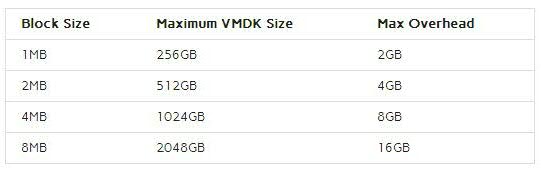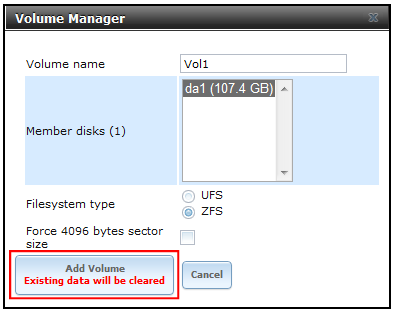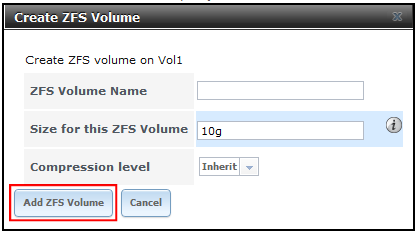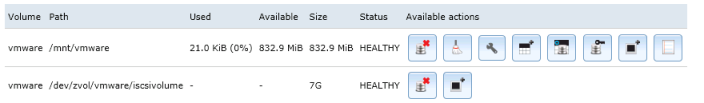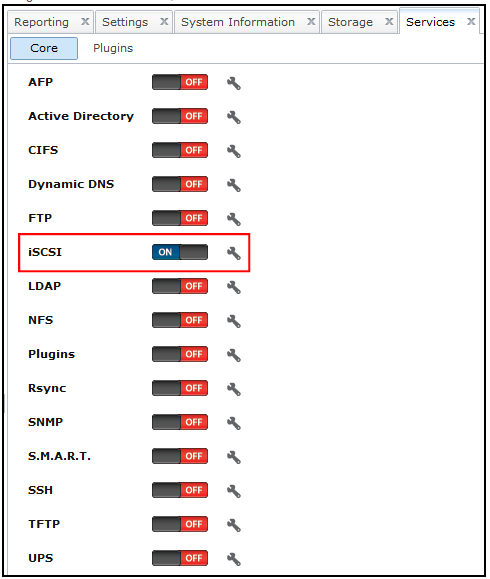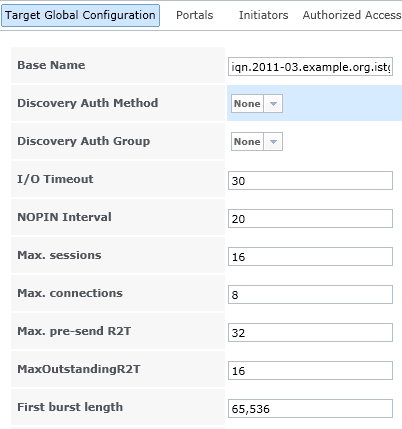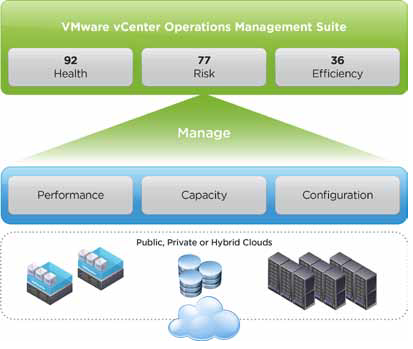
Ensure service levels, optimum resource usage and configuration compliance in dynamic virtual and cloud environments with VMware vCenter Operations Management Suite. Designed for VMware vSphere and built for cloud, vCenter Operations Management Suite sets the industry standard in operational efficiency and allows you to proactively ensure virtual/cloud infrastructure performance of your Microsoft Exchange, Oracle and SAP, provide continuous compliance with operational and regulatory requirements, and optimize resource utilization and cost.
What can it do?
- Intelligently Automate Operations Management to Maximize Efficiency and Agility
Automate performance, capacity, and configuration management with patented analytics and an integrated approach to management. Eliminate the finger pointing, improve team collaboration and reduce manual problem solving efforts by as much as 40% with automated root cause analysis.
