A Zombie VMDK is as mentioned usually a VMDK which isn’t used anymore by a VM. You can double check this by checking if the disk is still linked to the VM which it should be a part off. If it isn’t you can delete it from the datastore via the datastore browser. I would suggest moving it first before you delete is, just in case
Archive for July 2012
Storing a Virtual Machine Swapfile in a different location
By default, swapfiles for a virtual machine are located on a VMFS3 datastore in the folder that contains the other virtual machine files. However, you can configure your host to place virtual machine swapfiles on an alternative datastore.
Why move the Swapfiles?
- Place virtual machine swapfiles on lower-cost storage
- Place virtual machine swapfiles on higher-performance storage.
- Place virtual machine swapfiles on non replicated storage
- Moving the swap file to an alternate datastore is a useful troubleshooting step if the virtual machine or guest operating system is experiencing failures, including STOP errors, read only filesystems, and severe performance degradation issues during periods of high I/O.
vMotion Considerations
Note: Setting an alternative swapfile location might cause migrations with vMotion to complete more slowly. For best vMotion performance, store virtual machine swapfiles in the same directory as the virtual machine. If the swapfile location specified on the destination host differs from the swapfile location specified on the source host, the swapfile is copied to the new location which causes the slower migration. Copying host-swap local pages between source- and destination host is a disk-to-disk copy process, this is one of the reasons why VMotion takes longer when host-local swap is used.
Swapfile Moving Caveats
- If vCenter Server manages your host, you cannot change the swapfile location if you connect directly to the host by using the vSphere Client. You must connect to the vCenter Server system.
- Migrations with vMotion are not allowed unless the destination swapfile location is the same as the source swapfile location. In practice, this means that virtual machine swapfiles must be located with the virtual machine configuration file.
- Using host-local swap can affect DRS load balancing and HA failover in certain situations. So when designing an environment using host-local swap, some areas must be focused on to guarantee HA and DRS functionality.
DRS
If DRS decide to rebalance the cluster, it will migrate virtual machines to low utilized hosts. VMkernel tries to create a new swap file on the destination host during the VMotion process. In some scenarios, the host might not contain any free space in the VMFS datastore and DRS will not be able to vMotion any virtual machine to that host because the lack of free space. But the host CPU active and host memory active metrics were still monitored by DRS to calculate the load standard deviation used for its recommendations to balance the cluster. The lack of disk space on the local VMFS datastores influences the effectiveness of DRS and limits the options for DRS to balance the cluster.
High availability failover
The same applies when a HA isolation response occurs, when not enough space is available to create the virtual machine swap files, no virtual machines are started on the host. If a host fails, the virtual machines will only power-up on host containing enough free space on their local VMFS datastores. It might be possible that virtual machines will not power-up at-all if not enough free disk space is available
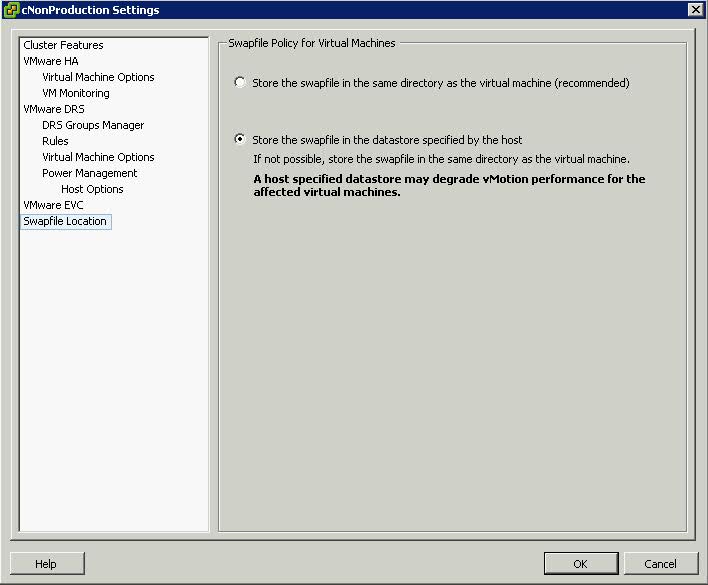
Procedure (Cluster Modification)
- Right click the cluster
- Edit Settings
- Click Swap File Location
- Select Store the Swapfile in the Datastore specified by the Host
Procedure (Host Modification)
If the host is part of a cluster, and the cluster settings specify that swapfiles are to be stored in the same directory as the virtual machine, you cannot edit the swapfile location from the host configuration tab. To change the swapfile location for such a host, use the Cluster Settings dialog box.
- Click the Inventory button in the navigation bar, expand the inventory as needed, and click the appropriate managed host.
- Click the Configuration tab to display configuration information for the host.
- Click the Virtual Machine Swapfile Location link.
- The Configuration tab displays the selected swapfile location. If configuration of the swapfile location is not supported on the selected host, the tab indicates that the feature is not supported.
- Click Edit.
- Select either Store the swapfile in the same directory as the virtual machine or Store the swapfile in a swapfile datastore selected below.
- If you select Store the swapfile in a swapfile datastore selected below, select a datastore from the list.
- Click OK.
- The virtual machine swapfile is stored in the location you selected.