Private VLANs are used to solve VLAN ID limitations and waste of IP addresses for certain network setups.
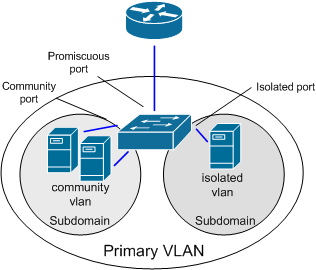
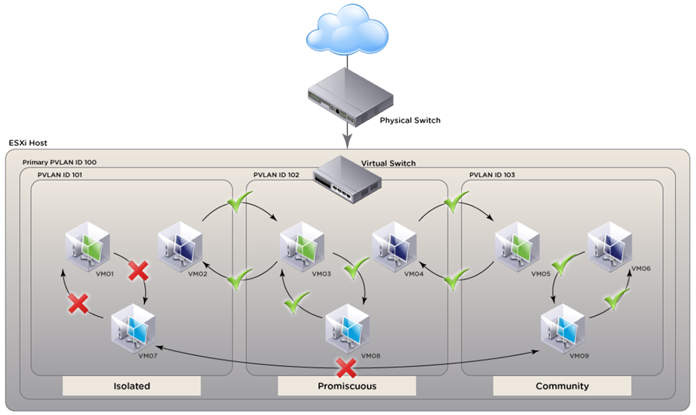
PVLANs segregate VLANs even further than normal, they are basically VLANs inside of VLANs. The ports share a subnet, but can be prevented from communicating. They use different port types:
Promiscuous ports – These will be the “open ports” of the PVLANs, they can communicate with all other ports.
Community ports – These ports can communicate with other community ports and promiscuous ports.
Isolated ports – These can ONLY communicate with promiscuous ports.
There are different uses for PVLANs. They are used by service providers to allow customer security while sharing a single subnet. Another use could be for DMZ hosts in an enterprise environment. If one host is compromised its ability to inflict damage to the other hosts will be severely limited.
How vSphere implements private VLANs
- vSphere does not encapsulate traffic in private VLANs. In other words, no secondary private VLAN is encapsulated in a primary private VLAN packet
- Traffic between virtual machines on the same private VLAN but on different hosts will need to move through the physical switch. The physical switch must be private VLAN aware and configured appropriately so traffic can reach its destination
Configuring and Assigning a Primary VLAN and Secondary VLAN
- Right click the Distributed switch and select Edit Settings
- Select the Private VLAN tab
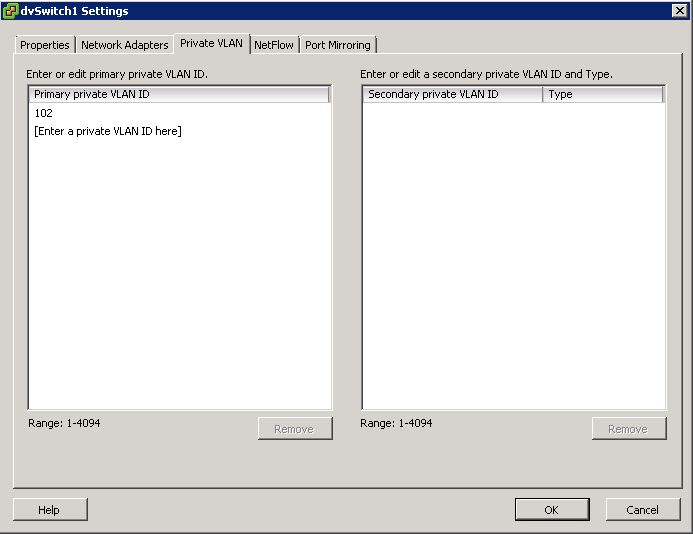
- On the Primary tab, add the VLAN that is used outside the PVLAN domain. Enter a private VLAN
- Note: There can be only one Promiscuous PVLAN and is created automatically for you
