What is the Platform Services Controller?
Platform Services Controller before installing or deploying vCenter Server
Installation Scenarios (Embedded or External)
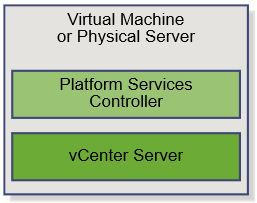
- When you install vCenter Server with an embedded Platform Services Controller, or deploy the vCenter Server Appliance with an embedded Platform Services Controller, vCenter Server, the vCenter Server components, and the services included in the Platform Services Controller are deployed on the same system.
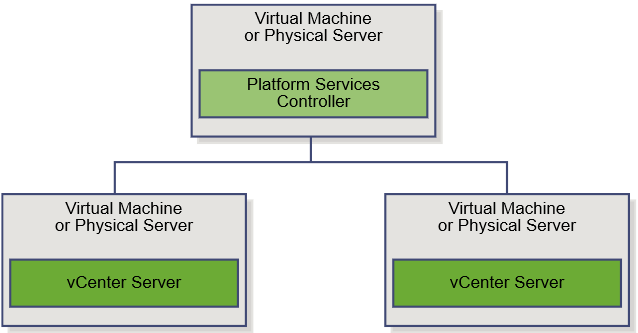
- When you install vCenter Server with an external Platform Services Controller, or deploy the vCenter Server Appliance with an external Platform Services Controller, vCenter Server and the vCenter Server components are deployed on one system, and the services included in the Platform Services Controller are deployed on another system.
Components included in the vCenter Server and vCenter Server Appliance installations
The VMware Platform Services Controller group of infrastructure services contains:
- vCenter Single Sign-On
- License service
- Lookup Service
- VMware Certificate Authority.
The vCenter Server group of services contains:
- vCenter Server
- vSphere Web Client
- Inventory Service
- vSphere Auto Deploy
- vSphere ESXi Dump Collector
- VMware vSphere Syslog Collector on Windows
- VMware Sphere Syslog Service for the vCenter Server Appliance
Scenario 1: vCenter with an embedded PSC
Advantages of vCenter with an embedded PSC
- The connection between vCenter Server and the Platform Services Controller is not over the network and vCenter Server is not prone to outages because of connectivity and name resolution issues between vCenter Server and the Platform Services Controller.
- You will need fewer Windows licenses.
- You will have to manage fewer virtual machines or physical servers.
- You do not need a load balancer to distribute the load across Platform Services Controller.
Disadvantages of vCenter with an embedded PSC
- There is a Platform Services Controller for each product which might be more than required. This consumes more resources.
- The model is suitable for small-scale environments
Scenario 2: vCenter Server with an External Platform Services Controller
vCenter Server and the Platform Services Controller are deployed on separate virtual machine or physical server. The Platform Services Controller can be shared across several vCenter Server instances. You can install a Platform Services Controller and then install several vCenter Server instances and register them with the Platform Services Controller. You can then install another Platform Services Controller, configure it to replicate data with the first Platform Services Controller, and then install vCenter Server instances and register them with the second Platform Services Controller.
Advantages of vCenter Server with an External Platform Services Controller
- Less resources consumed by the combined services in the Platform Services Controllers enables a reduced footprint and reduced maintenance
- Your environment can consist of more vCenter Server instances
Disadvantages of vCenter Server with an External Platform Services Controller
- The connection between vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller is over the network and is prone to connectivity and name resolution issues.
- If you install vCenter Server on Windows virtual machines or physical servers, you need more Microsoft Windows licenses.
- You must manage more virtual machines or physical servers
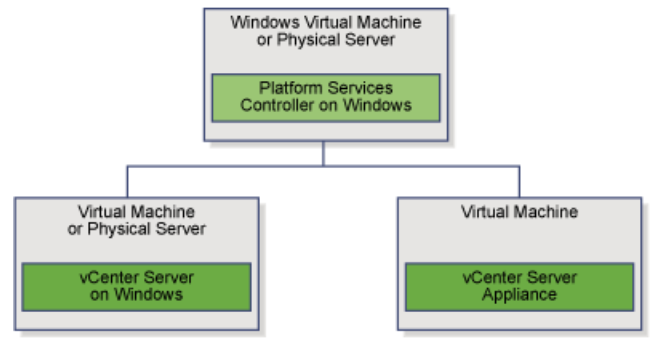
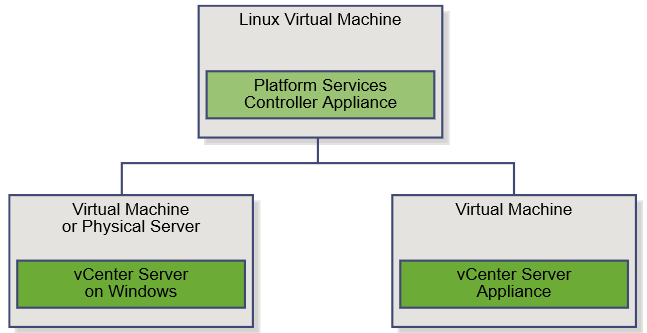
Scenario 3: Mixed Operating Systems
A vCenter Server instance installed on Windows can be registered with either a Platform Services Controller installed on Windows or a Platform Services Controller appliance.