- Proactively Manage Performance across the Entire Infrastructure
Get proactive warning of performance issues and capacity shortfalls before problems affect end users. Real-time performance dashboards let you meet SLAs by pinpointing building performance issues before end users notice. Optimize your infrastructure for efficiency and minimize risk of performance across your entire infrastructure, both virtual and physical.
- Gain Comprehensive Visibility and Manage Compliance with Cloud Automation
Gain better visibility into planned and unplanned configuration changes and remediate unwanted changes to ensure operational and regulatory compliance. Manage compliance automatically with out-of-the-box configuration templates. Ensure compliance with policy control and integrated smart alerts across both virtual and physical aspects of your datacenter infrastructure.
Key New Features
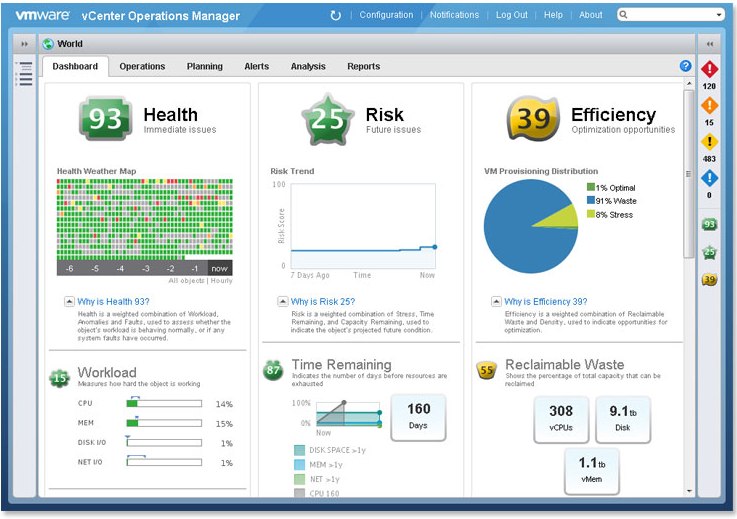
- Operations Management Dashboard
Provides comprehensive views into health, risk and efficiency scores of your cloud infrastructure. Quickly drill down to see what’s causing current workload conditions, pinpoint potential problems in the future and identify areas with inefficient use of resources.
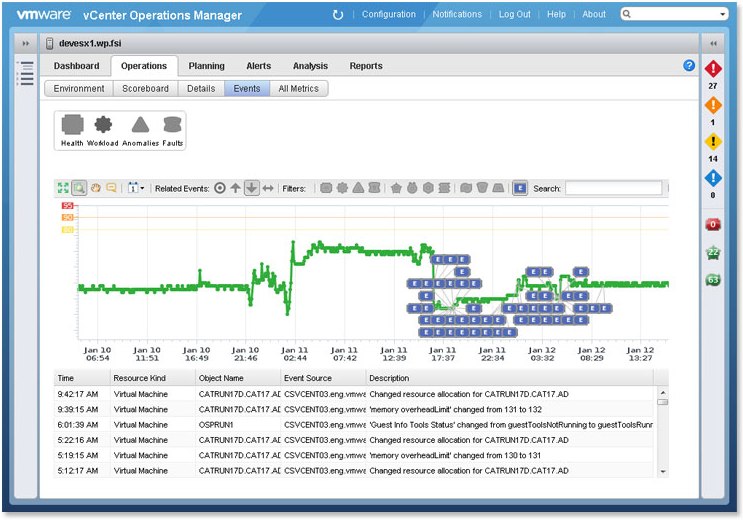
- Correlation of Performance and Change Events
Enables administrators to quickly understand and remediate performance issues arising from configuration changes
- Compliance Checking of vSphere Hosts
Allows administrators to maintain a compliant infrastructure and automated the hardening of vSphere hosts with pre-built security and compliance guidelines.
