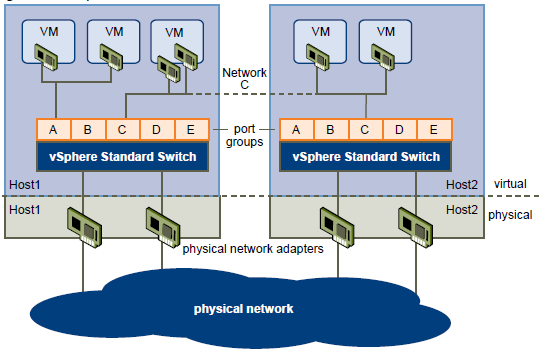
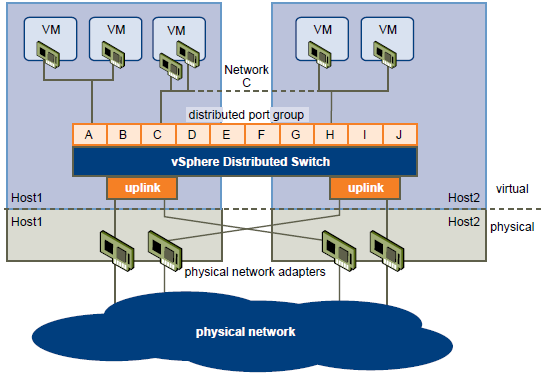
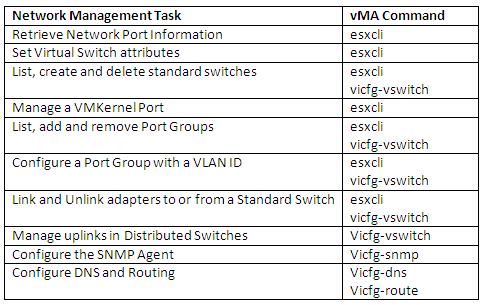
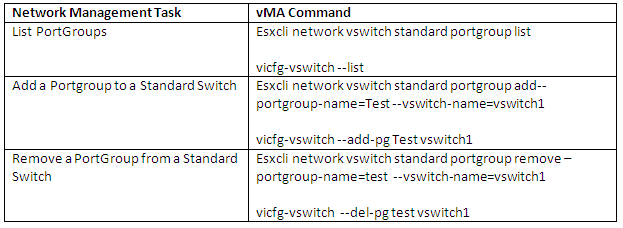
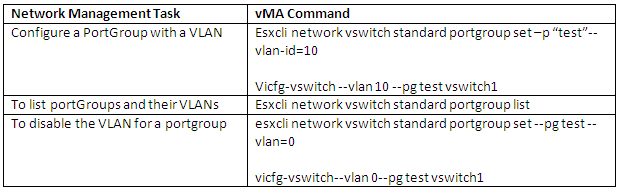
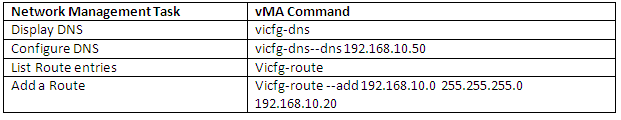
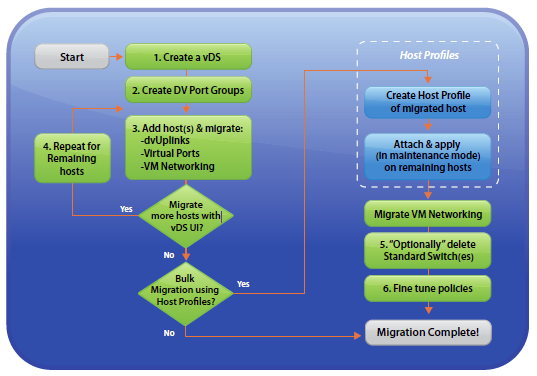
vSphere Standard Switch Architecture
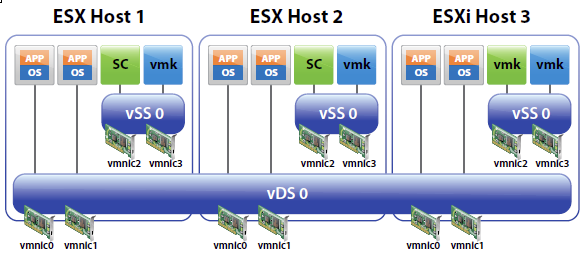
You can create abstracted network devices called vSphere standard switches. A standard switch can..
