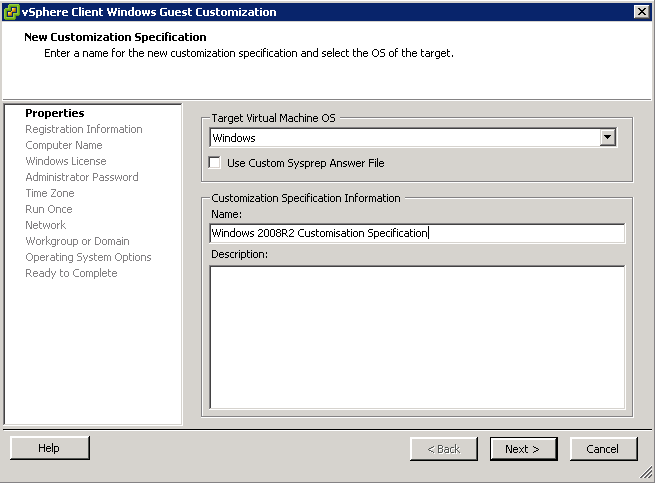
Understanding Clones
A clone is a copy of an existing virtual machine. The existing virtual machine is called the parent of the clone. When the cloning operation is complete, the clone is a separate virtual machine — though it may share virtual disks with the parent virtual machine.
- Changes made to a clone do not affect the parent virtual machine. Changes made to the parent virtual machine do not appear in a clone.
- A clone’s MAC address and UUID are different from those of the parent virtual machine.
If you want to save the current state of the virtual machine, so you can revert to that state in case you make a mistake, take a snapshot. If you want to make a copy of a virtual machine for separate use, create a clone.
Full and Linked Clones
There are two types of clone:
- A full clone is an independent copy of a virtual machine that shares nothing with the parent virtual machine after the cloning operation. Ongoing operation of a full clone is entirely separate from the parent virtual machine.
- A linked clone is a copy of a virtual machine that shares virtual disks with the parent virtual machine in an ongoing manner. This conserves disk space, and allows multiple virtual machines to use the same software installation.
Full Clones
A full clone is an independent virtual machine, with no need to access or maintain an ongoing connection to the parent virtual machine. Because a full clone does not share virtual disks with the parent virtual machine, full clones generally perform better than linked clones. However, full clones take longer to create than linked clones. Creating a full clone can take several minutes if the files involved are large.
Linked Clones
A linked clone is made from a snapshot of the parent. All files available on the parent at the moment of the snapshot continue to remain available to the linked clone. Ongoing changes to the virtual disk of the parent do not affect the linked clone, and changes to the disk of the linked clone do not affect the parent.
A linked clone must access the parent. Without access to the parent, a linked clone is disabled.
Linked clones are created swiftly, so you can easily create a unique virtual machine for each task you have. You can also easily share a virtual machine with other users by storing the virtual machine on your local network, where other users can quickly make a linked clone. This facilitates collaboration: for example, a support team can reproduce a bug in a virtual machine, and an engineer can quickly make a linked clone of that virtual machine to work on the bug
The Clone Virtual Machine Wizard
The Clone Virtual Machine Wizard guides through the process of making a clone. You do not need to locate and manually copy the parent virtual machine files. The Clone Virtual Machine Wizard automatically creates a new MAC address and other unique identifiers for the clone.
Warning: Before you power on the virtual machine clone, understand the following
- Virtual machines clones are issued a new Universally Unique Identifier (UUID). This affect user scripts and API calls to the UUID of the virtual machine.
- Virtual machines clones are issued new MAC addresses for attached virtual network adapters. This may have an effect on software or licensing that is sensitive to MAC address changes.
