The first step in planning a deployment is understanding how the following Terminal Sever components fit together
- Terminal Server
The server itself is at the core component of a Terminal Services deployment. This is the server that the clients connect to so they can access their applications
- Terminal Server Farm
A Terminal Server farm is a collection of Terminal Servers used to provide high availability and load balancing to clients on an organisational network. Client connections to Terminal Server Farms are mediated by Terminal Services Session Directory Servers. Terminal Server farms are more likely to be deployed at large sites than small ones
- License Servers
License servers provide Terminal Server Client Access Licenses (TS CALS) to Terminal Servers on the network. Unless a license server is deployed, clients are only able to connect to Terminal Services for a limited time only.
- Terminal Services Gateway Servers (TS Gateway)
These servers provide access to Terminal Servers to clients on untrusted networks. In Enterprise networks, you can use a TS Gateway server as a bridge between the standard internal network and a Terminal Server farm on a network protected by server isolation policies
Terminal Server Licensing
All clients that connect to a Terminal Server require a TS CAL. This license is not included with the O/S a client uses or a standard server license.
TS CALs are managed by a Terminal Server Licensing server
- What is the scope of the licensing server. Will it service clients in the domain or workgroup or manage the licenses for all clients in the forest
- How will the license server be activated with Microsoft. Automatic, Web Browser or Telephone
- How many license servers do you need for your organisation?
- What type of licenses will be deployed
Terminal Server Session Broker
The Terminal Server Session Broker service simplifies the process of adding more capacity to an existing Terminal Services Deployment. It enables Load Balancing of terminal services in a group and ensures the reconnection of clients to existing sessions in that group. In Terminal Server Session Broker, a group of Terminal Servers is called a Farm.
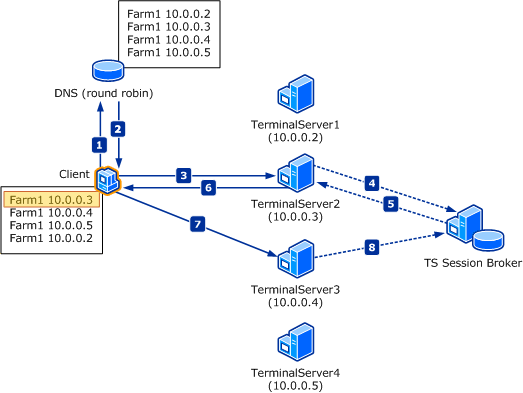
The Terminal Server Session Broker is a database which keeps track of TS sessions. TS can work with DNS Round Robin or with NLB. When configured with NLB, the Terminal Server Session Broker Service monitors all servers in the group and allocates clients to to the servers which have the most amount of free resource.
When used with DNS Round Robin, clients are still distributed, the main benefit being is that Terminal Server Session Broker remembers where a client is connected. TS Load Balancing is restricted to Windows 2008 Terminal Servers only
Clients must support RDP 5.2 or later
Each Terminal Server must have the same application configuration
The following diagram provides a more detailed representation of the traffic flow. In the diagrammed scenario, all terminal servers in the farm have host resource records in DNS that map to the terminal server farm name (“Farm1”). Therefore, any terminal server in the farm can act as a redirector and process the initial connection requests
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc772418(v=ws.10).aspx
Terminal Server Gateway Server
Plan the deployment of Terminal Server Gateway Servers when you need to enable RDP over HTTPS connections to RDP Servers located on Protected internal networks to clients on the internet or untrusted networks. TS Gateway servers are not limited to screened subnets between internal networks and the internet but can also be deployed to enable access to servers that are the subject of IPsec isolation policies