- Route traffic internally between virtual machines and link to external networks
- Combine the bandwidth of multiple network adaptors and balance communications traffic among them.
- Handle physical NIC failover.
- Have a default number of logical ports which for a standard switch is 120. You can
- Connect one network adapter of a virtual machine to each port. Each uplink adapter associated with a standard switch uses one port.
- Each logical port on the standard switch is a member of a single port group.
- Have one or more port groups assigned to it.
- When two or more virtual machines are connected to the same standard switch, network traffic between them is routed locally. If an uplink adapter is attached to the standard switch, each virtual machine can access the external network that the adapter is connected to.
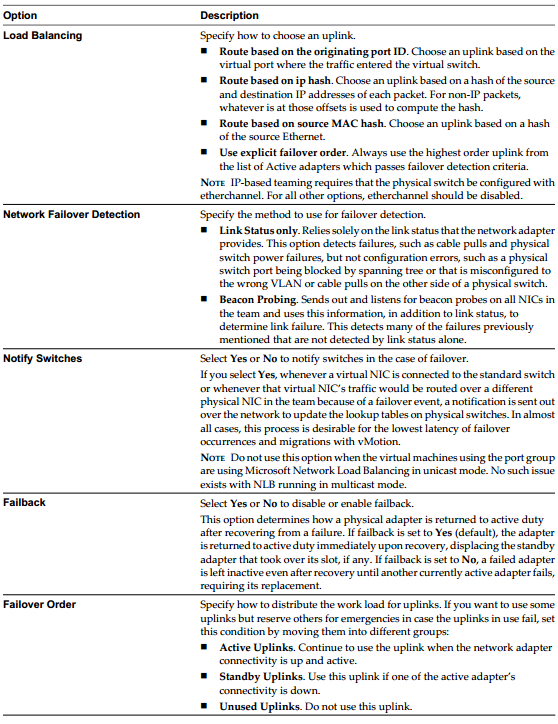
- vSphere standard switch settings control switch-wide defaults for ports, which can be overridden by port group settings for each standard switch. You can edit standard switch properties, such as the uplink configuration and the number of available ports.
Standard Switch
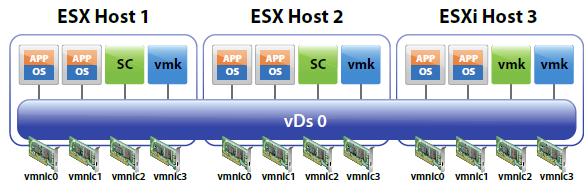
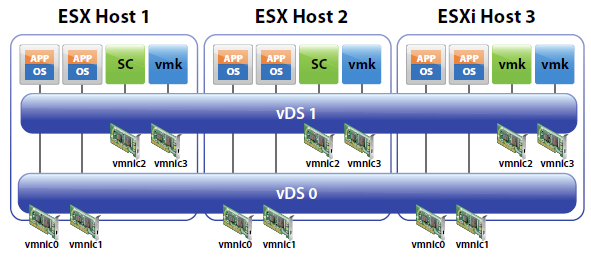
vSphere Distributed Switch Architecture
A vSphere distributed switch functions as a single switch across all associated hosts. This enables you to set network configurations that span across all member hosts, and allows virtual machines to maintain consistent network configuration as they migrate across multiple hosts
Like a vSphere standard switch, each vSphere distributed switch is a network hub that virtual machines can use.
- Enterprise Plus Licensed feature only
- VMware vCenter owns the configuration of the distributed switch
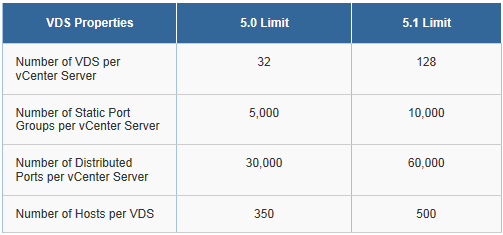
- Distributed switches can support up to 350 hosts
- You configure a Distributed switch on vCenter rather than individually on each host
- Provides support for Private VLANs
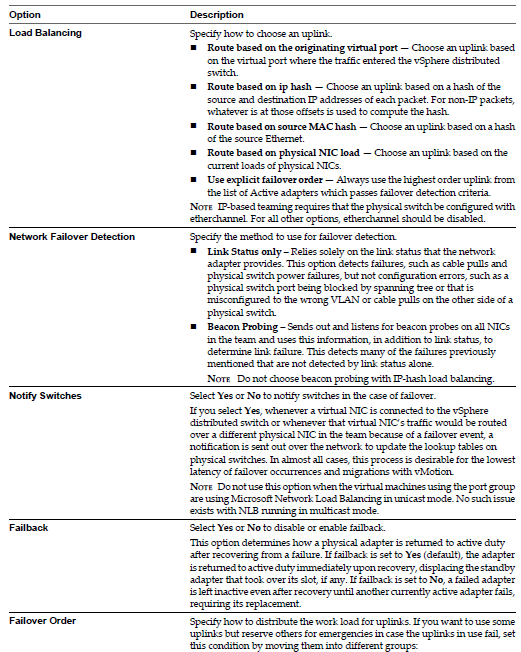
- Enable networking statistics and policies to migrate with VMs during vMotion
- A distributed switch can forward traffic internally between virtual machines or link to an external network by connecting to physical Ethernet adapters, also known as uplink adapters.