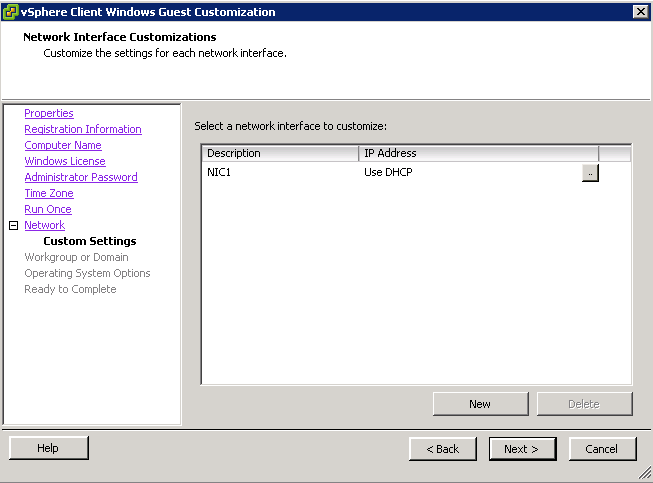
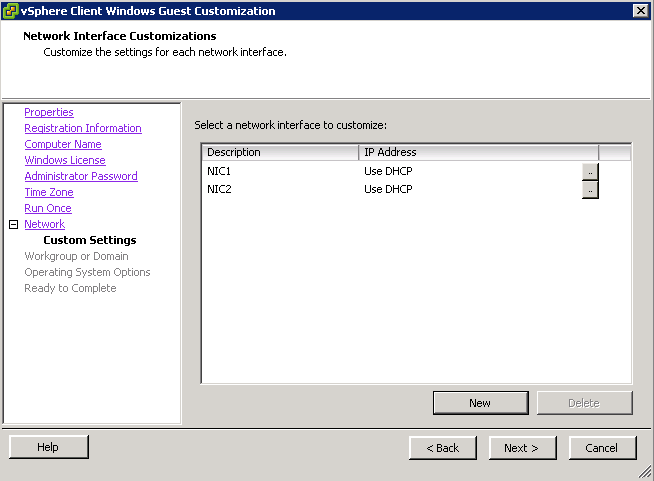
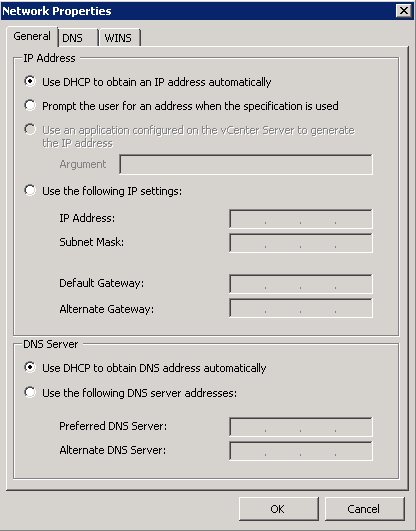
- Guest operating systems for virtual machine clones may share computer names and static IP addresses with their original counterparts. Be sure to account for this prior to power-on
