Happy New Year to everyone and all the best for 2013
Archive for December 2012
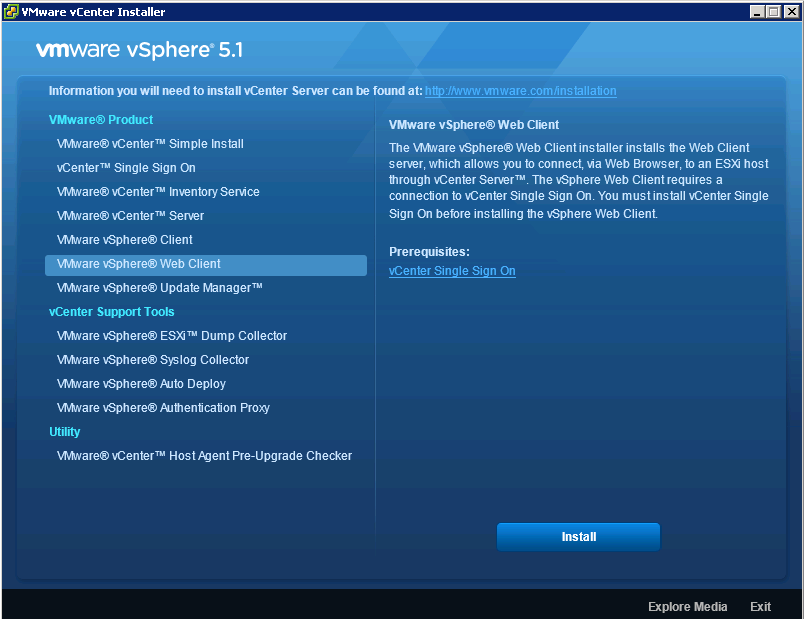
Installing VMware vCenter Server 5.1 using the Simple Install method
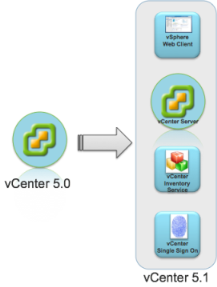
Architectural Changes
The vCenter Server 5.1 release includes significant architectural changes. You must understand these changes before attempting to freshly install or upgrade to vCenter Server 5.1 from older versions of the product. There are four separate services that constitute the vCenter Server 5.1 platform. These are below and must be installed in order
- vCenter Single Sign On (SSO)
- vCenter Inventory Service
- vCenter Server
- vSphere Web Client
Pre Requisites
Before installing vCenter Server 5.1, vSphere 5.1 requires you to install vCenter Single Sign On and install the Inventory Service. You can install vCenter Single Sign On, Inventory Service, and vCenter Server all on a single host machine using the vCenter Server Simple Install option. This option is appropriate for small deployments.
Alternatively, you can install vCenter Single Sign On, vCenter Inventory Service, and vCenter Server separately to customize the location and configuration of the components. (I found this to be the best way)
You also need Adobe Flash installed for the vSphere Web Client
If you are running vCenter as a Virtual Machine in Workstation then you will need at least 2GB RAM or more!
This blog will focus on installing vCenter Single Sign On, Inventory Service, and vCenter Server all on a single host machine running Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise
Instructions
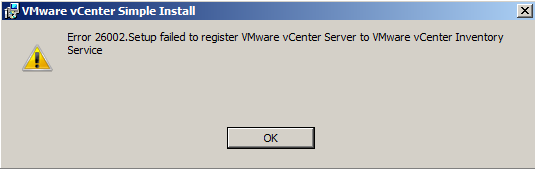
Note: It may be best to install each component separately. I encountered a few errors when I went through the Simple Install Method. See screenprint below
- Download the ISO or installer from the VMware website
- Make sure you have the .NET Framework installed
- Attach the ISO or run the installer on your designated vCenter Server
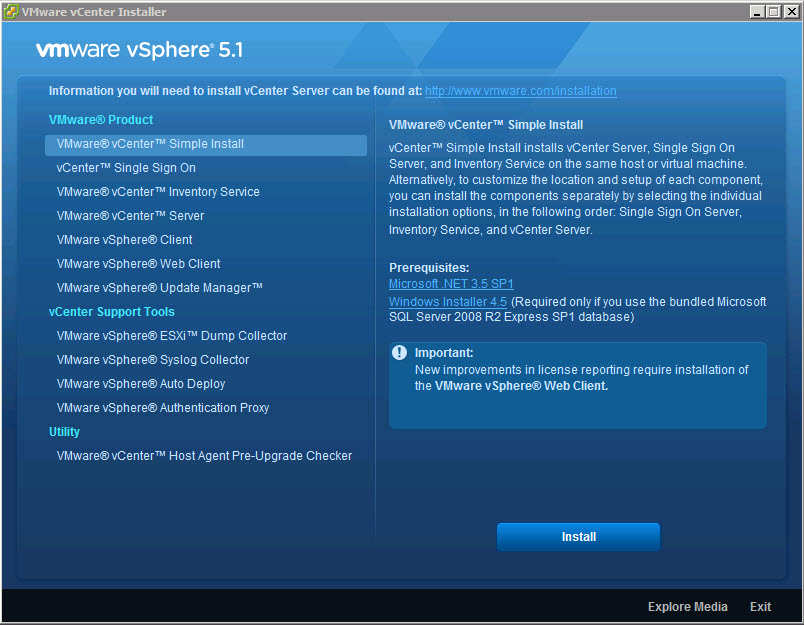
- Select VMware vCenter Server Simple Install and Click Install
- Click Next
- Click Next
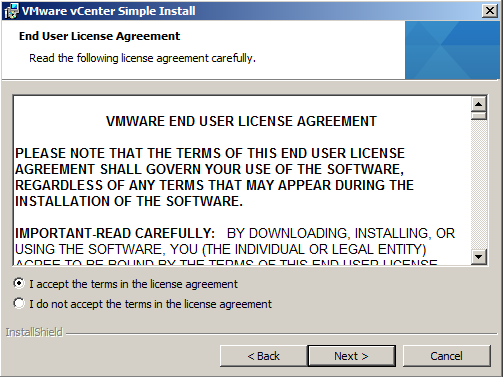
- Select I accept the terms in the license agreement and click Next
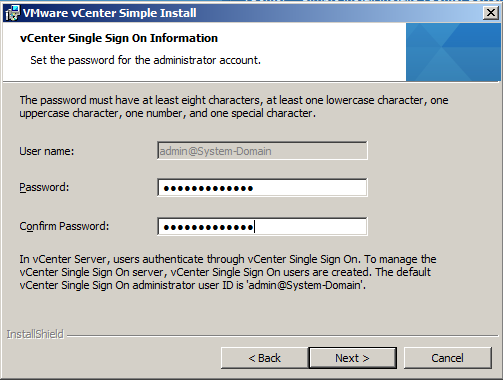
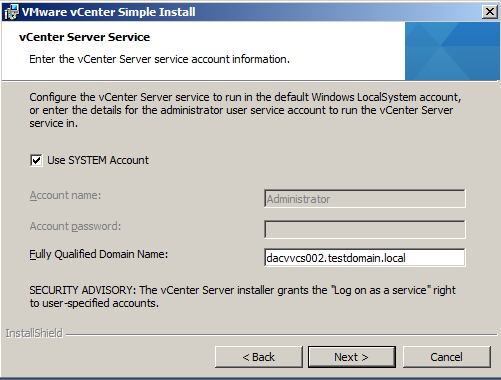
- Put in a Strong Password and click Next. This is a local account not tied to AD or the Windows host. After SSO is installed, you can configure it for one or more LDAP/AD server and other identity sources.
