What is Netflow?
It’s a Cisco protocol that was developed for analysing network traffic. It has become an industry standard spec for collecting types of network data for monitoring and reporting. Data sources being switches and routers etc
- A network Analysis Tool for monitoring the network and for gaining visibility into VM Traffic
- A tool that can be used for profiling, intrusion detection, networking forensics and compliance
- Supported on Distributed Virtual Switches in vSphere 5
- Sarbanes Oxley compliance
- Not really for packet sniffing,more for profiling the top 10 network flows etc
How is it implemented?
It is implemented in vSphere 5 dvSwitches
What types of flow does Netflow capture?
- Internal Flow. Represents intrahost virtual machine traffic. Traffic between VM’s on the same host
- External Flow. Represents interhost virtual machine traffic and physical machine to virtual machine traffic. Traffic between VM’s on different hosts or VM’s on different switches
What is a flow?
A flow is a sequence of packets that share the same 7 properties
- Source IP Address
- Destination IP Address
- Source Port
- Destination Port
- Input Interface ID
- Output interface ID
- Protocol
Flows
A flow is unidirectional. Flows are processed and stored as flow records by supported network devices such as dvSwitches. The flow records are then sent to a NetFlow Collector for additional analysis.
Although efficient, NetFlow can put an additional strain on your network or the dvSwitch as it requires extra processing and additional storage on the host for the flow records to be processed and exported.
Third Party NetFlow Collectors – What do they do?
Third Party vendors have NetFlow Collector Products which can include the following features
- Accepts and stores network flow records
- Includes a storage system for long term storage on flow based data
- Mines, aggregates and reports on the collected data
- Customised user interface (Web based usually)
Reporting
The Netflow Collector reports on various kinds of networking information including
- Top network or bandwidth flows
- The IP Addresses which are behaving irregularly
- The number of bytes a VM has sent and received in the past 24 hours
- Unexpected application traffic
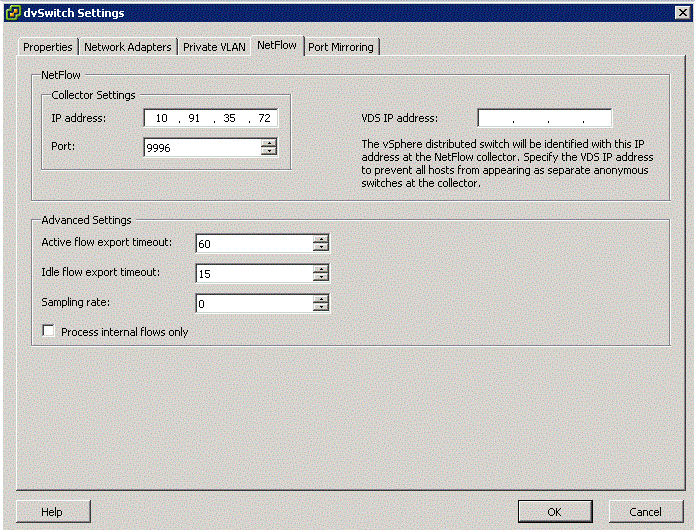
Configuring Netflow
- Go to Networking Inventory View
- Select dvSwitch and Edit Settings
- Click Netflow tab to see the box above
Description of options
- Collector IP Address and Port
The IP Address and Port number used to communicate with the Netflow collector system. These fields must be set for Netflow Monitoring to be enabled for the dvSwitch or for any port or port group on the dvSwitch
- VDS IP Address
An optional IP Address which is used to identify the source of the network flow to the NetFlow collector. The IP Address is not associated with a network port and it does not need to be pingable. This IP Address is used to fill the Source IP of the NetFlow packets. This IP Address allows the Netflow collector to interact with the dvSwitch as a single switch, rather than seeing a separate unrelated switch for each associated host. If this is not configured, the hosts management address is used instead.
- Active flow export timeout
The number of seconds after which active flows (flows where packets are sent) are forced to be exported to the NetFlow collector. The default is 300 and can range from 0-3600
- Idle flow export timeout
The The number of seconds after which idle flows (flows where no packets have been seen for x number of seconds) are forced to be exported to the collector.The default is 15 and can range from 0-300
- Sampling Rate
The value that is used to determine what portion of data that Netflow collects. If the sampling rate is 2, it collects every other packet. If the rate is 5, the data is collected form every 5th packet. 0 counts every packet
- Process internal flows only
Indicates whether to limit analysis to traffic that has both the source and destination virtual machine on the same host. By default the checkbox is not selected which means internal and external flows are processed. You might select this checkbox if you already have NetFlow deployed in your datacenter and you want to only see the floes that cannot be seen by your existing NetFlow collector.
After configuring Netflow on the dvSwitch, you can then enable NetFlow monitoring on a distributed Port Group or an uplink.


Leave a Reply