Procedure
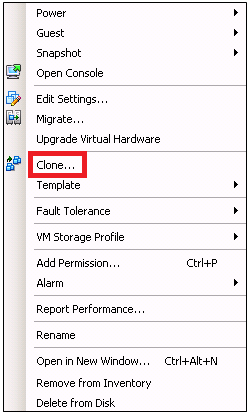
Right click on the VM you want to clone
- Select Clone
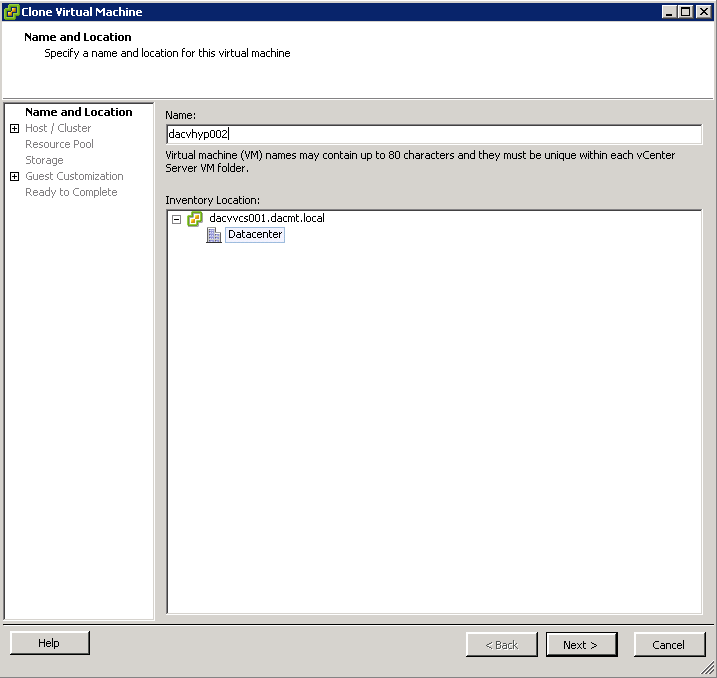
- Put in a name and choose your Inventory location
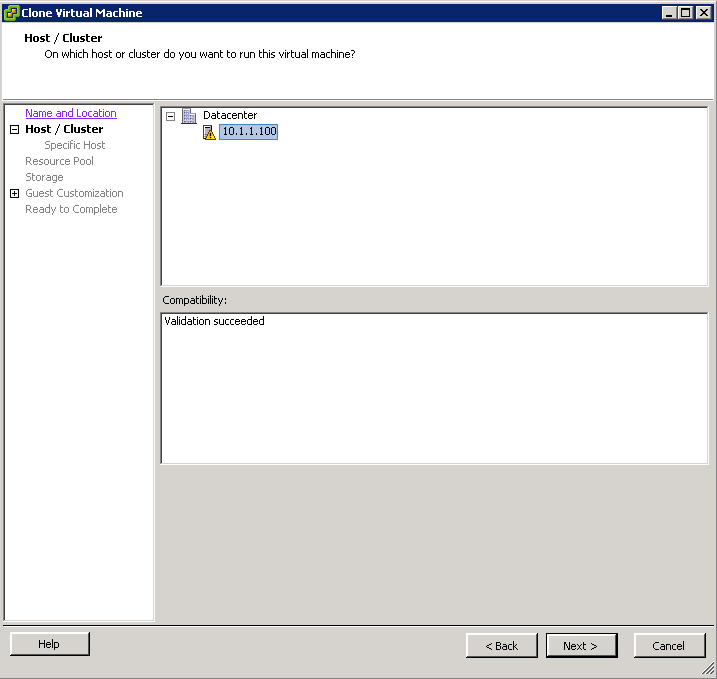
- Choose the Host
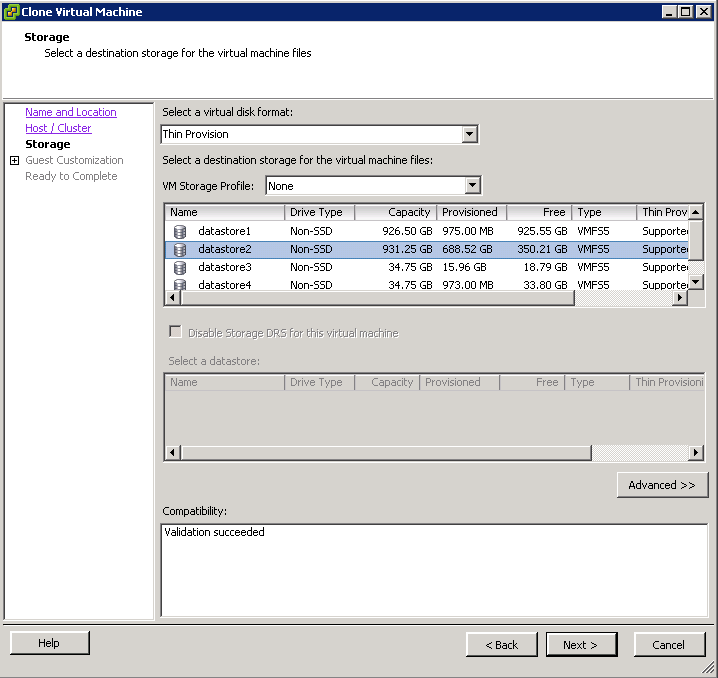