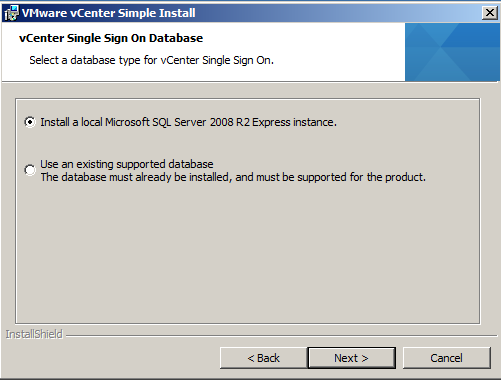
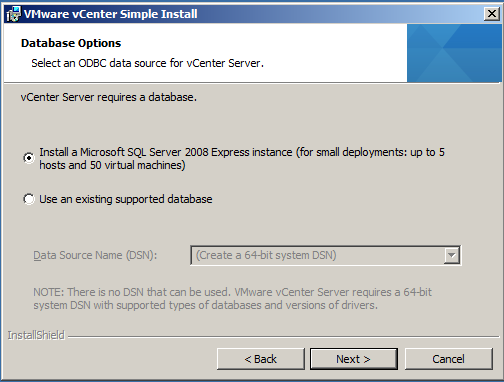
- For this demo, we will just be using the Express Instance
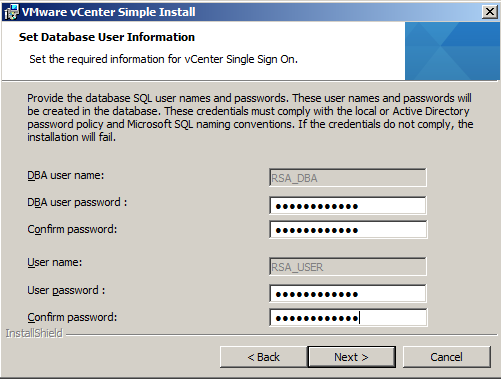
- Put in the passwords for the RSA_USER and RSA_DBA accounts
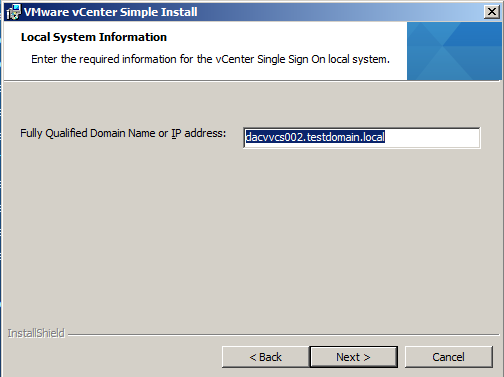
- The FQDN should be in here automatically. If you get an error saying nslookup cannot perform a lookup against this address then check your DNS server
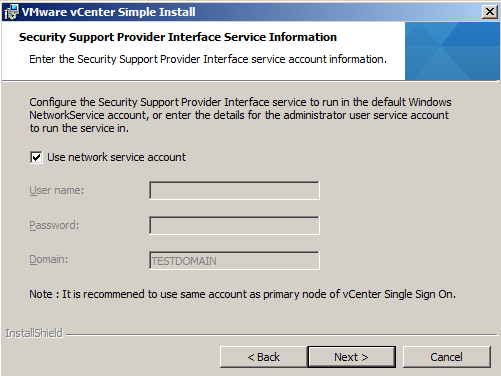
- Use Network Service Account or put in a Username and Password
- Click Next
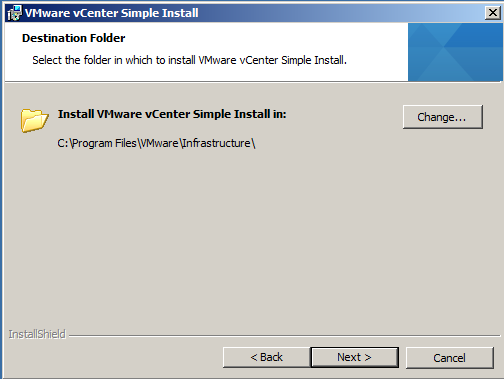
- Choose the location to save into and click Next
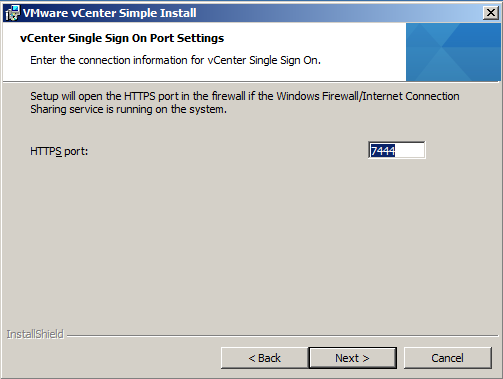
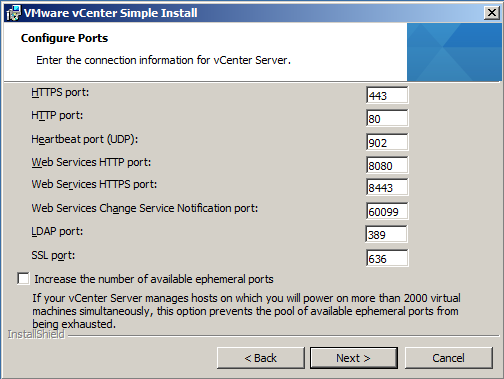
- Check HTTP Port
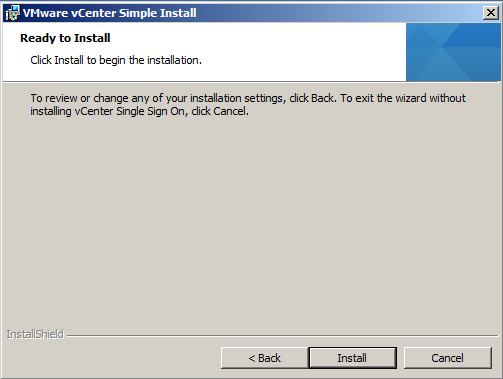
- Click Install and allow SQL DB to be installed and SSO
- When this has finished you will get the screen below
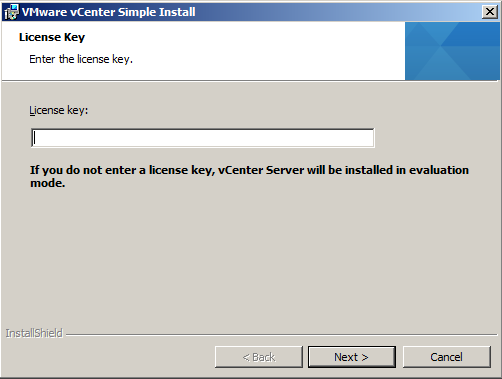
- Put in a license key or just click Next if you are using it in Evaluation Mode
- Click Next
- Click Next
- Click Next
- Click Next
- Click Next
- Click Install and then Finish
- Install the vSphere 5 Web Client (Just follow the prompts)
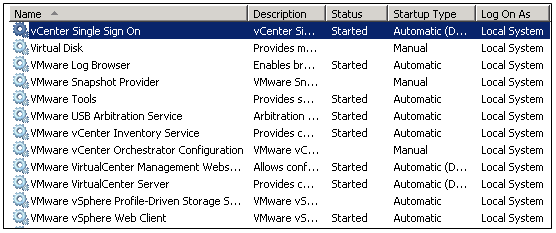
- Next check all the vCenter and Webservices and SSO are running
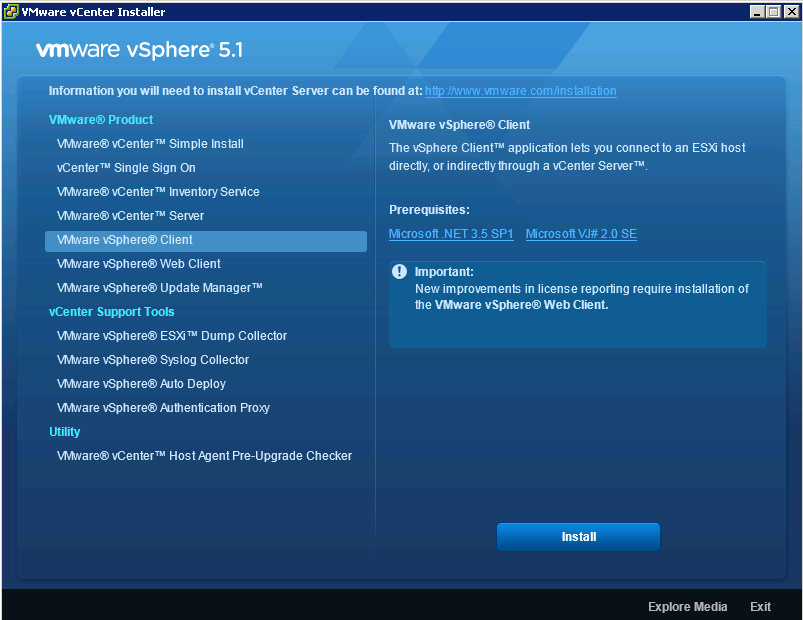
- Install the vSphere 5 client
- Make sure you have downloaded and installed Adobe Flash
- Just a quick point, make sure your vCenter Server has +2GB RAM or things just don’t work very well especially if you are running SSO, Inventory and vCenter on the same box as a test
- You also may need to adjust your firewall for port 9443
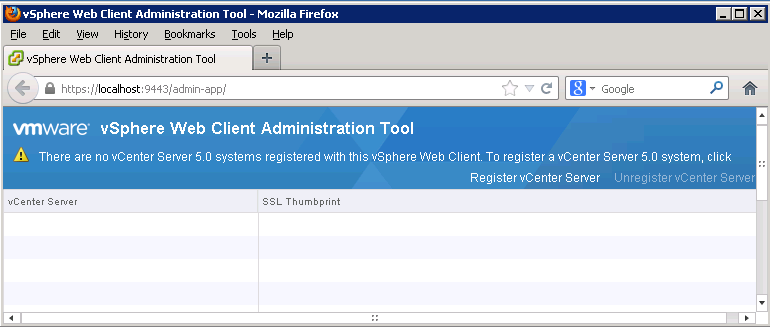
- If you are running 5.1 rather than 5.0, it is best to log into the vSphere Web Client first before on https://localhost:9443/vsphere-client/ using your SSO Login admin@System-Domain + inital setup password before logging into the vSphere Web Admin Assistant on https://localhost:9443/admin-app or you will get an error such as the below
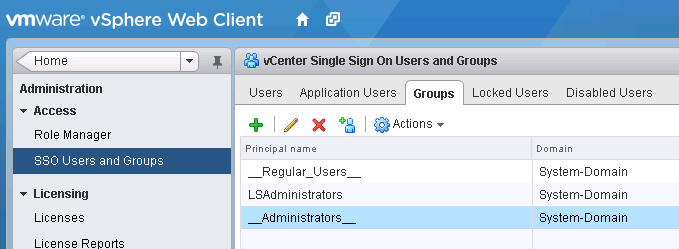
- Log into vSphere web client as admin (admin@System-Domain, this is the default user added during install of vcenter)
- Go to Administration -> SSO Users and Groups
- Go to Groups tab and click on __Administrators__
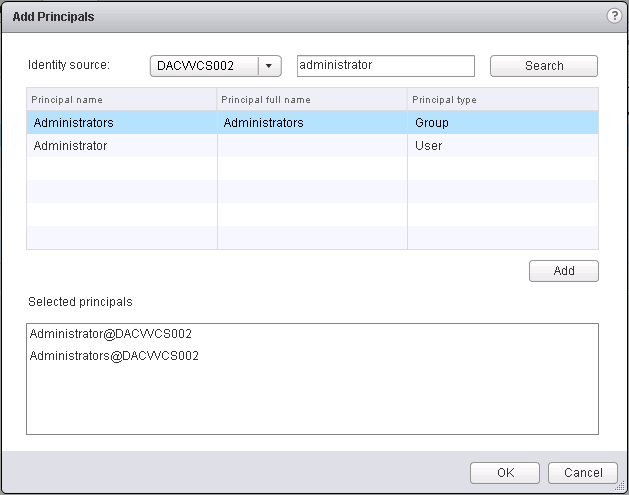
- Click on the little man icon to Add Principals
- Select the local vCenter server as the identity source and search for a local user. See Screenprint) you can add your Admins Group or any other group
- Then add that user and click OK.