- Example of a Mixed Operating Systems Environment with an External Platform Services Controller on Windows
- Example of a Mixed Operating Systems Environment with an External Platform Services Controller Appliance
- Both vCenter Server and the vCenter Server Appliance can be registered with the same Platform Services Controller within a domain
- Having many Platform Services Controllers that replicate their infrastructure data, allows you to ensure high availability of your system.
- If an external Platform Services Controller with which your vCenter Server instance or vCenter Server Appliance was initially registered, stops responding, you can repoint your vCenter Server or vCenter Server Appliance to another external Platform Services Controller in the domain
Enhanced Linked Mode Overview (http://kb.vmware.com/kb/210854)
- Enhanced Linked Mode connects multiple vCenter Server systems together by using one or more Platform Services Controllers.
- Enhanced Linked Mode lets you view and search across all linked vCenter Server systems and replicate roles, permissions, licenses, policies, and tags.
- When you install vCenter Server or deploy the vCenter Server Appliance with an external Platform Services Controller, you must first install the Platform Services Controller.
- With Enhanced Linked Mode, you can connect not only vCenter Server systems running on Windows but also many vCenter Server Appliances. You can also have an environment where multiple vCenter Server systems and vCenter Server Appliances are linked together.
During installation of the Platform Services Controller, you can select whether to create a new vCenter Single Sign-On domain or join an existing domain. You can select to join an existing vCenter Single Sign-On domain if you have already installed or deployed a Platform Services Controller, and have created a vCenter Single Sign-On domain. When you join an existing vCenter Single Sign-On domain, the data between the existing Platform Services Controller and the new Platform Services Controller is replicated, and the infrastructure data is replicated between the two Platform Services Controllers
If you install vCenter Server with an external Platform Services Controller, you first must deploy the Platform Services Controller on one virtual machines or physical server and then deploy vCenter Server on another virtual machines or physical server. While installing vCenter Server, you must select the external Platform Services Controller. Make sure that the Platform Services Controller you select is an external standalone Platform Services Controller. Selecting an existing Platform Services Controller that is a part of an embedded installation is not supported and cannot be reconfigured after the deployment.
Repoint the Connections Between vCenter Server and Platform Services Controller
If your environment contains external Platform Services Controller instances within a site that replicate the infrastructure data within a single domain, you can redirect the vCenter Server instances to another Platform Services Controller. If an external Platform Services Controller stops responding, you can repoint the vCenter Server instances to another Platform Services Controller within the same domain.
If you want to distribute the load of an external Platform Services Controller, you can repoint some of the vCenter Server instances to other Platform Services Controller instances in the same domain.
You can repoint the connections between a vCenter Server instance and the external Platform Services Controller instances in different vCenter Single Sign-On sites if the Platform Services Controller instances replicate the infrastructure data within a single domain. A site in the VMware Directory Service is a logical container in which you can group Platform Services Controller instances within a domain. You can name the sites in an intuitive way for easier implementation. Currently, the use of sites is for configuring Platform Services Controller High Availability groups behind a load balancer. vCenter Single Sign-On sites can be, for example, external Platform Services Controller instances that are deployed in multiple physical locations.
For more information, see the VMware knowledge base article at
http://kb.vmware.com/kb/2131191
Prerequisites
Verify that the external Platform Services Controller instances are within a single site and replicate the infrastructure data within a single domain.
Procedure
- Log in to the vCenter Server instance.
- For vCenter Server Appliance, log in to the vCenter Server Appliance shell as root
- For a vCenter Server instance installed on Windows, log in as an administrator to the virtual machine or physical server that you installed vCenter Server on.
- Run the cmsso-util script.
cmsso-util repoint –repoint-psc psc_fqdn_or_static_ip [–dc-port port_number] - where the square brackets [ ] enclose the command options.
Here, psc_fqdn_or_static_ip is the system name used to identify the Platform Services Controller. This system name must be an FQDN or a static IP address. - Use the –dc-port port_number option if the Platform Services Controller runs on a custom HTTPS port. The default value of the HTTPS port is 443.
- Log in to the vCenter Server instance by using the vSphere Web Client to verify that the vCenter Serveris running and can be managed.
The vCenter Server instance is registered with the new Platform Services Controller