- Choose your Virtual Disk Format
- Choose your Datastore
- Click Next
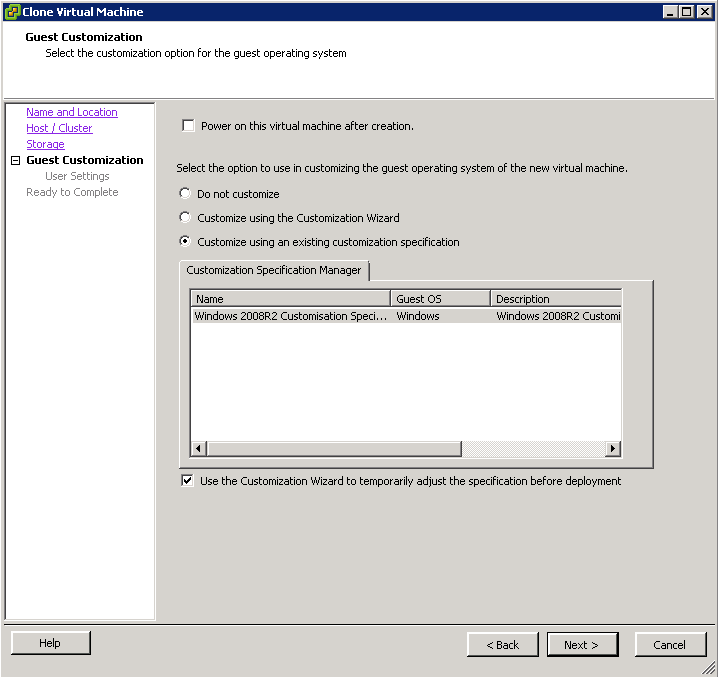
- Choose to Power on the Machine after creation
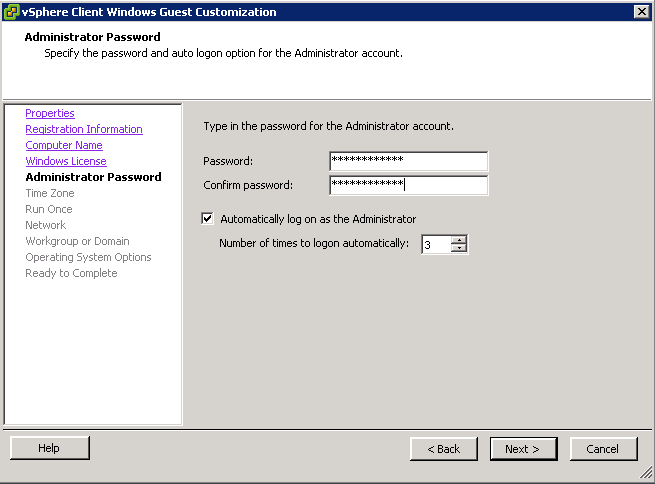
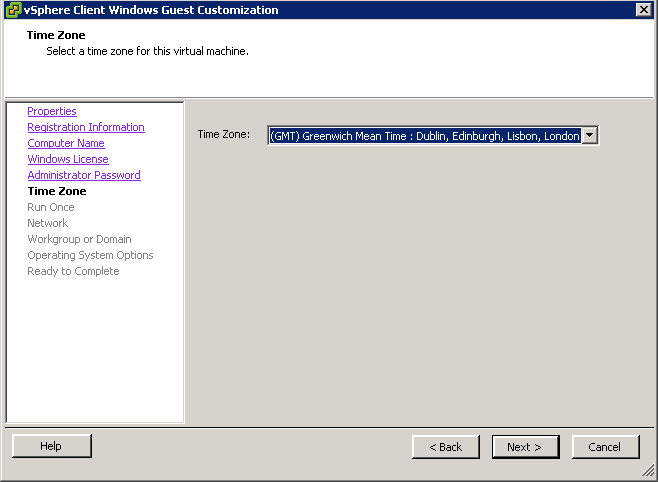
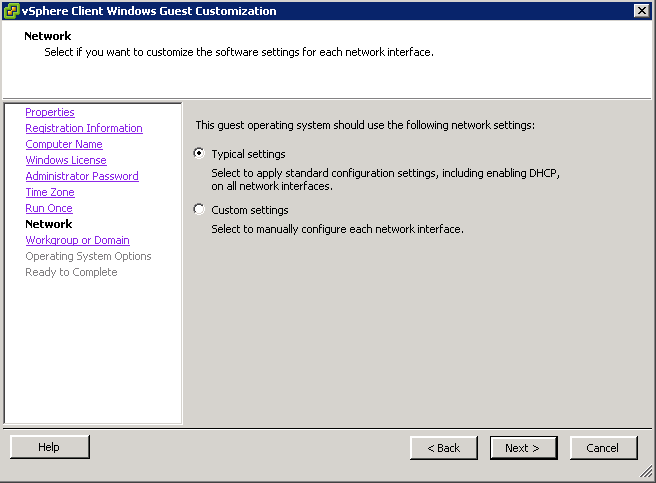