- Log in as the local user.
- You should see the vCenter listed after you log in, if not, you may need to reboot.
Useful VMware KB for troubleshooting known certificate error
http://blogs.vmware.com/kb/2012/10/implementing-ca-signed-ssl-certificates-with-vsphere-5-1.html
SSO Issues (Cannot log in using Domain account to vClient etc)
http://blogs.vmware.com/kb/2012/10/vsphere-sso-resources.html
http://longwhiteclouds.com/2012/09/26/vsphere-5-1-gotcha-with-single-sign-on-sso/
- Go to Administration
- Single Sign On and Discovery > Configuration
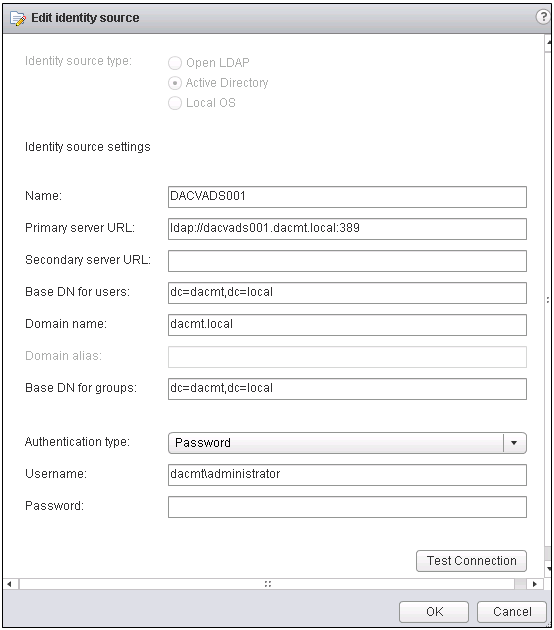
- Click the + sign to add a new identity source. E.g Active Directory Server.
- Fill in as per your domain. Note my lab domain is dacmt.local
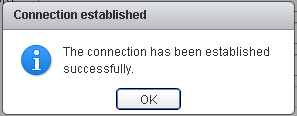
- Click Test Connection
- Wait for it to say Connection successful
- Change the order of the domains so AD is at the top
Registering vCenter Server 5 (Not 5.1)
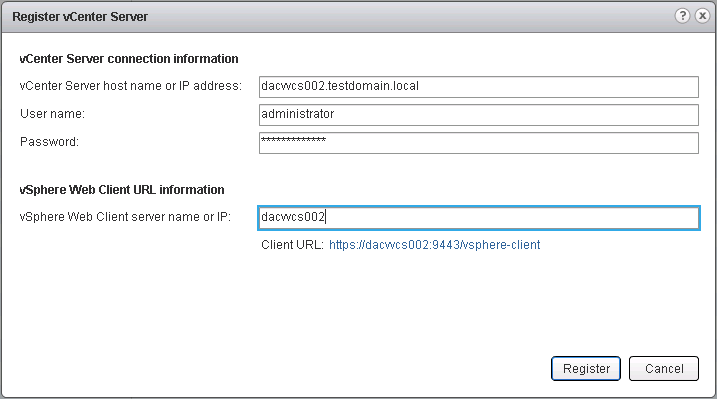
- Log into the vSphere Web Admin Assistant on https://localhost:9443/admin-app
- Click Register vCenter
- Enter the vCenter FQDN
- Enter the Username and Password
- Enter the vCenter hostname
- Click Register
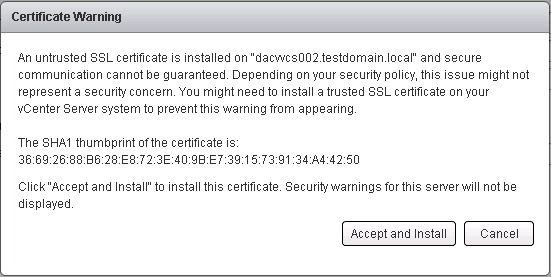
- Accept the certificate
Can you run vCenter 5 on Windows Servers 2012?
vCenter isn’t officially supported on Server 2012
What you will find is that the installation fails just before it tries to install the vSphere Profile-Driven Storage Service.
The reason why
To install that service, the vCenter service needs to be running. However, the vCenter service does not start properly in Windows Server 2012. This is due to a missing dependency. In particular, the VirtualCenter Server service relies on the ProtectedStorage service which was removed from Win8/Server 2012. The work around is the following open regedit and go to \System\CurrentControlSet\Services\vpxd and then open the DependOnService key and remove ProtectedStorage from the list. Reboot the machine and the vCenter service should come alive (might take a while). Then restart only the vCenter installation again once everything has come up (you need to wait for vCenter service to come alive which can take a few minutes). The install will continue from where it kicked off and finish
So the short version is, when the vCenter install fails, go to registry and remove ProtectedStorage dependency from the vpxd service, reboot and it should work. Restart the vcenter install and it will finish as per normal.
Should you delete files in the \WinSXS directory?
Recently following a clear out of my Windows 7 64bit laptop and running TreeSize to locate offending large files and folders, I found a 6GB folder called WinSXS. Not having a clue about what this folder was, I decided to investigate..
First of all “Can I delete the \Windows\Winsxs directory?”
To answer the question, the answer is actually: No.
Why?
Because the component store (\Winsxs) is needed to repair the OS binaries in the event that a file becomes corrupted or, in worst case scenarios, compromised. There are a few directories in the component store so let’s look at them and what their general role is in Windows. WinSxS folder replaces the old $NTUninstall folders from XP which is one of the reasons it grows after installing Updates
- \Winsxs\Catalogs: Contains security catalogs for each manifest on the system
- \Winsxs\InstallTemp: Temporary location for install events
- \Winsxs\Manifests: Component manifest for a specific component, used during operations to make sure files end up where they should
- \Winsxs\Temp: Temp directory used for various operations, you’ll find pending renames here
- \Winsxs\Backup: Backups of the manifest files in case the copy in \Winsxs\Manifests becomes corrupted
- \Winsxs\Filemaps: File system mapping to a file location
- \Winsxs\<big_long_file_name>: The payload of the specific component, typically you will see the binaries here.
Explanation
The Windows component store (C:\Windows\winsxs) directory is used during servicing operations within Windows installations. Servicing operations include, but are not limited to, Windows Update, Service Pack and hotfix installations.
The component store contains all of the files needed for a Windows installation and any updates to those files are also held within the component store as they are installed. This will cause the component store to grow over time as more updates, features or roles are added to the installation. The component store utilizes NTFS hard links between itself and other Windows directories to increase the robustness of the Windows platform.
The component store will show a large directory size due to the way the Windows Explorer shell accounts for hard links. The Windows shell will count each reference to a hard link as a single instance of the file for each directory the file resides in. For example, if a file named advapi32.dll was 700 KB in size and was contained in the component store and the \Windows\system32 directory, Windows Explorer would inaccurately report that it consumes 1400 KB of hard disk space
The component store cannot reside on another volume other than the system volume due to the use of NTFS hard links. Attempting to move the component store will result in the inability to properly install Windows updates, Service Packs, roles or features. Additionally, it is not recommended that files be manually removed or deleted from the component store.
To reduce the size of the component store directory on a Windows installation you can choose to make the service pack installation permanent and reclaim used space from the Service Pack files. Doing this will make the Service Pack permanent and it will not be removable.
To remove the Service Pack files from a Windows installation use the following in-box utilities:
- Windows Vista Service Pack 1 installed: VSP1CLN.EXE
- Windows Vista Service Pack 2 or Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 installed: Compcln.exe
- Windows 7 Service Pack 1 or Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 installed: DISM /online /Cleanup-Image /SpSuperseded or Disk Cleanup Wizard (cleanmgr.exe)
Scavenging may also be proactively performed on Windows Vista and Windows 2008 installations by forcing a removal event on the system. Scavenging will attempt to remove any unneeded system binaries from the installation and allow Windows to reclaim the disk space. To issue an uninstall event on a Windows installation, simply add and remove any unneeded system component that is not already installed and reboot the Windows installation. Scavenging will be performed during the subsequent reboot of the operating system.
NOTE: Scavenging is performed automatically on Windows 7 and Windows 2008 R2 installation
TechNet Virtual Labs
What are TechNet Virtual Labs?
TechNet Virtual Labs enable you to quickly evaluate and test Microsoft’s newest products and technologies through a series of guided, hands-on labs that you can complete in 90 minutes or less. There is no complex setup or installation required, and you can use TechNet Virtual Labs online immediately, free
What Labs are available?
- Exchange Server
- SQL Server 2012
- SQL Server 2008 R2
- Internet Information Services (IIS)
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows Small Business Server
- Windows Azure
- Windows 7
- Forefront Security
- System Center
- Microsoft Lync Server
- Microsoft Office
- Sharepoint
Link
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/virtuallabs/default.aspx
Server 2012 Labs
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windowsserver/hh968267.aspx
VMware Hands On Labs Test Drive
What is it?
The Hands on Lab Portal is using the Project Nee Application developed by Mike D. and Curtis P. who have been part of the VMworld Hands on Labs Program for over 4 years. The Application is built for the web (HTML 5) and can run its workload from any vCloud resource (all you need to do is connect to a vCloud API and you are set) It looks like the design in the portal can serve many different use cases (think SalesForce model) – the first of which were the Education Environment and our VMware Hands on Labs.
