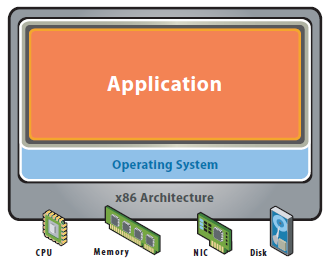
Before Virtualisation
- Single O/S Image per machine
- Software and Hardware tightly coupled
- Running multiple applications on the same machine can create conflicts
- Underutilised resources
- Inflexible and costly infrastructure
- Datacenter space taken up in multiple physical servers
- High Management, Support and Operating costs
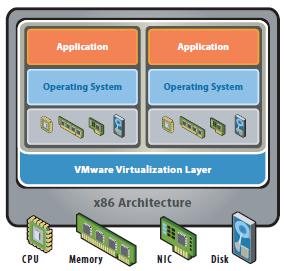
After Virtualisation
- Hardware independence of operating system and applications
- Virtual machines can be provisioned to any system
- Can manage OS and application as a single unit by encapsulating them into virtual machines
- Power Savings
- Rack space savings
- Feature rich flexibility (vMotion, Storage vMotion, DRS, HA)
- Rapidly provision test and development servers
Virtual Infrastructure now
While virtualization has been a part of the IT landscape for decades, it is only recently (in 1998) that VMware delivered the benefits of virtualization to industry-standard x86-based platforms which now form the majority of desktop, laptop and server shipments. A key benefit of virtualisation is the ability to run multiple O/S’s on a single virtual system and share the underlying hardware resource
There are 2 types of architecture – Hosted architecture (VMware Workstation) and Bare metal Architecture (ESX/ESXi)
We can now take advantage of features such as
- The latest generation of x86-based systems feature processors with 64-bit extensions supporting very large memory capacities. This enhances their ability to host large, memory-intensive applications, as well as allowing many more virtual machines to be hosted by a physical server deployed within a virtual infrastructure.
- The VMKernel runs individual VMMs for each VM responsible for the execution of the VM
- The VMM which is a thin layer providing virtual x86 hardware to the overlying O/S including memory management, CPU scheduling, networking and storage
- Hardware Assist (Intel VD and AMD V)
- Paravirtualisation hardware
- DirectPath
- Direct Memory Access
- AMD RVI and Intel EPT
- Emulated Hardware
- DRS
- HA
- sDRS
- I/O Control for Networking and Storage
- NPIV
- Passthrough devices
- Shares, Reservations and Limits
- Resource Pools
- Clustered file system VMFS
- Raw Disk Mappings
- 3 Virtual Disk types (Eager zeroed thick, Lazy Zeroed thick and Thin)
- Memory reclamation techniques


Leave a Reply