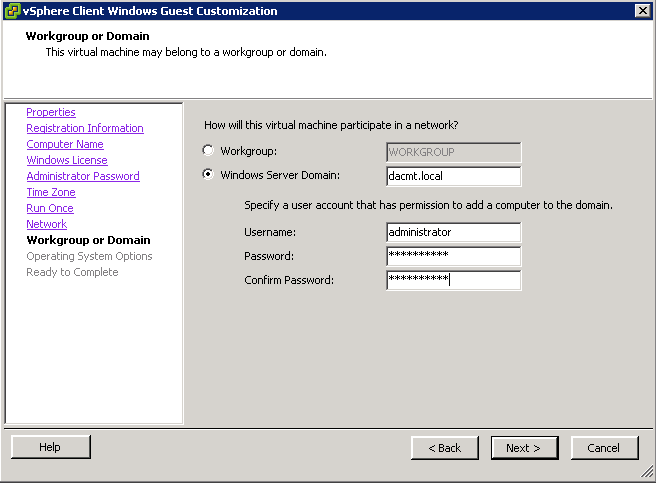
- Choose one of the 2 Customisation options (I have an existing specification)
- It is not recommended to choose Do Not Customise
- Click Next
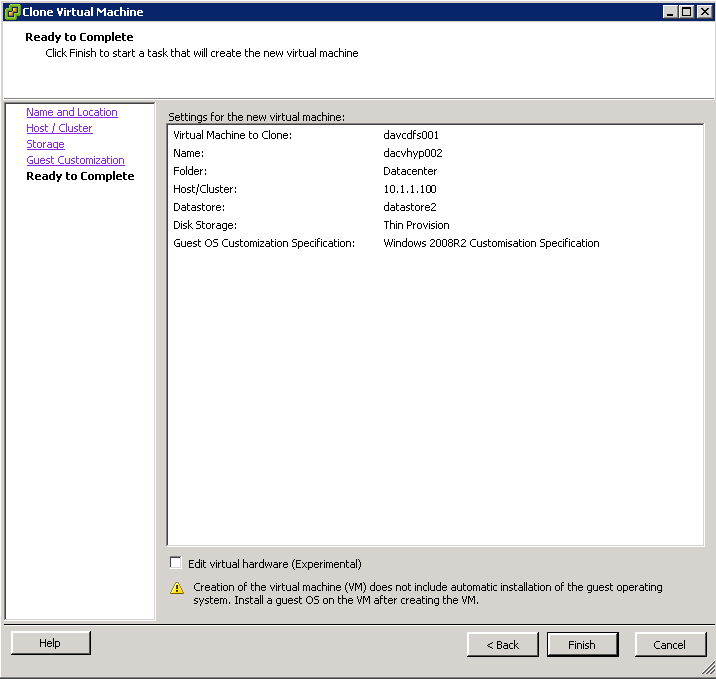
- Review and edit virtual hardware if you need to
- Finish