The VMware Hands-on Labs are now available online! VMware currently have 10 VMworld Labs and will be adding more during the next few weeks – in total they plan to have all 36 labs and add more along the way. The public beta has over one thousand users and is growing every day.
To participate in this exciting effort, register your interest below.
http://www.surveymethods.com/EndUser.aspx?AA8EE2FBAAEDF7FDAB
HOL Poster
Force Windows Recycle Bins to Empty for Every User on a System
If you have multiple user accounts logging into a Windows computer or server and are running low on space, you can easily empty the recycling bin for all users with a single command line, assuming your user account has administrator privileges.
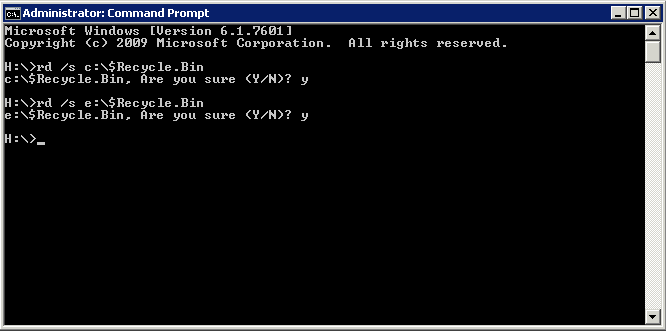
The Command for Windows 7 and Server 2008
rd /s (Drive):\$Recycle.Bin
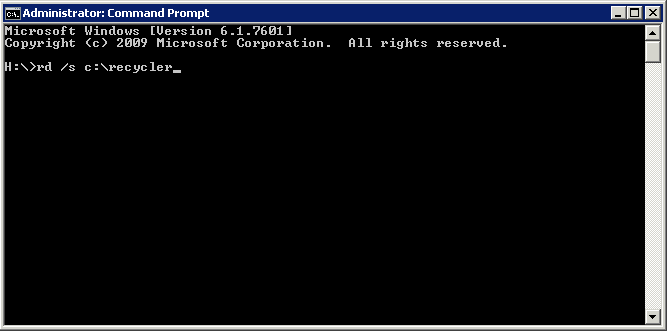
The Command for XP, Vista and 2003
rd /s (Drive):\Recycler
Change the Recycle Bin settings
You can change the settings of the Recycle Bin to suit the way you work. For example, if you rarely empty the Recycle Bin because you want to avoid discarding files you might someday want to recover, you can increase the maximum storage size of the Recycle Bin. You can also turn off the delete confirmation dialog box that appears every time you send files to the Recycle Bin, or even choose not to move files to the Recycle Bin and instead immediately remove them from your computer when you delete them.
- On the desktop, right-click Recycle Bin, and then click Properties.
- Click the General tab, and then do any of the following:
- To set the maximum storage size of the Recycle Bin, enter a number in the Maximum size box, which sets the Recycle Bin’s maximum size (measured in megabytes) for the selected Recycle Bin under Recycle Bin Location.
- To turn off the delete confirmation dialog box, clear the Display delete confirmation dialog check box.
- To immediately remove files from your computer when you delete them, click Do not move files to the Recycle Bin. If you do this, your files will always be permanently removed when deleted.
Installing a new version of vCenter 5 on SQL Server 2008
Pre Requisites
- This blog will target an existing Microsoft SQL 2008 R2 Server
- Make sure you are able to log into SQL Management Studio
- vCenter 5 installer for obtaining the script which will set this all up automatically
- vSphere Installation and Setup Guide. Page 176 onwards
Instructions
- Log into your SQL Server and run SQL Management Studio as a System Admin
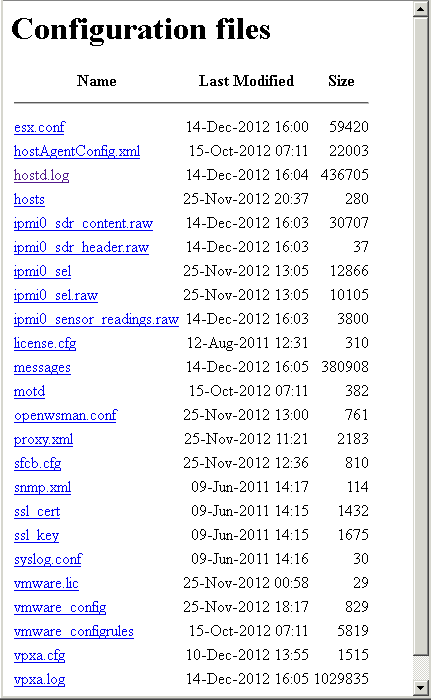
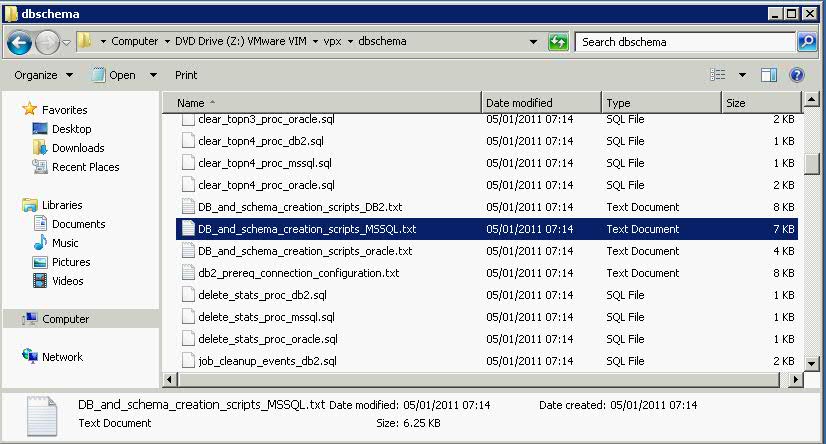
- Attach your vCenter Installer ISO to your SQL DB VM and navigate to DVDdrive/vpx/dbschema or DVDrive/vCenter Server/dbschema
- Copy the DB_and_schema_creation_scripts_MSSQL.txt to your desktop
- You now need to run through this script and customize the location of the data and log files and the user account and password if you wish
- The vpxuser that is created by this script is not subject to any security policy. Change the passwords as appropriate. The vpxuser will have DBO Privileges on both the VCDB and the MSDB databases.
- Logon to a Query Analyzer session with the sysadmin (SA) or a user account with sysadmin privileges and run the following script once amended. Note that I haven’t changed the locations, everything is stored on C:\ as I am only testing and change the vpxuser password
- A more detailed breakdown is detailed below the script
use [master]
go
CREATE DATABASE [VCDB] ON PRIMARY
(NAME = N’vcdb’, FILENAME = N’C:\VCDB.mdf’ , SIZE = 20000KB , FILEGROWTH = 10% )
LOG ON
(NAME = N’vcdb_log’, FILENAME = N’C:\VCDB.ldf’ , SIZE = 10000KB , FILEGROWTH = 10%)
COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
go
use VCDB
go
sp_addlogin @loginame=[vpxuser], @passwd=N’UseaStrongPassword!’, @defdb=’VCDB’, @deflanguage=’us_english’
go
ALTER LOGIN [vpxuser] WITH CHECK_POLICY = OFF
go
CREATE USER [vpxuser] for LOGIN [vpxuser]
go
CREATE SCHEMA [VMW]
go
ALTER USER [vpxuser] WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA =[VMW]
go
–User should have DBO Privileges or VC_ADMIN_ROLE and VC_USER_ROLE database roles
sp_addrolemember @rolename = ‘db_owner’, @membername = ‘vpxuser’
go
if not exists (SELECT name FROM sysusers WHERE issqlrole=1 AND name = ‘VC_ADMIN_ROLE’)
CREATE ROLE VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT ALTER ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT REFERENCES ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT INSERT ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT CREATE TABLE to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT CREATE VIEW to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT CREATE Procedure to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
if not exists (SELECT name FROM sysusers WHERE issqlrole=1 AND name = ‘VC_USER_ROLE’)
CREATE ROLE VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT SELECT ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT INSERT ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT DELETE ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT UPDATE ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
sp_addrolemember VC_ADMIN_ROLE , [vpxuser]
go
sp_addrolemember VC_USER_ROLE , [vpxuser]
go
use MSDB
go
CREATE USER [vpxuser] for LOGIN [vpxuser]
go
–User should have DBO Privileges or VC_ADMIN_ROLE
sp_addrolemember @rolename = ‘db_owner’, @membername = ‘vpxuser’
go
if not exists (SELECT name FROM sysusers WHERE issqlrole=1 AND name = ‘VC_ADMIN_ROLE’)
CREATE ROLE VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
go
grant select on msdb.dbo.syscategories to VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
grant select on msdb.dbo.sysjobsteps to VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT SELECT ON msdb.dbo.sysjobs to VC_ADMIN_ROLE
GO
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_job TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_delete_job TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobstep TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_update_job TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobserver TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobschedule TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_category TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
sp_addrolemember VC_ADMIN_ROLE , [vpxuser]
go
A breakdown of the script
This DB_and_schema_creation_scripts_MSSQL.txt file describes how to use optional scripts to create a Microsoft SQL database for vCenter Server and to create the database schema. If you do not use these scripts, you can create the database manually and allow the vCenter Server installer to create the database schema.
To prepare a SQL Server database to work with vCenter Server, you generally need to create a SQL Server database user with database operator (DBO) rights. When you do this, you must make sure that the database user login has the db_owner fixed database role on the vCenter Server database and on the MSDB database. (The db_owner role on the MSDB database is required for installation and upgrade only. You can revoke this role after the installation or upgrade process is complete.) The purpose of granting DBO permissions to the vCenter Server database user is to enable the vCenter Server installer to create the vCenter Server database schema.
For environments in which the user cannot have DBO permissions on the vCenter Server database, you can instead run scripts that create the vCenter Server database schema before you run the vCenter Server installer.
