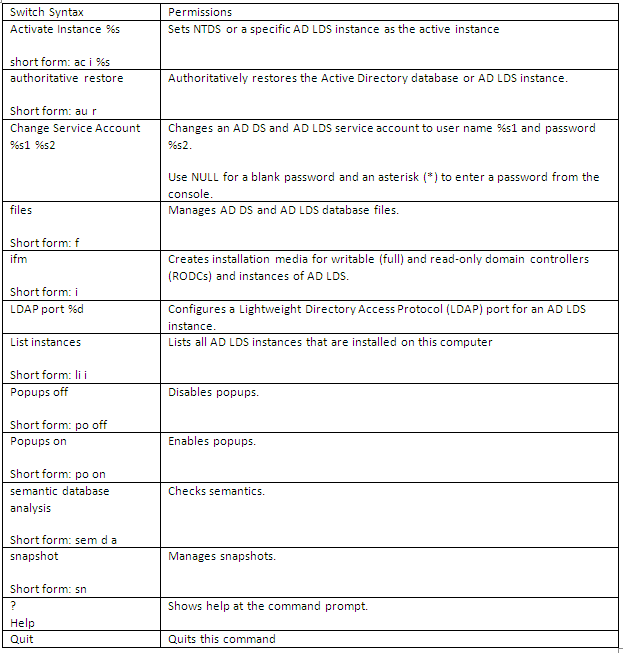
What does Dsdbutil.exe do?
Dsdbutil is a command-line tool that is built into Windows Server 2008. It is available if you have the AD LDS server role installed. To use dsdbutil, you must run the dsdbutil command from an elevated command prompt It performs database maintenance of the Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) store, facilitates configuration of Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) communication ports, and views AD LDS instances that are installed on a computer
What does Dsmgmt.exe do?
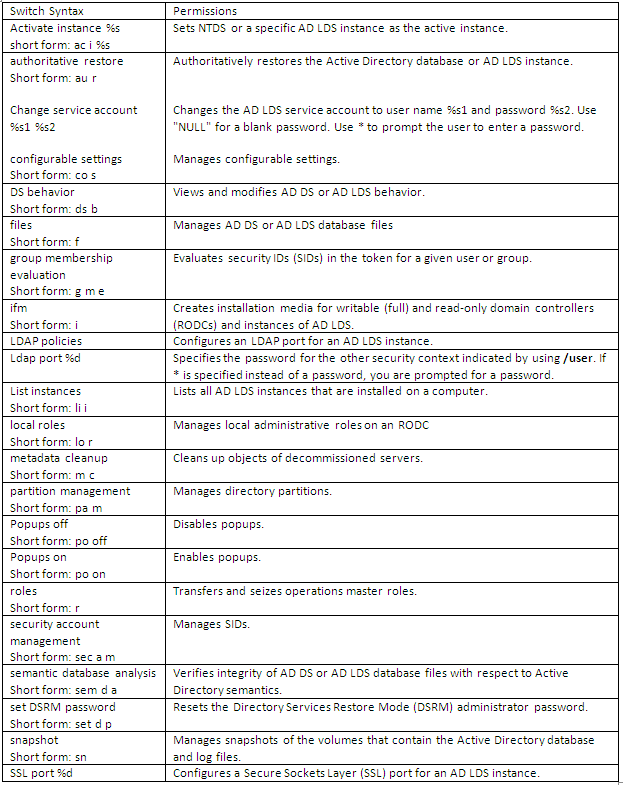
Dsmgmt is a command-line tool which is available if you have the AD LDS server role installed. To use dsmgmt, you must run the dsmgmt command from an elevated command prompt. To open an elevated command prompt, click Start, right-click Command Prompt, and then click Run as administrator. It facilitates managing Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) application partitions, managing and controlling flexible single master operations (FSMO), and cleaning up metadata that is left behind by abandoned Active Directory domain controllers and AD LDS instances. (Abandoned domain controllers and AD LDS instances are those that are removed from the network without being uninstalled.)
What does Gpfixup.exe do?
This tool is used to fix domain name dependencies in Group Policy Objects (GPOs) and Group Policy links after a domain rename operation
What does ldp.exe do?
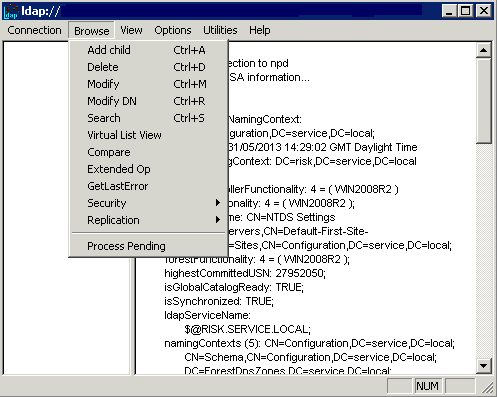
This GUI tool is a Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) client that allows users to perform operations (such as connect, bind, search, modify, add, delete) against any LDAP-compatible directory, such as Active Directory. LDP is used to view objects stored in Active Directory along with their metadata, such as security descriptors and replication metadata. LDP is a GUI-based, Windows Explorer–like utility with a scope pane on the left that is used for navigating through the Active Directory namespace, and a details pane on the right that is used for displaying the results of the LDAP operations. Any text displayed in the details pane can be selected with the mouse and “copied” to the Clipboard.
