Changing Path Policies
You can change path policies with
- esxcli
- vicfg-mpath
What Path Policies are there?
- Most Recently Used (MRU)
Selects the first working path, discovered at system boot time. If this path becomes unavailable, the ESXi/ESX host switches to an alternative path and continues to use the new path while it is available. This is the default policy for Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs) presented from an Active/Passive array. ESXi/ESX does not return to the previous path if, or when, it returns; it remains on the working path until it, for any reason, fails.
Note: The preferred flag, while sometimes visible, is not applicable to the MRU pathing policy and can be disregarded
- Fixed (Fixed)
Uses the designated preferred path flag, if it has been configured. Otherwise, it uses the first working path discovered at system boot time. If the ESXi/ESX host cannot use the preferred path or it becomes unavailable, the ESXi/ESX host selects an alternative available path. The host automatically returns to the previously-defined preferred path as soon as it becomes available again. This is the default policy for LUNs presented from an Active/Active storage array.
- Round Robin (RR)
Uses an automatic path selection rotating through all available paths, enabling the distribution of load across the configured paths. For Active/Passive storage arrays, only the paths to the active controller will be used in the Round Robin policy. For Active/Active storage arrays, all paths will be used in the Round Robin policy.
Note: This policy is not currently supported for Logical Units that are part of a Microsoft Cluster Service (MSCS) virtual machine.
- Fixed path with Array Preference
The VMW_PSP_FIXED_AP policy was introduced in ESXi/ESX 4.1. It works for both Active/Active and Active/Passive storage arrays that support Asymmetric Logical Unit Access (ALUA). This policy queries the storage array for the preferred path based on the array’s preference. If no preferred path is specified by the user, the storage array selects the preferred path based on specific criteria.
Note: The VMW_PSP_FIXED_AP policy has been removed from ESXi 5.0. For ALUA arrays in ESXi 5.0, the MRU Path Selection Policy (PSP) is normally selected but some storage arrays need to use Fixed. To check which PSP is recommended for your storage array, see the Storage/SAN section in the VMware Compatibility Guide or contact your storage vendor.
Notes:
- These pathing policies apply to VMware’s Native Multipathing (NMP) Path Selection Plug-ins (PSP). Third-party PSPs have their own restrictions.
- Round Robin is not supported on all storage arrays. Please check with your array documentation or storage vendor to verify that Round Robin is supported and/or recommended for your array and configuration. Switching to a unsupported or undesirable pathing policy can result in connectivity issues to the LUNs (in a worst-case scenario, this can cause an outage).
Changing Path Policies with ESXCLI
- Ensure your device is claimed by the NMP plugin. Only NMP devices allow you to change the path policy.
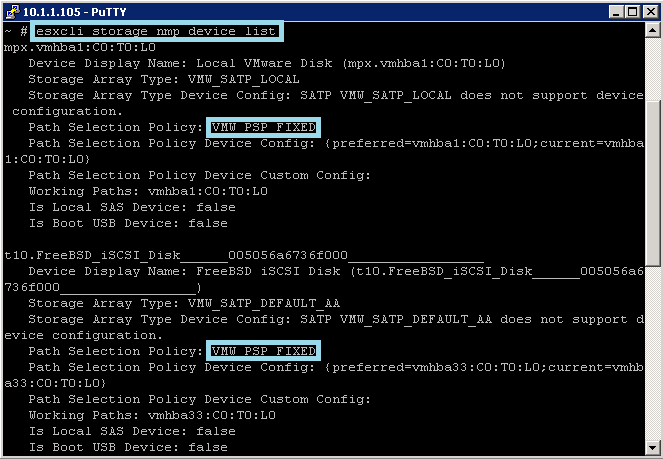
- esxcli storage nmp device list
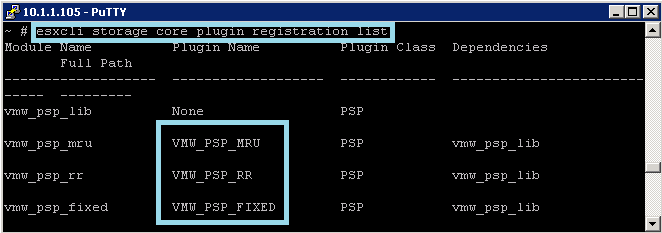
- Retrieve the list of path selection policies on the system to see which values are valid for the –psp option when you set the path policy.
- esxcli storage core plugin registration list
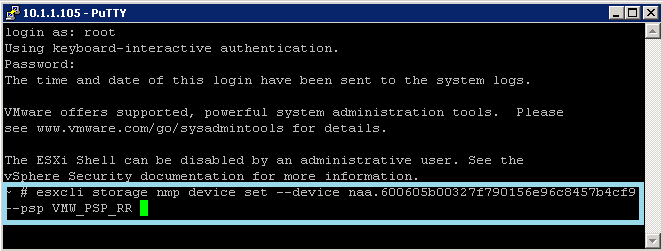
- Set the path policy using esxcli.
- esxcli storage nmp device set - -device naa.xxx - -psp VMW_PSP_RR
(Optional) If you specified the VMW_PSP_FIXED policy, you must make sure the preferred path is set correctly.
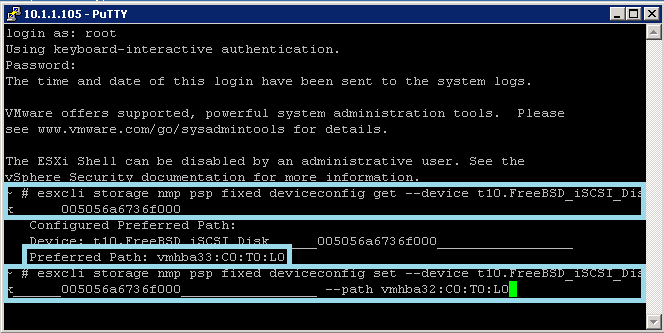
- Check which path is the preferred path for a device.
- esxcli storage nmp psp fixed deviceconfig get - -device naa.xxx b If necessary, change the preferred path.
- Set the preferred path to vmhba32:C0:T0:L0
- esxcli storage nmp psp fixed deviceconfig set - -device naa.xxx –path vmhba32:C0:T0:L0
- Run the command with –default to clear the preferred path selection.