You can use the DB_and_schema_creation_scripts_MSSQL.txt script to create a database, user, and permissions for successful installation of vCenter Server.
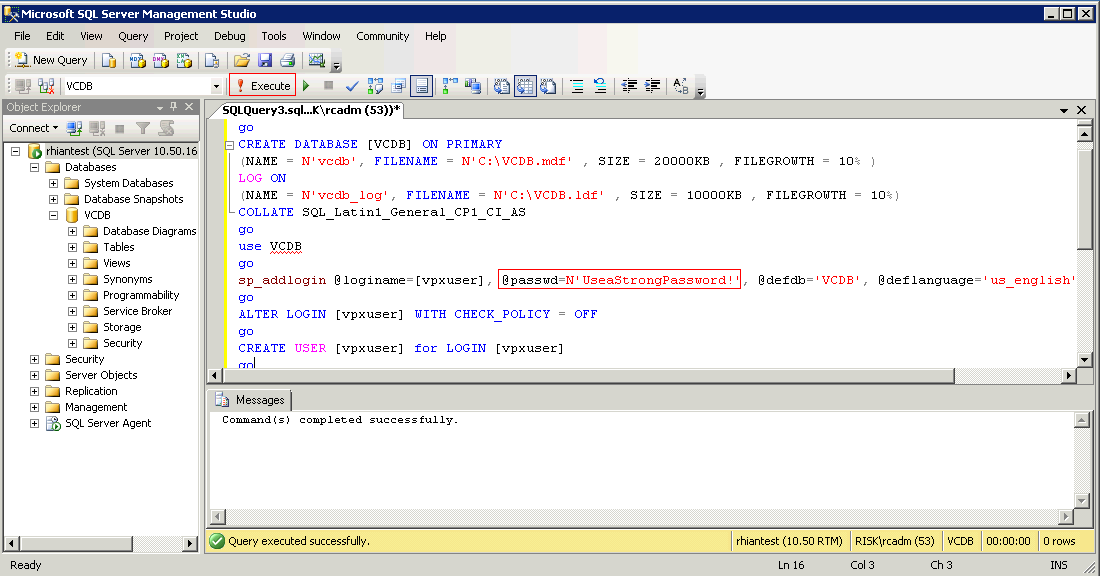
- The first part of this script as listed below. (Highlights in blue where changes can be made)
- You must change the Password or you may get an error that the Password does not conform to the Password Complexity rules.(Highlighted in red on screenprint)
- Also I had to make the SIZE=20000KB and 10000KB respectively as SQL would not let me create a DB with the original values in the script
- Paste the following into a SQL Management Studio Query Window and click Execute. (Highlighted in red on screenprint) See screenprint below script
use [master]
go
CREATE DATABASE [VCDB] ON PRIMARY
(NAME = N’vcdb‘, FILENAME = N’C:\VCDB.mdf’ , SIZE = 20000KB , FILEGROWTH = 10% )
LOG ON
(NAME = N’vcdb_log’, FILENAME = N’C:\VCDB.ldf’ , SIZE = 10000KB , FILEGROWTH = 10%)
COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS
go
use VCDB
go
sp_addlogin @loginame=[vpxuser], @passwd=N’UseaStrongPassword!‘, @defdb=’VCDB’, @deflanguage=’us_english’
go
ALTER LOGIN [vpxuser] WITH CHECK_POLICY = OFF
go
CREATE USER [vpxuser] for LOGIN [vpxuser]
go
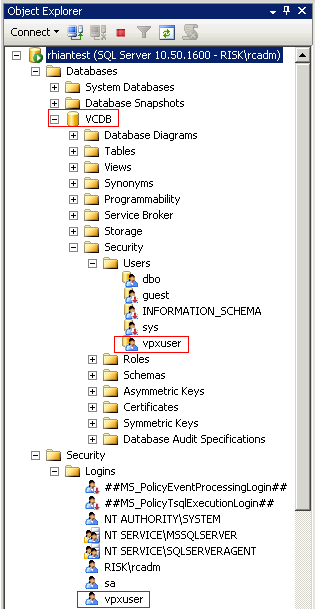
- You will see that this part of the script creates the VCDB Database and the user vpxuser under Security Logins and Databases > VCDB > Security > Users
- Next copy and paste the following script into a new SQL Query Windows
use VCDB
go
CREATE SCHEMA [VMW]
go
ALTER USER [vpxuser] WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA =[VMW]
go
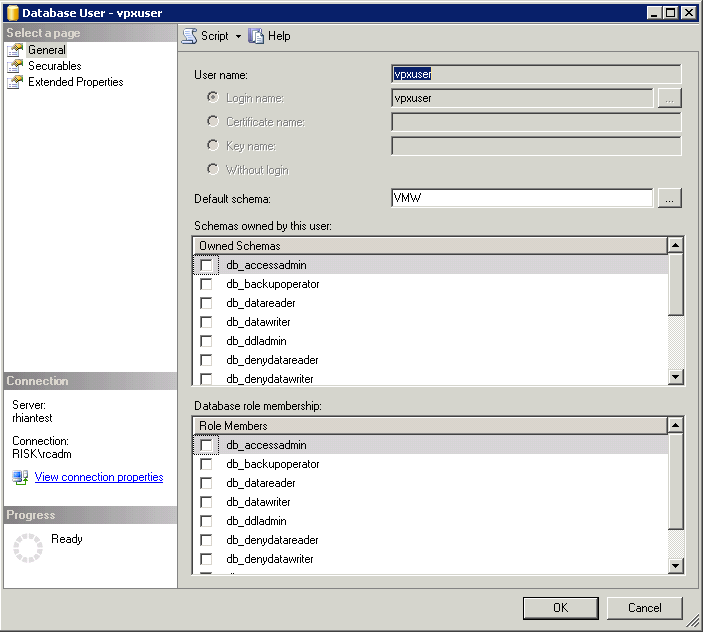
- Navigate to Databases > VCDB > Security > Users > vpxuser > Properties
- Check that VMW is the Default Schema for the vpxuser
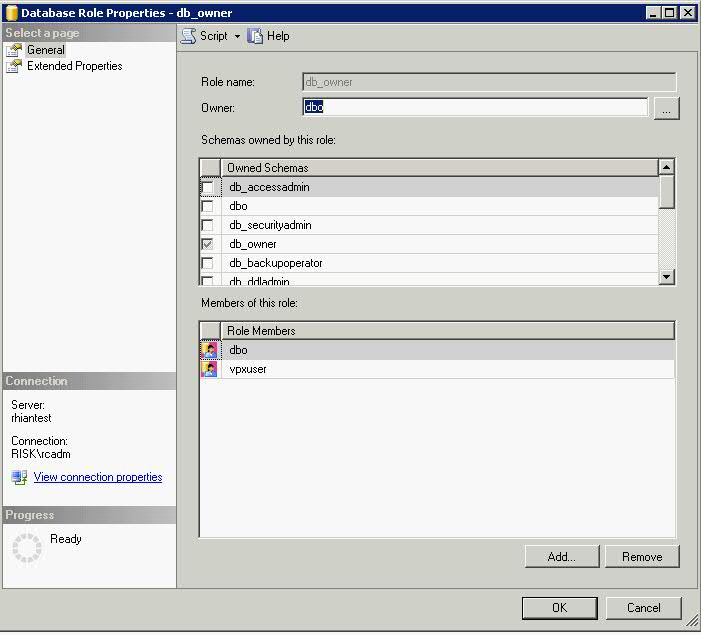
- Next the vpxuser should have DBO Privileges or VC_ADMIN_ROLE and VC_USER_ROLE database roles
- Copy the script below into a new SQL Query Window and click Execute
sp_addrolemember @rolename = ‘db_owner’, @membername = ‘vpxuser‘
go
- It gives the vpxuser the db_owner role
- The rest of the script follows on as below
if not exists (SELECT name FROM sysusers WHERE issqlrole=1 AND name = ‘VC_ADMIN_ROLE’)
CREATE ROLE VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT ALTER ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT REFERENCES ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT INSERT ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT CREATE TABLE to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT CREATE VIEW to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
GRANT CREATE Procedure to VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
if not exists (SELECT name FROM sysusers WHERE issqlrole=1 AND name = ‘VC_USER_ROLE’)
CREATE ROLE VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT SELECT ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT INSERT ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT DELETE ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT UPDATE ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON SCHEMA :: [VMW] to VC_USER_ROLE
go
sp_addrolemember VC_ADMIN_ROLE , [vpxuser]
go
sp_addrolemember VC_USER_ROLE , [vpxuser]
go
use MSDB
go
CREATE USER [vpxuser] for LOGIN [vpxuser]
go
sp_addrolemember @rolename = ‘db_owner’, @membername = ‘vpxuser‘
go
if not exists (SELECT name FROM sysusers WHERE issqlrole=1 AND name = ‘VC_ADMIN_ROLE’)
CREATE ROLE VC_ADMIN_ROLE;
go
grant select on msdb.dbo.syscategories to VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
grant select on msdb.dbo.sysjobsteps to VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT SELECT ON msdb.dbo.sysjobs to VC_ADMIN_ROLE
GO
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_job TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_delete_job TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobstep TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_update_job TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobserver TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_jobschedule TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
GRANT EXECUTE ON msdb.dbo.sp_add_category TO VC_ADMIN_ROLE
go
sp_addrolemember VC_ADMIN_ROLE , [vpxuser]
go
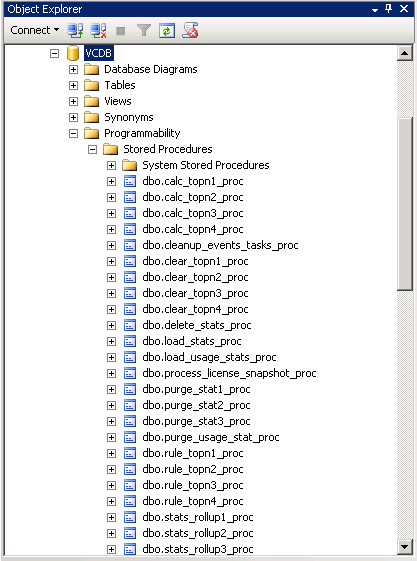
- Run the scripts in sequence on the VCDB database.The objects created by these scripts need to be owned by the “dbo” user.
