A VMware vSphere Storage Appliance (VSA) is a virtual appliance that provides small and medium businesses with the benefit of VMware vSphere vMotion and High Availability without requiring shared storage
VSA runs on an ESXi host. A VSA cluster is a group of ESXi hosts each running its own VSA instance
A VSA cluster enables the following features
- Shared Datastores for all hosts in the cluster
- vMotion and HA
- Datastore Replication
- Hardware and Software Datastore failover capabilities
VSA is an alternative to SAN storage
- A SAN system provides a centralised array of storage
- A VSA cluster provides a distributed array of storage
- Elimates the need to purchase expensive SAN storage
VSA Cluster Architecture
The architecture of a VSA cluster includes the physical servers that have local hard disks, ESXi as the operating system of the physical servers, and the vSphere Storage Appliance virtual machines that run clustering services to create volumes that are exported as the VSA datastores.
vSphere Storage Appliance supports the creation of a VSA cluster with two or three members. A vSphere Storage Appliance uses the hard disks of an ESXi host to create two volumes of the same size. It exports one of the volumes as a datastore. The other volume is a replica of the volume that is exported by another vSphere Storage Appliance from another host in the VSA cluster
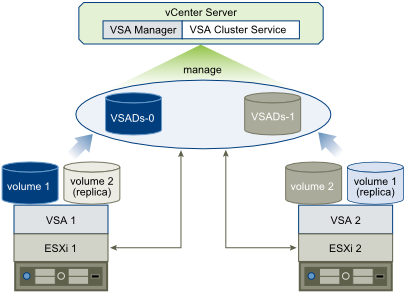
VSA Cluster with 2 hosts
In a VSA cluster with two VSA cluster members, an additional service called VSA cluster service runs on the vCenter Server machine. The service participates as a member in the VSA cluster, but it does not provide storage. To remain online, a VSA cluster requires that more than half of the members are also online. If one instance of a vSphere Storage Appliance fails, the cluster can remain online only if the remaining VSA cluster member and the VSA cluster service are online.
A VSA cluster with 2 members has 2 VSA datastores and maintains a replica of each datastore
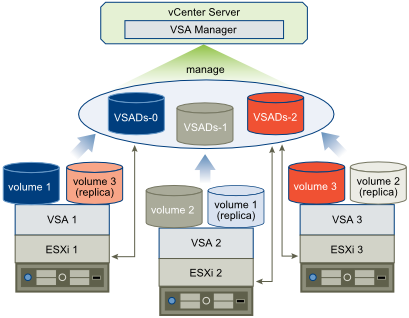
VSA Cluster with 3 hosts
A VSA cluster with 3 members has 3 VSA datastores and maintains a replica of each datastore. This configuration does not require the VSA cluster service running on the vCenter Server system
How does it work?
VSA uses the hard disks of the ESXi 5 hosts to maintain a datastore and its replica. VSA created 2 volumes of the same size. It exports one of the volumes as a datastore. The other volume is a replica of the volume that is exported by another VSA from another host in the VSA cluster. A VSA cluster with 2 members has 2 VSA datastores and maintains a replica of each datastore
A VSA cluster with 3 members has 3 datastores and maintains a replica of each datastore
How is Data accessed?
Data is accessed in the VSA cluster using the NFS Version 3 protocol. The NFS exports are used as ESXi datastores which provide shared storage to members in the VSA cluster. The default RAID configuration for the VSA cluster is RAID 10
vCenter server continues to manage the ESXi hosts and the VM’s. vCenter can only manage one VSA cluster at a time
VSA Manager
A VSA cluster is created and managed by the VSA Manager. This is a vCenter Server 5.0 extension that you install on a vCenter Server system. After you install VSA Manager, the VSA Manager tab is displayed in the vSphere client. The VSA Manager is used to do the following
- Deploying a VSA Cluster
- Mounting as datastores the volumes that each VSA instance exports
- Monitoring and maintaining and troubleshooting a VSA cluster
More Information