NCIS
Windows® 7 and Windows Server® 2008 R2 include a feature called Network Connectivity Status Indicator (NCSI), which is part of a broader feature called Network Awareness. Network Awareness collects network connectivity information and makes it available through an application programming interface (API) to services and applications on a computer running Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2. With this information, services and applications can filter networks (based on attributes and signatures) and choose the networks that are best suited to their tasks. Network Awareness notifies services and applications about changes in the network environment, thus enabling applications to dynamically update network connections.
Network Awareness collects network connectivity information such as the Domain Name System (DNS) suffix of the computer and the forest name and gateway address of networks that the computer connects to. When called on by Network Awareness, NCSI can add information about the following capabilities for a given network:
- Connectivity to an intranet
- Connectivity to the Internet (possibly including the ability to send a DNS query and obtain the correct resolution of a DNS name)
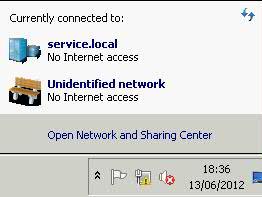
What you will see
A yellow warning triangle in the System Tray looking like
and
What does Windows check, and in what order, before it announces that there are connectivity problems and displays the yellow triangle formed icon down at the task bar
Windows checks a Microsoft site for connectivity, using the Network Connectivity Status Indicator site.
- NCSI performs a DNS lookup on www.msftncsi.com, then requests http://www.msftncsi.com/nc
si.txt . This file is a plain-text file and contains only the text Microsoft NCSI.
- NCSI sends a DNS lookup request for dns.msftncsi.com. This DNS address should resolve to 131.107.255.255. If the address does not match, then it is assumed that the internet connection is not functioning correctly.
The exact sequence of when which test is run is not documented; however, a little bit of digging around with a packet sniffing tool like Wireshark reveals some info.
It appears that on any connection, the first thing NCSI does is requests the text file (step 1 above). NCSI expects a 200 OK response header with the proper text returned. If the response is never received, or if there is a redirect, then a DNS request for dns.msftncsi.com is made. If DNS resolves properly but the page is inaccessible, then it is assumed that there is a working internet connection, but an in-browser authentication page is blocking access to the file. This results in the pop-up balloon above. If DNS resolution fails or returns the wrong address, then it is assumed that the internet connection is completely unsuccessful, and the “no internet access” error is shown.
The order of events appears to be slightly different depending on whether the wireless network is saved, has been connected to before even if it is not in the saved connections list, and possibly depending on the encryption type. The DNS and HTTP requests and responses showing up in Wireshark were not always consistent, even connecting to the same network, so it’s not entirely clear what causes different methods of detection under different scenario
Resolving this issue
- http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee126135%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
- Check you can ping your DNS Servers
- Check you can ping your Gateway
- Check your server is listed correctly in DNS
- Check DNS suffixes
- Check proxy servers if you have any
- Check your router
- Check other servers have connection
- Turn off the Indicator in Group Policy.
- If everything checks out ok, Go into GPMC and Expand Computer Configuration, expand Administrative Templates, expand System, expand Internet Communication Management, and then click Internet Communication settings. In the details pane, double-click Turn off Windows Network Connectivity Status Indicator active tests, and then click Enabled
- Change the Registry key to not query the server: HKLM/system/currentcontrol
set/servic es/nlasvc/ parameters /internet – set enable activeprobing to 0