- Right click on VCDB in SQL Management Studio and select New Query
- Open the scripts one at a time in the query analyzer window and press F5 to execute each script in the order shown here.
- You can navigate to the vCenter installer folder from the SQL Server and literally just drag and drop the following files into a SQL Query window
- Important: Do this in order
- VCDB_mssql.SQL
- load_stats_proc_mssql.sql
- purge_stat1_proc_mssql.sql
- purge_stat2_proc_mssql.sql
- purge_stat3_proc_mssql.sql
- purge_usage_stats_proc_mssql.sql
- stats_rollup1_proc_mssql.sql
- stats_rollup2_proc_mssql.sql
- stats_rollup3_proc_mssql.sql
- cleanup_events_mssql.sql
- delete_stats_proc_mssql.sql
- upsert_last_event_proc_mssql.sql
- load_usage_stats_proc_mssql.sql
- TopN_DB_mssql.sql
- calc_topn1_proc_mssql.sql
- calc_topn2_proc_mssql.sql
- calc_topn3_proc_mssql.sql
- calc_topn4_proc_mssql.sql
- clear_topn1_proc_mssql.sql
- clear_topn2_proc_mssql.sql
- clear_topn3_proc_mssql.sql
- clear_topn4_proc_mssql.sql
- rule_topn1_proc_mssql.sql
- rule_topn2_proc_mssql.sql
- rule_topn3_proc_mssql.sql
- rule_topn4_proc_mssql.sql
- process_license_snapshot_mssql.sql
- process_temptable0_proc_mssql.sql
- process_temptable1_proc_mssql.sql
- process_temptable2_proc_mssql.sql
You can also run the following scripts to enable database health monitoring.
- job_dbm_performance_data_mssql.sql
- process_performance_data_mssql.sql
- Grant the execute privilege for all the store procedures you created to the vCenter Server database user you created (vpxuser)
- grant execute on purge_stat1_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on purge_stat2_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on purge_stat3_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on purge_usage_stat_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on stats_rollup1_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on stats_rollup2_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on stats_rollup3_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on cleanup_events_tasks_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on delete_stats_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on upsert_last_event_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on load_usage_stats_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on load_stats_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on calc_topn1_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on calc_topn2_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on calc_topn3_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on calc_topn4_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on clear_topn1_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on clear_topn2_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on clear_topn3_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on clear_topn4_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on rule_topn1_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on rule_topn2_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on rule_topn3_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on rule_topn4_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on process_license_snapshot_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on process_temptable0_proc tovpxuser
- grant execute on process_temptable1_proc tovpxuser
- grant execute on process_temptable2_proc tovpxuser
- grant execute on process_performance_data_proc to vpxuser
- grant execute on process_performance_data_mssql.sql to vpxuser
- For all supported editions of Microsoft SQL Server (except Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express), ensure that the SQL Agent is running. Run these additional scripts to set up scheduled jobs on the database.
- Right click the VCDB DB and drag the below scripts into the query window and execute. These scripts ensure that the SQL Server Agent service is running.
- job_schedule1_mssql.sql
- job_schedule2_mssql.sql
- job_schedule3_mssql.sql
- job_cleanup_events_mssql.sql
- job_topn_past_day_mssql.sql
- job_topn_past_week_mssql.sql
- job_topn_past_month_mssql.sql
- job_topn_past_year_mssql.sql
- job_property_bulletin_mssql.sql
Create an ODBC Connection
- On your vCenter Server system, select Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Data Sources (ODBC).
- Click the System DSN tab and do one of the following.
To modify an existing SQL Server ODBC connection, select the connection from the System Data
Source list and click Configure.
To create a new SQL Server ODBC connection, click Add, select SQL Native Client, and click
Finish.
- Type an ODBC datastore name (DSN) in the Name text box. “VMware vCenter Server”
- (Optional) Type an ODBC DSN description in the Description text box.
- Select the server name from the Server drop-down menu. Type the SQL Server host name in the text box if it is not in the drop-down menu.
- Select one of the authentication methods.
- Integrate Windows authentication. Optionally, enter the Service Principal Name (SPN).
- SQL Server authentication. Type your SQL Server login name and password.
- Select the database created for the vCenter Server system from the Change the default database to menu.
- Click Finish.
For SQL Server 2005 and SQL Server 2008 editions, test the data source by selecting Test Data Source and clicking OK from the ODBC Microsoft SQL Server Setup menu. - Verify that the SQL Agent is running on your database server.
Run the vCenter Installer in the vCenter Server
- Run the vCenter Server installer and, when prompted, provide the database user login.
Youtube Video
Courtesy of Wee Kiong Tan
Error: Customization of the guest operating system ‘rhel5_64Guest’ is not supported in this configuration
The problem
An error appears when you try and deploy a VMware template following an upgrade of VMware and/or vCenter
“Customization of the guest operating system ‘rhel5_64Guest’ is not supported in this configuration. Microsoft Vista (TM) and Linux guests with Logical Volume Manager are supported only for recent ESX host and VMware Tools versions.”
The Resolution
- Turn the VM Template back into a Virtual Machine
- Power On
- Install VMware Tools
- Check no additional hardware has been changed. Sometimes changing the SCSI controller from LSI Parallel to LSI SAS can cause issues on Linux machines
- Power Off machine
- Convert the VM back to a template
VMware vMA
What is the VMware vSphere vMA?
The vSphere Management Assistant (vMA) is a SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11‐based virtual machine that includes prepackaged software such as the vSphere command‐line interface, and the vSphere SDK for Perl.
Why use vMA?
- vMA allows administrators to run scripts or agents that interact with ESXi hosts and vCenter Server systems without having to authenticate each time.
- Used to remotely manage ESXi hosts
- Central location to execute system management scripts
vMA Capabilities
- vMA provides a flexible and authenticated platform for running scripts and programs.
- As administrator, you can add vCenter Server systems and ESXi hosts as targets and run scripts and programs on these targets. Once you have authenticated while adding a target, you need not login again while running a vSphere CLI command or agent on any target.
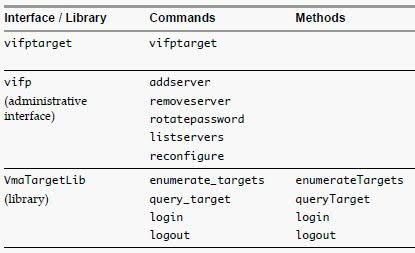
- As a developer, you can use the APIs provided with the VmaTargetLib library to programmatically connect to vMA targets by using Perl or Java.
- vMA enables reuse of service console scripts that are currently used for ESXi administration, though minor modifications to the scripts are usually necessary.
- vMA comes preconfigured with two user accounts, namely, vi‐admin and vi‐user.
- As vi‐admin, you can perform administrative operations such as addition and removal of targets. You can also run vSphere CLI commands and agents with administrative privileges on the added targets.
- As vi‐user, you can run the vSphere CLI commands and agents with read‐only privileges on the target.
- You can make vMA join an Active Directory domain and log in as an Active Directory user. When you run commands from such a user account, the appropriate privileges given to the user on the vCenter Server system or the ESXi host would be applicable.
- vMA can run agent code that make proprietary hardware or software components compatible with VMware ESX. These code currently run in the service console of existing ESX hosts. You can modify most of these agent code to run in vMA, by calling the vSphere API, if necessary. Developers must move any agent code that directly interfaces with hardware into a provider.
vMA Component Overview
When you install vMA, you are licensed to use the virtual machine that includes all vMA components.
- SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP1 – vMA runs SUSE Linux Enterprise Server on the virtual machine. You can move files between the ESXi host and the vMA console by using the vifs vSphere CLI command.
- VMware Tools – Interface to the hypervisor.
- vSphere CLI – Commands for managing vSphere from the command line. See the vSphere Command‐Line Interface Installation and Reference Guide.
- vSphere SDK for Perl – Client‐side Perl framework that provides a scripting interface to the vSphere API. The SDK includes utility applications and samples for many common tasks.
- Java JRE version 1.6 – Runtime engine for Java‐based applications built with vSphere Web Services SDK.
- vi‐fastpass ‐ Authentication component.
Requirements
- AMD Opteron, rev E or later
- Intel processors with EM64T support with VT enabled.
- vSphere 5.0
- vSphere 4.1 or later
- vSphere 4.0 Update 2 or later
- vCenter Application 5.0
vSphere Authentication Mechanism
vMA’s authentication interface allows users and applications to authenticate with the target servers using vi‐fastpass or Active Directory. While adding a server as a target, the Administrator can determine if the target needs to use vi‐fastpass or Active Directory authentication. For vi‐fastpass authentication, the credentials that a user has on the vCenter Server system or ESXi host are stored in a local credential store. For Active Directory authentication, the user is authenticated with an Active Directory server.
When you add an ESXi host as a fastpass target server, vi‐fastpass creates two users with obfuscated passwords on the target server and stores the password information on vMA:
- vi‐admin with administrator privileges
- vi‐user with read‐only privileges
The creation of vi‐admin and vi‐user does not apply for Active Directory authentication targets. When you add a system as an Active Directory target, vMA does not store any information about the credentials. To use the Active Directory authentication, the administrator must configure vMA for Active Directory.
