Applies To: Windows Server 2008
Access-based enumeration hides files and folders that users do not have permission to access. By default, this feature is not enabled for DFS namespaces. You can enable access-based enumeration of DFS folders by using the Dfsutil command, enabling you to hide DFS folders from groups or users that you specify. To control access-based enumeration of files and folders in folder targets, you must enable access-based enumeration on each shared folder by using Share and Storage Management.
Caution
Access-based enumeration does not prevent users from getting a referral to a folder target if they already know the DFS path. Only the share permissions or the NTFS file system permissions of the folder target (shared folder) itself can prevent users from accessing a folder target. DFS folder permissions are used only for displaying or hiding DFS folders, not for controlling access, making Read access the only relevant permission at the DFS folder level
In some environments, enabling access-based enumeration can cause high CPU utilization on the server and slow response times for users.
Requirements
To enable access-based enumeration on a namespace, all namespace servers must be running at least Windows Server 2008. Additionally, domain-based namespaces must use the Windows Server 2008 mode
To use access-based enumeration with DFS Namespaces to control which groups or users can view which DFS folders, you must follow these steps:
- Enable access-based enumeration on a namespace.
- Control which users and groups can view individual DFS folders.
Method
To enable access-based enumeration on a namespace by using Windows Server 2008, you must use the Dfsutil command
- Open an elevated command prompt window on a server that has the Distributed File System role service or Distributed File System Tools feature installed.
- Type the following command, where <namespace_root> is the root of the namespace
dfsutil property abde enable \\<namespace_root>
For example, to enable access-based enumeration on the domain-based namespace \\contoso.office\public type the following command:
dfsutil property abde enable \\contoso.office\public
Controlling which users and groups can view individual DFS folders
By default, the permissions used for a DFS folder are inherited from the local file system of the namespace server. The permissions are inherited from the root directory of the system drive and grant the DOMAIN\Users group Read permissions. As a result, even after enabling access-based enumeration, all folders in the namespace remain visible to all domain users.
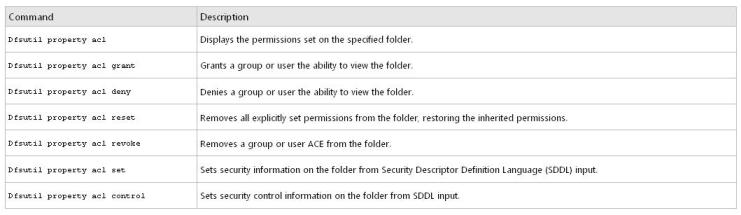
To limit which groups or users can view a DFS folder, you must use the Dfsutil command to set explicit permissions on each DFS folder
dfsutil property acl grant DOMAIN\Account:R (…) Protect Replace
For example, to block inherited permissions (by using the Protect parameter) and replace previously defined ACEs (by using the Replace parameter) with permissions that allow the Domain Admins and CONTOSO\Trainers groups Read (R) access to the \\contoso.office\public\training folder, type the following command:
dfsutil property acl grant \\contoso.office\public\training ”CONTOSO\Domain Admins”:R CONTOSO\Trainers:R Protect Replace
Permission table