What is the System Information Volume folder?
The System Information Volume folder contains information that shouldn’t necessarily be interfered with however there are situations where this folder can become extremely large and unmanageable. Below are several bulleted points of possible data which may exist in this folder
- System Restore points. You can disable System Restore from the “System” control panel.
- Distributed Link Tracking Service databases for repairing your shortcuts and linked documents.
- Content Indexing Service databases for fast file searches. This is also the source of the cidaemon.exe process: That is the content indexer itself, busy scanning your files and building its database so you can search for them quickly.
- Information used by the Volume Snapshot Service (also known as “Volume Shadow Copy”) so you can back up files on a live system.
- Longhorn systems keep WinFS databases here
The Problem with System Information Folder
We encountered an issue where on checking this folder on a drive showed it was taking up nearly 80GB space! We opened Folder and Search Options and selected to Show Hidden Files, Folders and Drives and un-ticked Hide Protected Operating System Files to see this folder. Unfortunately you generally cannot access this folder unless you do the following
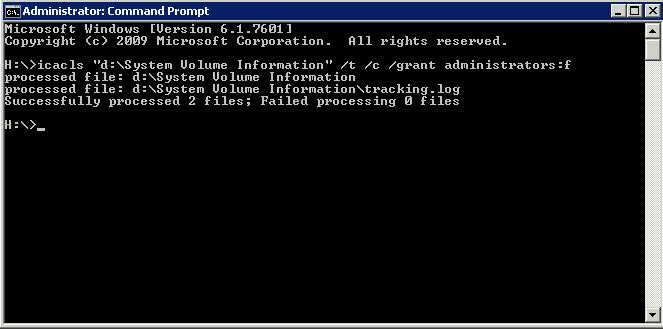
- Open cmd.exe
- Type icacls “d:\System Volume Information” /t /c /grant Administrators:f to take ownership of the folder
- /t = Traverse all folders
- /c = Continue on file errors (access denied) Error messages are still displayed
Commands to check the space
Here are some commands that you could use in the Command Prompt console in administrator mode in order to view and resize the space allocated for the System Volume Information Folder.
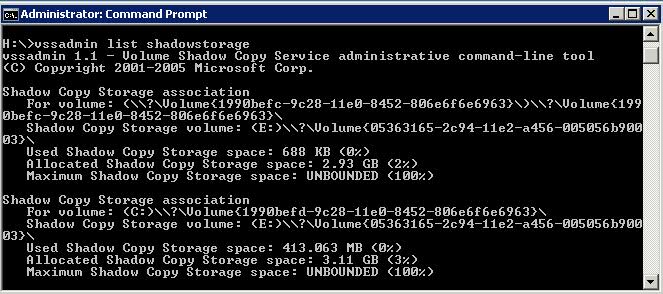
- To View the Storage Space allocated for this folder: Open Command Prompt with “Run as Administrator” option and type the following – vssadmin list shadownstorage
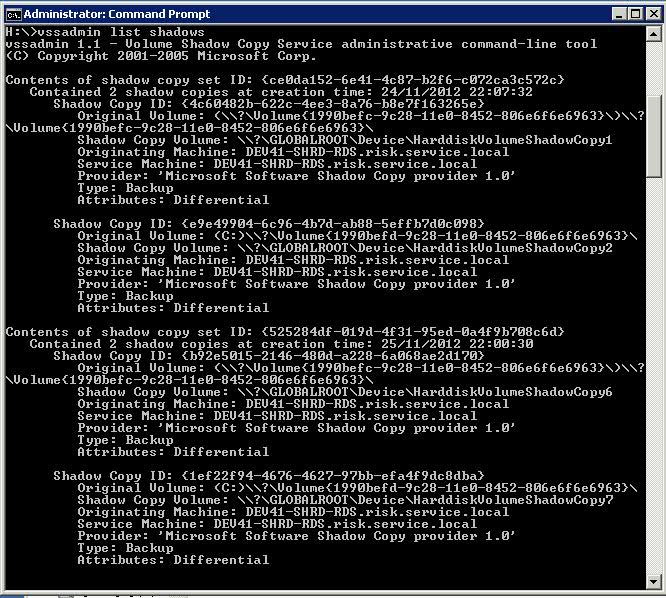
- To see the restore information stored there: Open Command Prompt with “Run as Administrator” option and type the following – vssadmin list shadows
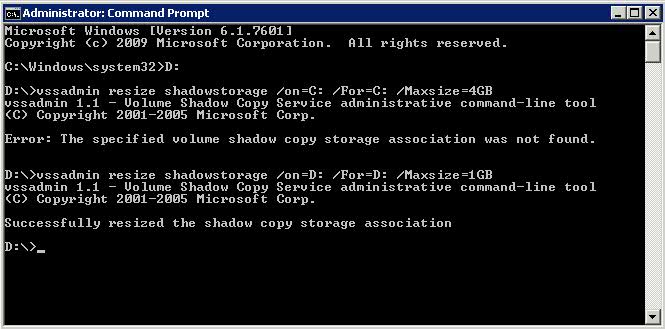
- To resize the maximum allocated space: Open Command Prompt with “Run as Administrator” option and type the following – vssadmin resize shadowstorage /on=[here add the drive letter]: /For=[here add the drive letter]: /Maxsize=[here add the maximum size]
- E.g. vssadmin resize shadowstorage /on=D: /For=D: /Maxsize=4GB
Notes
If the System Information Folder is very large,you may want to check the following
- Install and Run Treesize which will give you a good insight into what folders you have
- Check System Restores
- Check in Disk Management if any of your disks are enabled for Shadow Copies and reduce the amount of disk space these are allowed to take
- Check DFS Folders
- Check what your backup software is doing. A high volume of data can sometimes be due to VSS shadow copies not being cleaned up after a VSS capable backup program backs up data on the drive in question.
- Stop the Microsoft Software Shadow Copy Provider
- Stop the Volume Shadow Copy Service