Provides pro-active notifications of building health, performance and capacity issues in the environment. Automated root cause analysis identifies the offending metric across all layers of the infrastructure
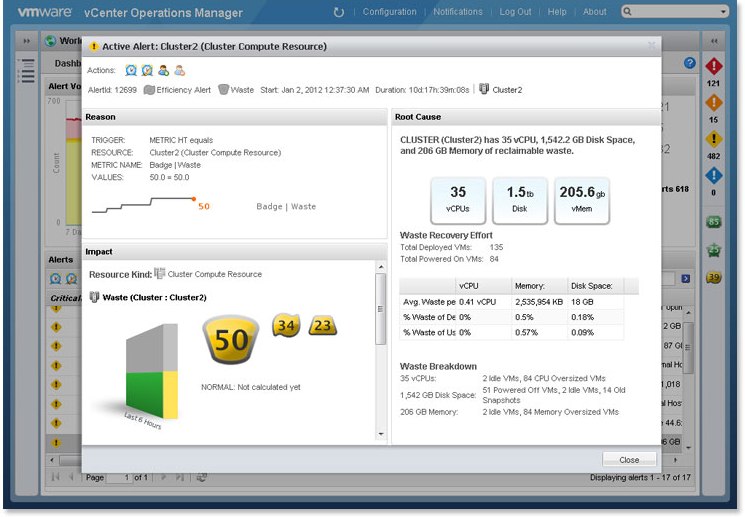
- Capacity Planning, Reporting and Optimization
These views help administrators optimize VM density; identify areas of reclaimable waste and chronic capacity shortfalls. Configurable alerts notify of changing capacity conditions in production and non-production areas.
- Integrated Cost Metering and Reporting
These capabilities provide visibility into the financial value of consumed resources and enable administrators to optimize provisioned capacity for lowest cost without sacrificing performance.
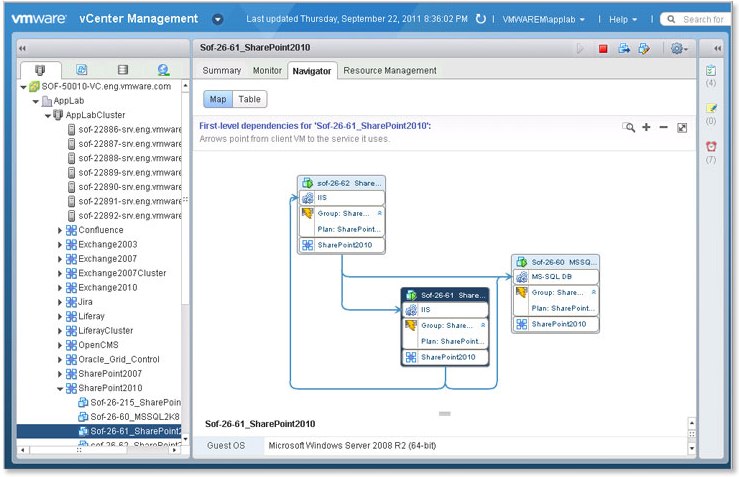
- Discovery and Visualization of Application and Infrastructure Dependencies
This brings application-level awareness to infrastructure and operations teams to ensure service levels and disaster recovery protection for all critical application services. Application components and version numbers are named automatically and updated continuously
What’s Included in the vCenter Operations Management Suite?
- VMware vCenter Operations Manager
VMware vCenter Operations Manager uses patented analytics and an integrated approach to operations management to provide the intelligence and visibility needed to proactively ensure service levels, optimum resource usage and configuration compliance in dynamic virtual and cloud environments.
- VMware vCenter Configuration Manager
VMware vCenter Configuration Manager™ automates configuration management across virtual and physical servers and desktops, increasing efficiency by eliminating manual, error-prone and time-consuming work. This enables enterprises to maintain continuous compliance by detecting
changes and comparing them to configuration and security policies.
- VMware vCenter Infrastructure Navigator
VMware vCenter Infrastructure Navigator automatically discovers and visualizes application and infrastructure dependencies. It provides visibility into the application services running over the virtual-machine infrastructure and their interrelationships for day-to-day operational management.
- VMware vCenter Chargeback Manager
VMware vCenter Chargeback Manager™ enables accurate cost measurement, analysis and reporting of virtual machines, providing visibility into the actual cost of the virtual infrastructure required to support business services.
Compare Editions
http://www.vmware.com/products/datacenter-virtualization/vcenter-operations-management/compare-editions.html