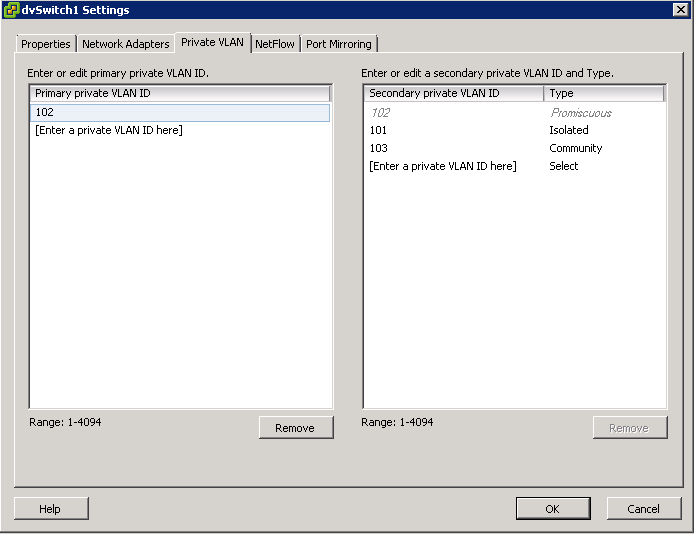
- For each new Secondary Private VLAN, click Enter a private VLAN ID here under Secondary Private VLAN ID and enter the number of the Secondary Private VLAN
- Click anywhere in the dialog box, select the secondary private VLAN that you added and select Isolated or Community for the port type
Diagram of Configuration courtesy of VMware
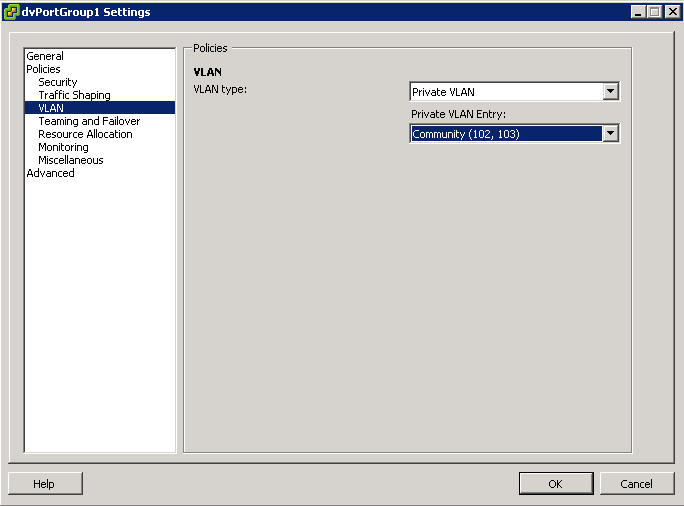
After the primary and secondary private VLANs are associated for the VDS, use the association to configure the VLAN policy for the distributed port group
- Right click the Distributed Port Group in the networking inventory view and select Edit Settings
- Select policies
- Select the VLAN type to use and click OK
Useful KB Article
Private VLAN (PVLAN) on vNetwork Distributed Switch – Concept Overview KB
Troubleshooting PVLANs
- Ensure that VLANs and PVLANs are properly configured on the physical switch.
- Promiscuous (Primary) PVLAN can communicate with all interfaces on the VLAN. There can only be one Primary PVLAN per VLAN.
- VMs in an Isolated (Secondary) PVLAN can only communicate with the Promiscuous port, not with other VMs in the Isolated PVLAN. To prevent communication between two VMs using PVLANs, place them in the Isolated PVLAN.
- VMs in the same Community (Secondary) PVLAN can communicate with each other and the Promiscuous port. There can be multiple Community PVLANs in the same PVLAN. Ensure that VMs are members of the same Community PVLAN if communication is required between them.
- Ensure that the correct port groups have been configured for each PVLAN.
- Verify that the VM(s) in question are configured to use the appropriate port group.