After adding a target server, you must initialize vi‐fastpass so that you do not have to authenticate each time you run vSphere CLI commands. If you run a vSphere CLI command without initializing vi‐fastpass, you will be asked for username and password. You can initialize vi‐fastpass by using one of the following methods:
- Run vifptarget -s esx1.testdomain.local
- Call the Login method in a Perl or Java program
Installing vMA
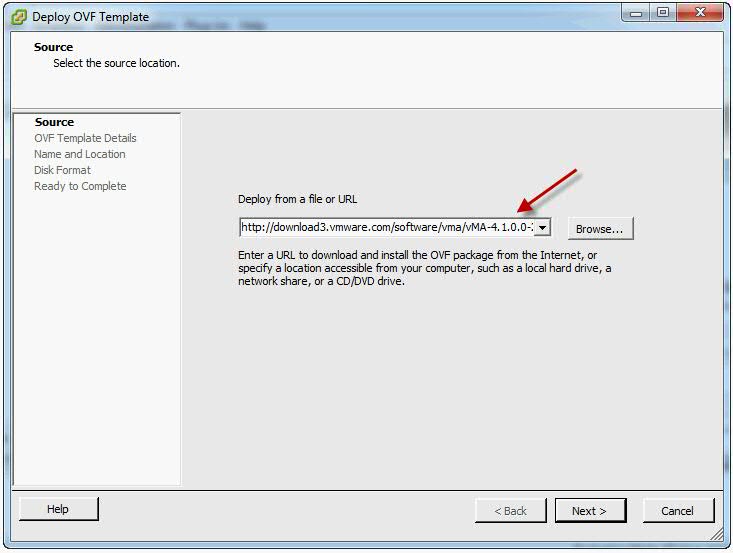
Download the vMA from the following location
https://my.vmware.com/web/vmware/details?productId=229&downloadGroup=VMA50
- Use a vSphere Client to connect to a system that is running the supported version of ESXi or vCenter Server.
- If connected to a vCenter Server system, select the host to which you want to deploy vMA in the inventory pane.
- Select File > Deploy OVF Template. The Deploy OVF Template wizard appears.
- Select Deploy from a file or URL if you have already downloaded and unzipped the vMA virtual appliance package.
- Click Browse, select the OVF, and click Next.
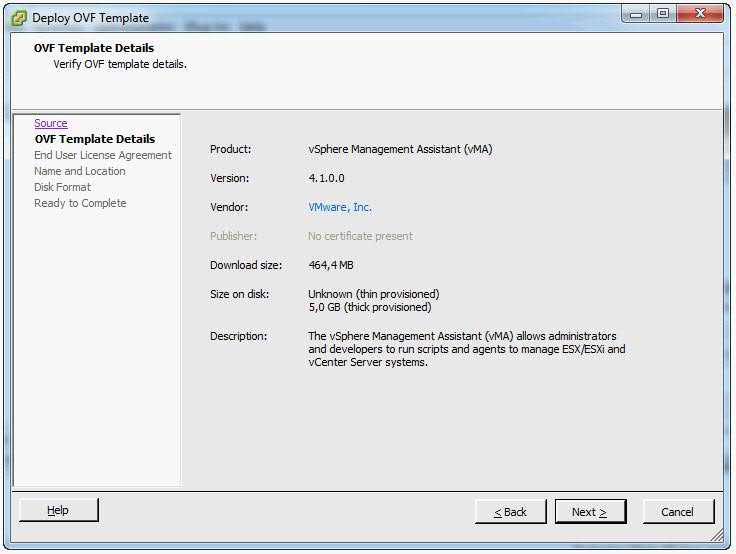
- Click Next when the OVF template details are displayed.
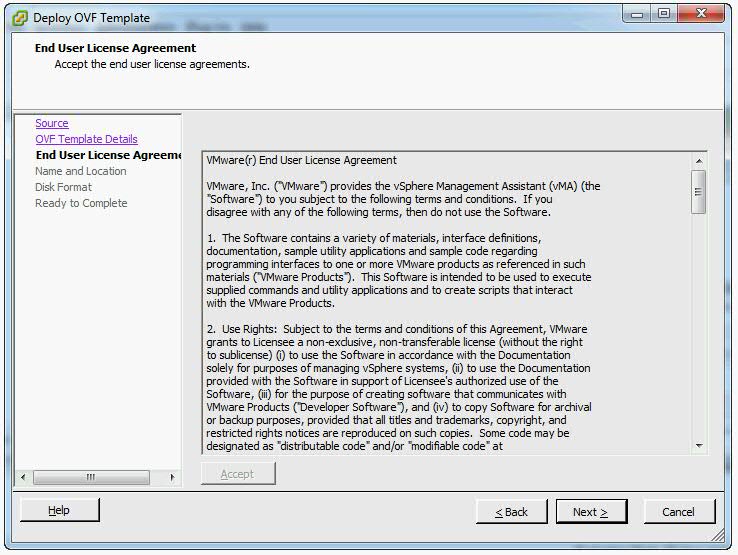
- Accept the license agreement and click Next.
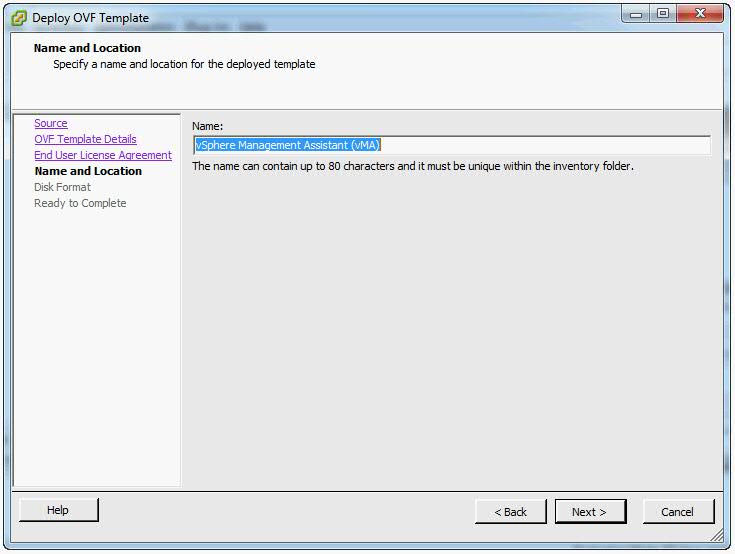
- Specify a name for the virtual machine. You can also accept the default virtual machine name. Select an inventory location for the virtual machine when prompted. If you are connected to a vCenter Server system, you can select a folder.
- If connected to a vCenter Server system, select the resource pool for the virtual machine. By default, the top‐level root resource pool is selected.
- If prompted, select the datastore to store the virtual machine on and click Next.
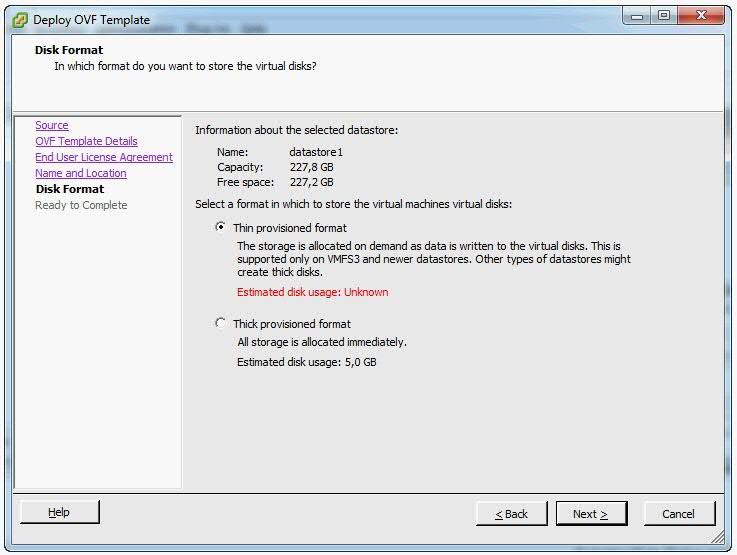
- Select the required disk format option and click Next.
- Finish
- IMPORTANT. Enure that vMA is connected to the management network on which the vCenter Server system and the ESXi hosts that are intended vMA targets are located.
- Review the information and click Finish.
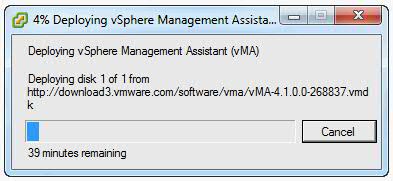
- The wizard deploys the vMA virtual machine to the host that you selected. The deploy process can take several minutes.
- In the vSphere Client, right‐click the virtual machine, and click Power On.
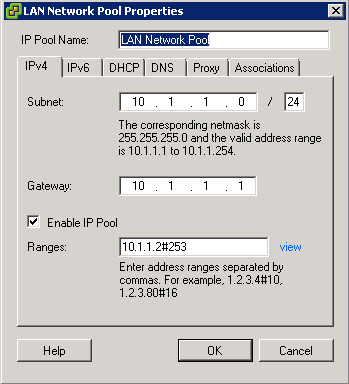
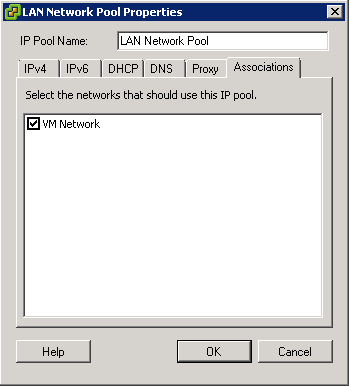
- You may encounter a network IP Pool error message. If you do follow the link below and make sure you set up your IP pools like the example below
- http://kb.vmware.com.Id=2007012
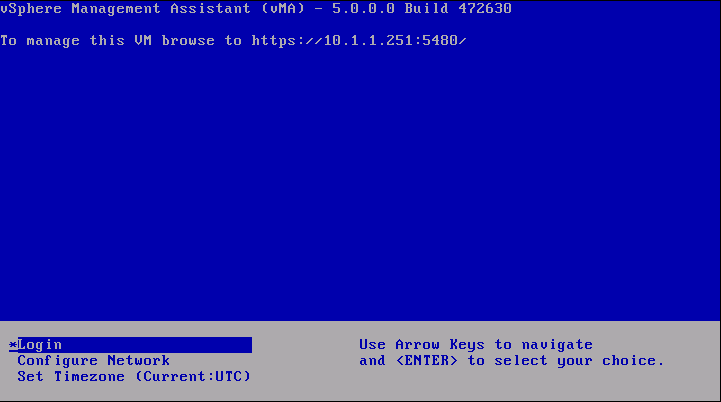
- Select the Console tab and answer the network configuration prompts
- When prompted, specify a password for the vi‐admin user. You will first have to enter the old password which is vmware. The system will then only accept a strong password for the change
- vMA is now configured and the vMA console appears. The console displays the URL from which you can access the Web UI.