- Connect through PowerShell to ldp.exe
- Click Connection
- Put in your DC Name
- You are then connected and ready to use the tool
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc756988%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
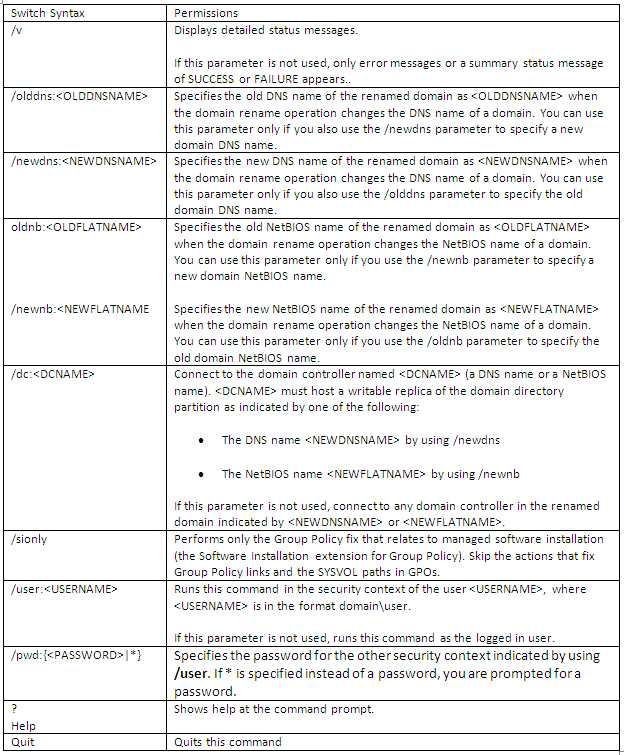
What does Netdom.exe do?
This command-line tool enables administrators to manage Windows Server 2003 and Windows 2000 domains and trust relationships from the command line. You can join a machine to a domain, manage computer accounts for domain member workstations and member servers, establish one-way or two-way trust relationships between domains, including certain kinds of trust relationships, verify and/or reset the secure channel for the following configurations and manage trust relationships between domains
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc781853%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
What does Nltest.exe do?
Nltest.exe is available if you have the AD DS or the AD LDS server role installed. It is also available if you install the Active Directory Domain Services Tools that are part of the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) This tool can do the following
- Get a list of domain controllers
- Force a remote shutdown
- Query the status of trust
- Test trust relationships and the state of domain controller replication in a Windows domain
- Force a user-account database to synchronize on Windows NT version 4.0 or earlier domain controllers
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731935%28v=WS.10%29.aspx
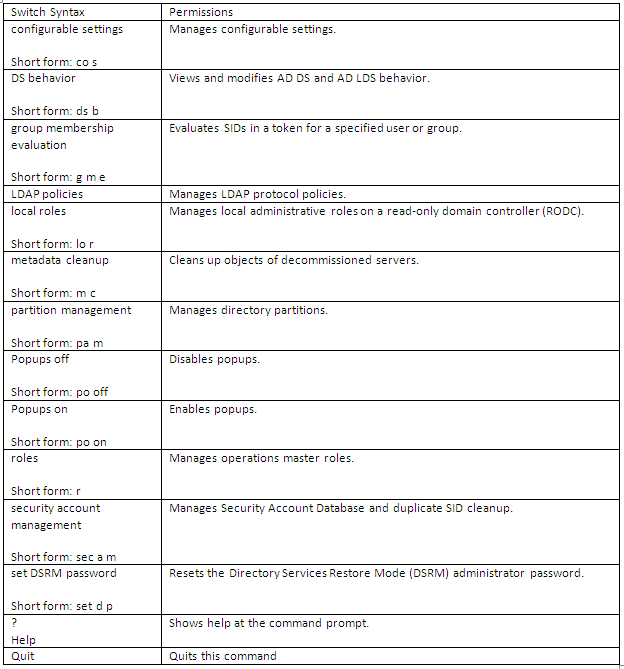
What does Ntdsutil.exe do?
Ntdsutil.exe is a command-line tool that provides management facilities for Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) and Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS). You can use the ntdsutil commands to perform database maintenance of AD DS, manage and control single master operations, and remove metadata left behind by domain controllers that were removed from the network without being properly uninstalled. This tool is intended for use by experienced administrators.
What does Repadmin do?
This command-line tool assists administrators in diagnosing replication problems between Windows domain controllers.
Administrators can use Repadmin to view the replication topology (sometimes referred to as RepsFrom and RepsTo) as seen from the perspective of each domain controller. In addition, Repadmin can be used to manually create the replication topology (although in normal practice this should not be necessary), to force replication events between domain controllers, and to view both the replication metadata and up-to-dateness vectors.
Repadmin.exe can also be used for monitoring the relative health of an Active Directory forest. The operations replsummary, showrepl, showrepl /csv, and showvector /latency can be used to check for replication problems.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc736571%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
What does W32tm.exe do?
W32tm.exe is used to configure Windows Time service settings. It can also be used to diagnose problems with the time service. W32tm.exe is the preferred command line tool for configuring, monitoring, or troubleshooting the Windows Time service. The W32Time service is not a full-featured NTP solution that meets time-sensitive application needs and is not supported by Microsoft as such
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc773263%28v=WS.10%29.aspx