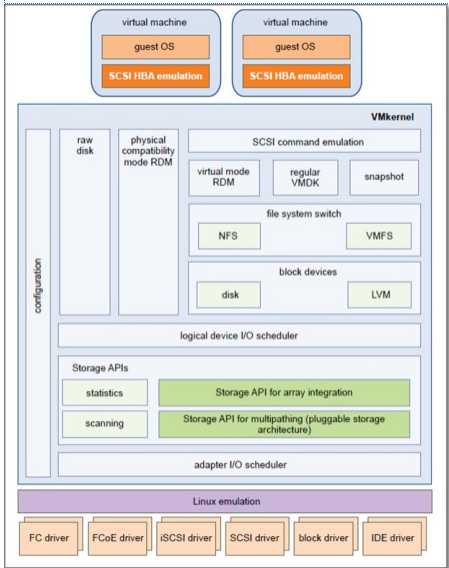
Storage Modules
The VMkernel is a high-performance operating system that runs directly on the ESXi host. The VMkernel manages most of the physical resources on the hardware, including memory, physical processors, storage, and networking controllers
To manage storage, VMkernel has a storage subsystem that supports several Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) including parallel SCSI, SAS, Fibre Channel, FCoE, and iSCSI. These HBAs connect a wide variety of active-active, active-passive, and ALUA storage arrays that are certified for use with the VMkernel.
The primary file system that the VMkernel uses is the VMware Virtual Machine File System (VMFS). VMFS is a cluster file system designed and optimized to support large files such as virtual disks and swap files. The VMkernel also supports the storage of virtual disks on NFS file systems.
The storage I/O path provides virtual machines with access to storage devices through device emulation. This device emulation allows a virtual machine to access files on a VMFS or NFS file system as if they were SCSI devices. The VMkernel provides storage virtualization functions such as the scheduling of I/O requests from multiple virtual machines and multipathing.
In addition, VMkernel offers several Storage APIs that enable storage partners to integrate and optimize their products for vSphere.
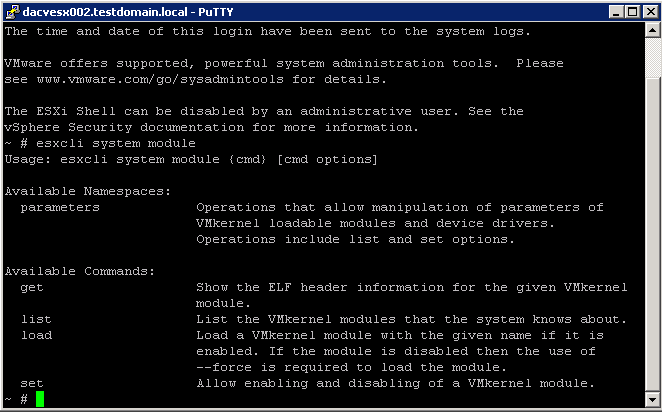
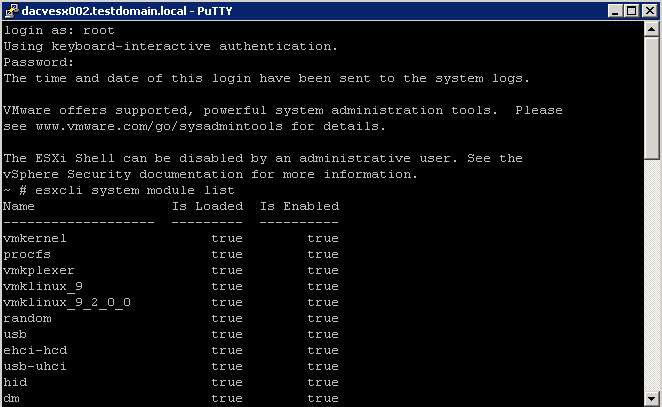
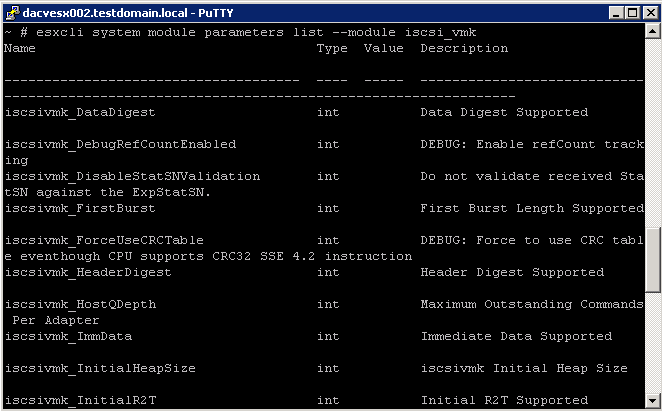
The following graphic illustrates the basics of the VMkernel core, with special attention to the storage stack. Storage‐related modules reside between the logical device I/O scheduler and the adapter I/O scheduler layerThe esxcli system module namespace allows you to view load and enable VMKernel modules.
To get an overview use this command:
- esxcli system module
- esxcli system module list
- esxcli system module parameters list –module ModuleName