- Each distributed switch can also have one or more distributed port groups assigned to it.
- Distributed port groups group multiple ports under a common configuration and provide a stable anchor point for virtual machines connecting to labeled networks.
- Each distributed port group is identified by a network label, which is unique to the current datacenter. A VLAN ID, which restricts port group traffic to a logical Ethernet segment within the physical network, is optional.
- Network resource pools allow you to manage network traffic by type of network traffic.
- In addition to vSphere distributed switches, vSphere 5 also provides support for third-party virtual switches.
TCP/IP Stack at the VMkernel Level
The VMware VMkernel TCP/IP networking stack provides networking support in multiple ways for each of the services it handles.
The VMkernel TCP/IP stack handles iSCSI, NFS, and vMotion in the following ways for both Standard and Distributed Virtual Switches
- iSCSI as a virtual machine datastore
- iSCSI for the direct mounting of .ISO files, which are presented as CD-ROMs to virtual machines.
- NFS as a virtual machine datastore.
- NFS for the direct mounting of .ISO files, which are presented as CD-ROMs to virtual machines.
- Migration with vMotion.
- Fault Tolerance logging.
- Port-binding for vMotion interfaces.
- Provides networking information to dependent hardware iSCSI adapters.
- If you have two or more physical NICs for iSCSI, you can create multiple paths for the software iSCSI by configuring iSCSI Multipathing.
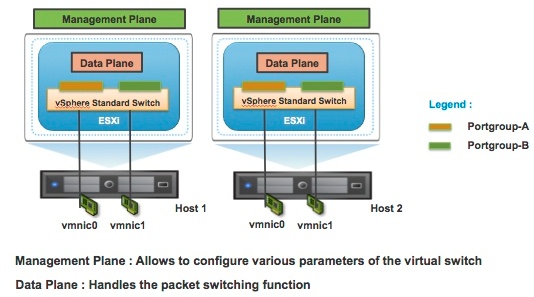
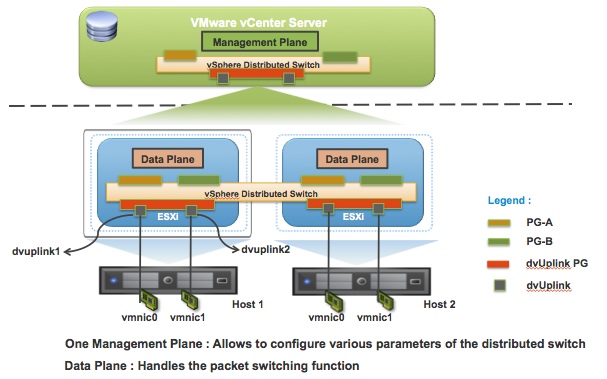
Data Plane and Control Planes
vSphere network switches can be broken into two logical sections. These are the data plane and the management plane.
- The data plane implements the actual packet switching, filtering, tagging, etc.
- The management plane is the control structure used to allow the operator to configure the data plane functionality.
- With the vSphere Standard Switch (VSS), the data plane and management plane are each present on each standard switch. In this design, the administrator configures and maintains each VSS on an individual basis.
Virtual Standard Switch Control and Data Plane
With the release of vSphere 4.0, VMware introduced the vSphere Distributed Switch. VDS eases the management burden of per host virtual switch configuration by treating the network as an aggregated resource. Individual host-level virtual switches are abstracted into a single large VDS that spans multiple hosts at the Datacenter level. In this design, the data plane remains local to each VDS, but the management plane is centralized with vCenter Server acting as the control point for all configured VDS instances.
Virtual Distributed Switch Control and Data Plane