Upgrading or Updating
Upgrading
IMPORTANT: You cannot upgrade a previous version of vMA to vMA 5.0. You must install a fresh vMA 5.0 instance.
Updating
You can download software updates including security fixes from VMware and components included in vMA, such as the SUSE Linux Enterprise Server updates and JRE.
- Access the Web UI on Port 5480
- Log in as vi‐admin.
- Click the Update tab and then the Status tab.
- Open the Settings tab and then from the Update Repository section, select a repository.
- Click Check Updates.
- Click Install Updates.
- You can also set an automatic download schedule for updates
Configure vMA for Active Directory Authentication
Configure vMA for Active Directory authentication so that ESXi hosts and vCenter Server systems added to Active Directory can be added to vMA without having to store the passwords in vMA’s credential store. This is a more secure way of adding targets to vMA.
- Ensure that the DNS server configured for vMA is the same as the DNS server of the domain. You can change the DNS server by using the vMA Console or the Web UI
- Ensure that the domain is accessible from vMA.
- Ensure that you can ping the ESXi and vCenter server systems that you want to add to vMA and that pinging resolves the IP address to , where domainname is the domain to which vMA is to be added.
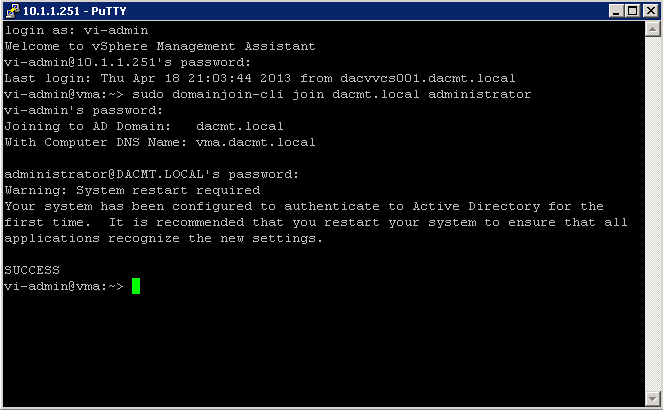
- From the vMA console, run the following command
- sudo domainjoin-cli join dacmt.local administrator
- When prompted, provide the Active Directory administratorʹs password.
- On successful authentication, the command adds vMA as a member of the domain. The command also adds entries in the /etc/hosts file with vmaHostname.domainname.
- Restart vMA
- Now, you can add an Active Directory target to vMA
- Note: You can also access the Web UI
Add Target Servers to vMA
After you configure vMA, you can add target servers that run the supported vCenter Server or ESXi version. For vCenter Server, and ESXi system targets, you must have the name and password of a user who can connect to that system
To add a vCenter Server system as a vMA target for Active Directory Authentication
- Log in to vMA as vi‐admin.
- Add a server as a vMA target by running the following command
vifp addserver vc1.mycomp.com –authpolicy adauth –username ADDOMAIN\user1
Here, –authpolicy adauth indicates that the target needs to use the Active Directory authentication. If you run this command without the –username option, vMA prompts for the name of the user that can connect to the vCenter Server system. You can specify this user name as shown in the following example:
If –authpolicy is not specified in the command, then fpauth is taken as the default authentication policy.
- Verify that the target server has been added by typing
vifp listservers –long
- Set the target as the default for the current session:
vifptarget –set | -s
- Verify that you can run a vSphere CLI command without authentication by running a command on one of the ESXi hosts, for example:
esxcli –server –vihost network nic list
- The command runs without prompting for authentication information.
IMPORTANT: If the name of a target server changes, you must remove the target server by using vifp removeserver with the old name, then add the server using vifp addserver with the new name
To add a vCenter Server system as a vMA target for fastpass Authentication
- Log in to vMA as vi‐admin
- Add a server as a vMA target by running the following command:
vifp addserver vc2.mycomp.com –authpolicy fpauth
Here, –authpolicy fpauth indicates that the target needs to use the fastpass authentication.
- Specify the username when prompted: MYDOMAIN\user1Specify the password for that user when prompted.
- Review and accept the security risk information.
- Verify that the target server has been added.
vifp listservers –long
- Set the target as the default for the current session.
vifptarget –set | -s
- Verify that you can run a vSphere CLI command without authentication by running a command on one of the ESXi hosts, for example:
esxcli –server –vihost network nic list
IMPORTANT: If the name of a target server changes, you must remove the target server by using vifp removeserver with the old name, then add the server using vifp addserver with the new name
To add an ESXi host as a vMA target
- Log in to vMA as vi‐admin.
- Run addserver to add a server as a vMA target.
vifp addserver Serverxyz
- You are prompted for the target server’s root user password.Specify the root password for the ESXi host that you want to add.
- vMA does not retain the root password. Instead, vMA adds vi‐admin and vi‐user to the ESXi host, and stores the obfuscated passwords that it generates for those users in the VMware credential store.
In a vSphere client connected to the target server, the Recent Tasks panel displays information about the users that vMA adds. The target server’s Users and Groups panel displays the users if you select it.
- Verify that the target server has been added:
vifp listservers
- Set the target as the default for the current session.
vifptarget –set | -s Serverxyz
- Verify that you can run a vSphere CLI command without authentication by running a command, for example:
esxcli network nic list
Running vSphere CLI for the Targets
If you have added multiple target servers, by default, vMA executes commands on the first server that you added. You should specify the server explicitly when running commands.
To run vSphere CLI for the targets
- Add servers as vMA targets.
vifp addserver vCenterserver
vifp addserver serverxyz
- Verify that the target server has been added:
vifp listservers
- Run vifptarget.
vifptarget -s serverxyz
- The command initializes the specified target server. Now, this server will be taken as the default target forthe vSphere CLI or vSphere SDK for Perl scripts.
- Run vSphere CLI or vSphere SDK for Perl scripts, by specifying the target server. For example:
esxcli –server serverxyz network nic list
Target Management Example Sequence
The following sequence of commands adds an ESXi host, lists servers, runs vifptarget to enable vi‐fastpass, runs a vSphere CLI command, and removes the ESXi host.
- vifp addserver serverxyz.company.com
- Type password: <password, not echoed to screen>
- vifp listservers
- serverxyz.company.com ESX
- vifptarget –set serverxyz.company.com
- esxcli storage core path list
cdrom vmhba0:1:0 (0MB has 1 paths and policy of fixed
Local 0:7:1 vmhba0:1:0 On active preferred
- vifp removeserver server1.company.com
- <password, not echoed to screen>
Enable the vi-user for the first time
- Log into vMA as vi-admin
- Set a password for the vi-user account
- sudo passwd vi-user
Note: The vi-admin is not “root” and receives all its privileges from the configuration of sudo. Sudo is a delegation system that allows “root” to allow other users privileges above and beyond merely being a “user.”
Adding another user alongside vi-admin and vi-user
‘sudo useradd username -p password’
Use vmkfstools to manage VMFS Datastores
Useful Command Ref
http://vmetc.com/wp-content/uploads/2007/11/man-vmkfstools.txt
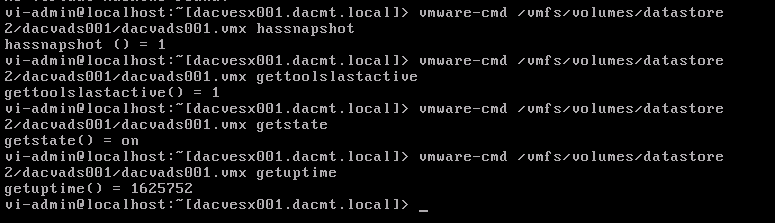
Use vmware-cmd to manage VMs
Useful Command Ref
http://www.vmware.com/support/
Example showing 4 different commands
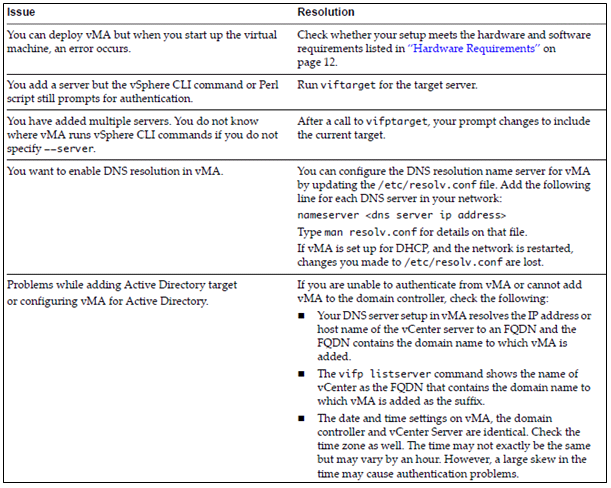
Troubleshoot common vMA errors and conditions
VMware TV
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cIh4QT0-hdY
Changing the IP Address or Hostname of vMA
https://communities.vmware.com/people/ravinder1982/blog/2012/06/15/changing-ip-address-or-hostname-of-vma